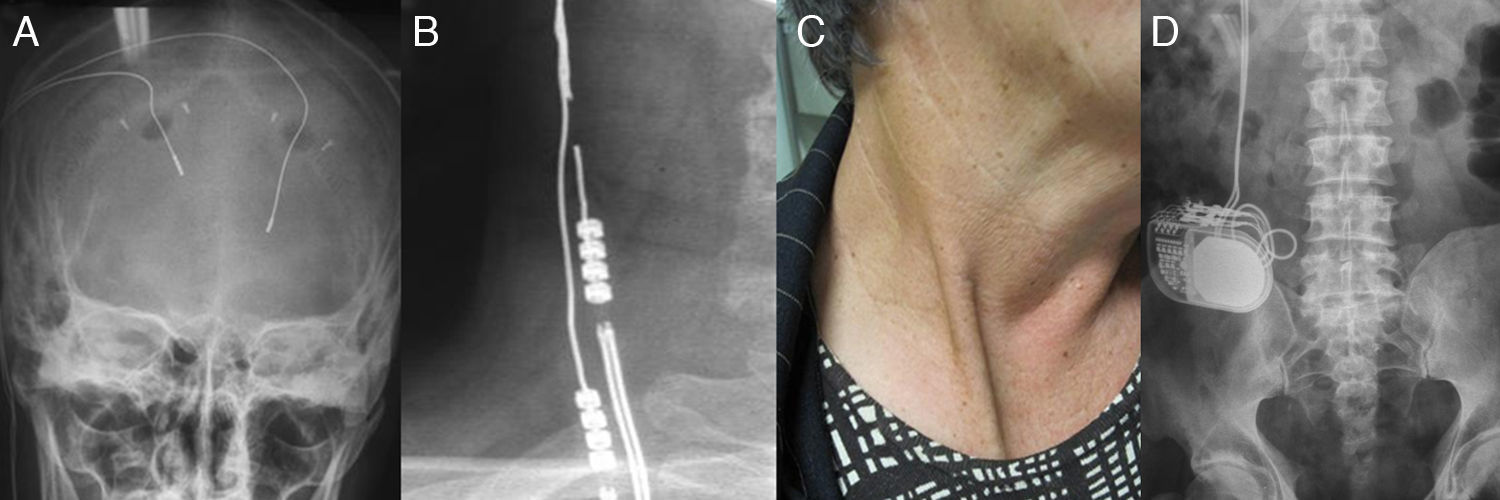
La estimulación cerebral profunda es una técnica quirúrgica que ha alcanzado un importante desarrollo para el tratamiento de diferentes trastornos del movimiento como la enfermedad de Parkinson, el temblor o la distonía. Debido al importante crecimiento en el número de pacientes tratados, se han publicado cada vez con mayor frecuencia nuevas complicaciones de la cirugía. El bowstringing se define como una tensión anormal de las extensiones eléctricas situadas entre los electrodos y la batería, acompañada de una sensación de dolor y tensión a nivel cervical, en la zona donde se encuentran los cables.
Presentamos el caso clínico de una mujer de 56 años con enfermedad de Parkinson que fue tratada con la implantación bilateral de electrodos subtalámicos. Después de un accidente de tráfico presentó ruptura del electrodo derecho, que fue recambiado. Seis meses más tarde acude por dolor y tensión en el cuello. Fue necesario realizar un abordaje cervical a los cables para extirpar el tejido cicatricial que se había formado.
El bowstringing es una complicación poco habitual en este tipo de cirugía, y aunque algunos pacientes refieren molestias y tensión en el cuello, pocas veces es necesario su abordaje quirúrgico.
Deep brain stimulation (DBS) is an established surgical therapy for intractable movement disorders, such as Parkinson's disease, essential tremor and dystonia. As the number of treated patients has increased rapidly, new sets of problems about complications of DBS have arisen. Bowstringing is defined as abnormal tethering of leads between the pulse generators and stimulating electrode, associated with pain and contracture of the neck over the extension cable.
We report the case of a 56-year-old woman with a history of advanced Parkinson's disease who had been treated by implantation of a bilateral, subthalamic nucleus, deep brain stimulator. A car accident caused the rupture of the right electrode, which was replaced. Six months after the replacement the patient presented disabling pain and tension in the neck where deep brain extension cables were located. A cervical incision was performed to excise scar tissue.
Bowstringing is a rare complication of DBS and although patients sometimes report discomfort and tension in the cervical region, surgical procedures are not normally required.
Article

If it is the first time you have accessed you can obtain your credentials by contacting Elsevier Spain in suscripciones@elsevier.com or by calling our Customer Service at902 88 87 40 if you are calling from Spain or at +34 932 418 800 (from 9 to 18h., GMT + 1) if you are calling outside of Spain.
If you already have your login data, please click here .
If you have forgotten your password you can you can recover it by clicking here and selecting the option ¿I have forgotten my password¿.