The aims of our study were to evaluate tumour response in a series of patients with vestibular schwannoma (VS) treated with linear accelerator stereotactic radiosurgery (LINAC-RS), to describe the complications and to analyze the variables associated with the response to treatment.
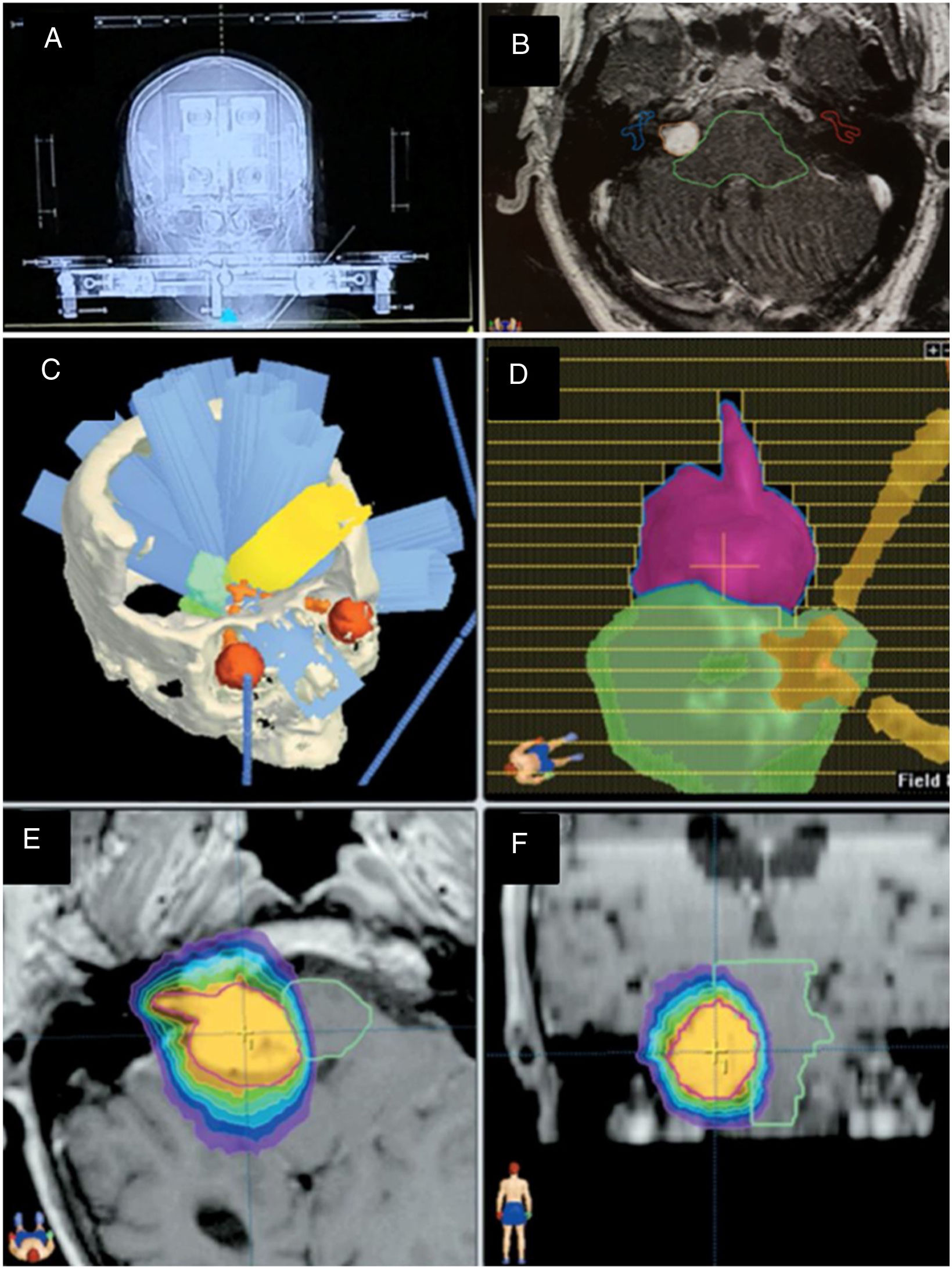
Material and methodsThis retrospective descriptive study included 64 patients treated from 2010 to 2016 with a minimum follow-up of one year, excluding patients with neurofibromatosis. Clinical–radiological parameters were evaluated. The treatment was performed using LINAC-RS. The prescribed dose was 12Gy at 90% isodose.
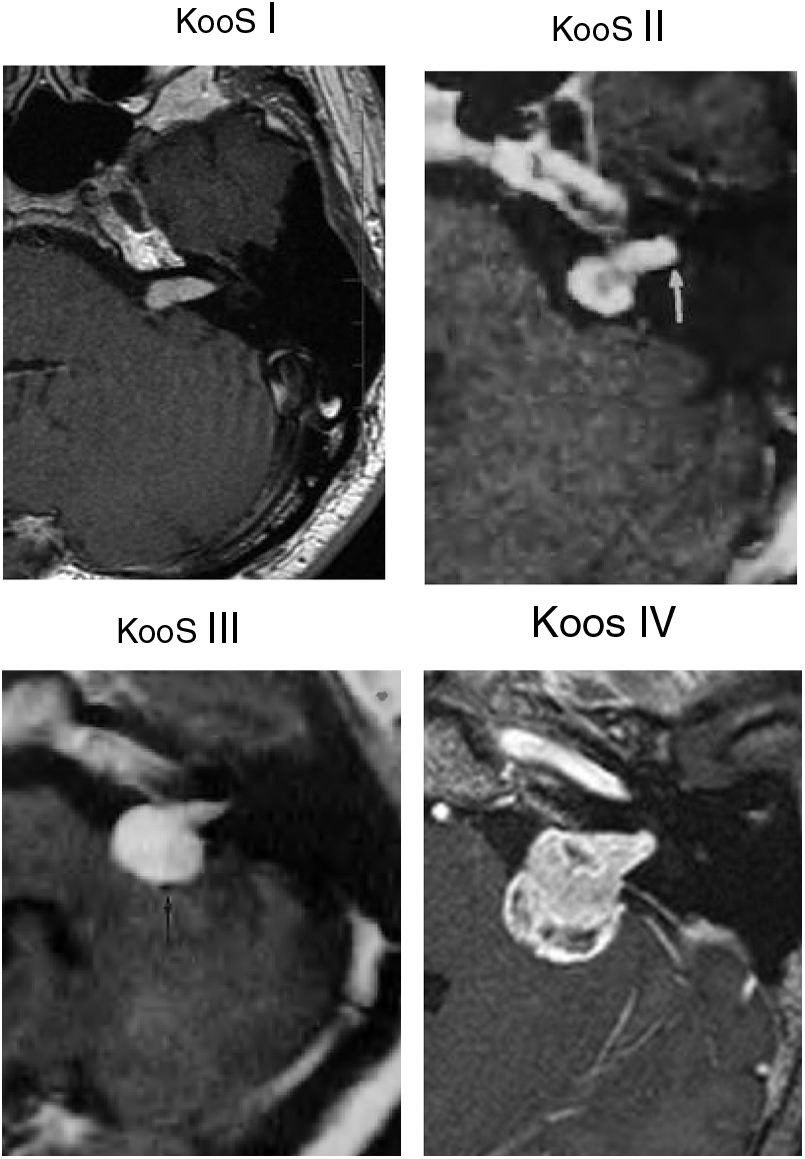
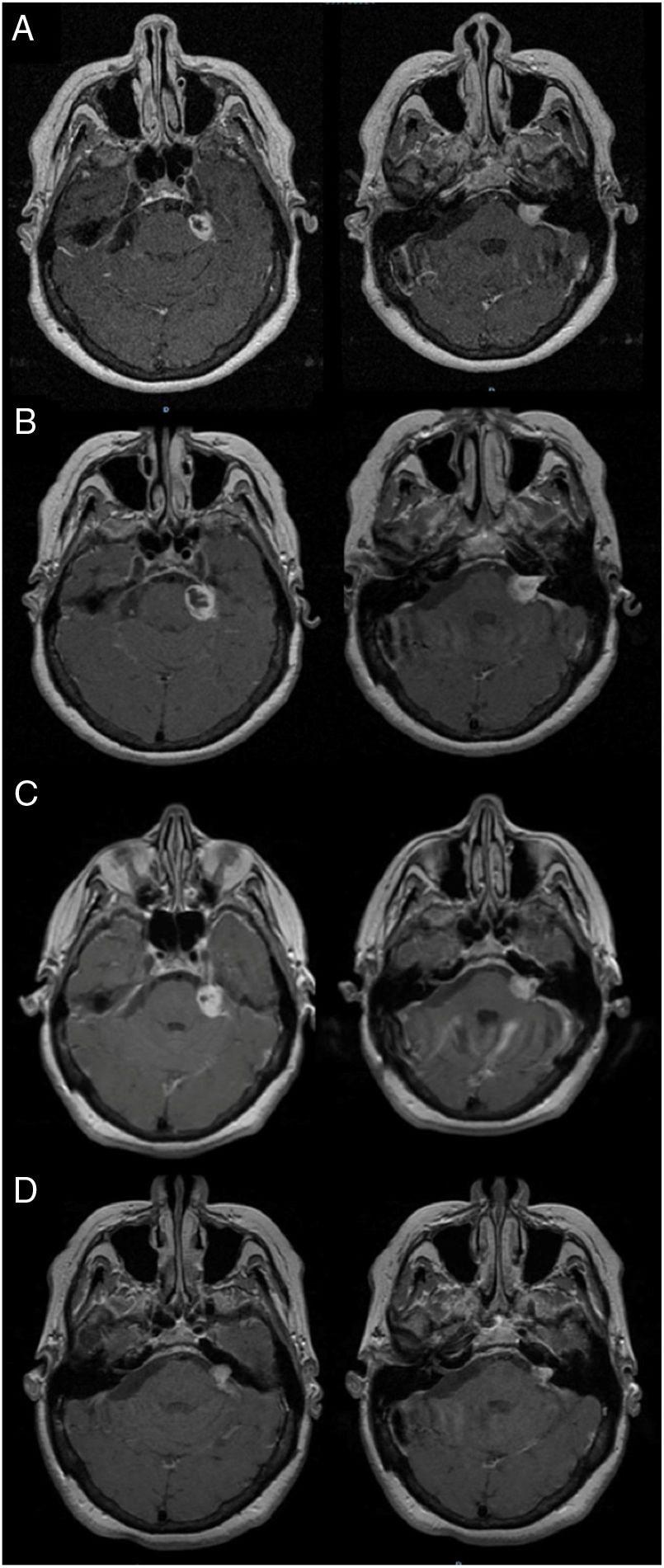
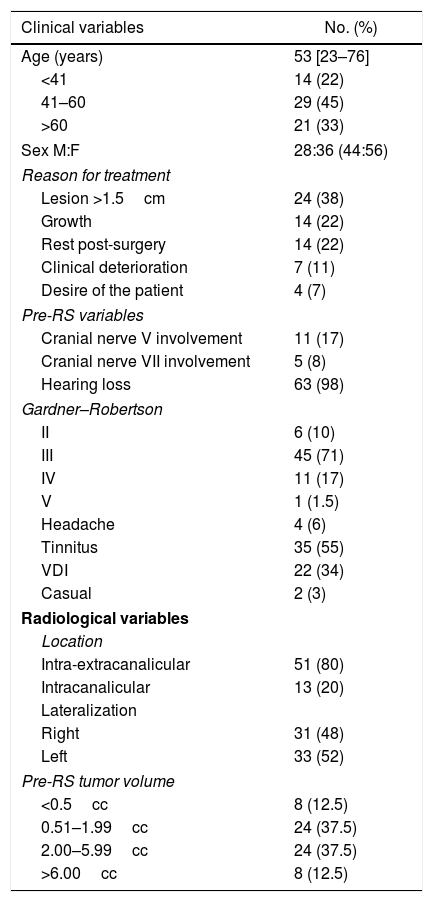
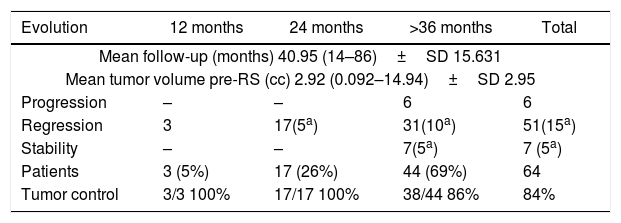
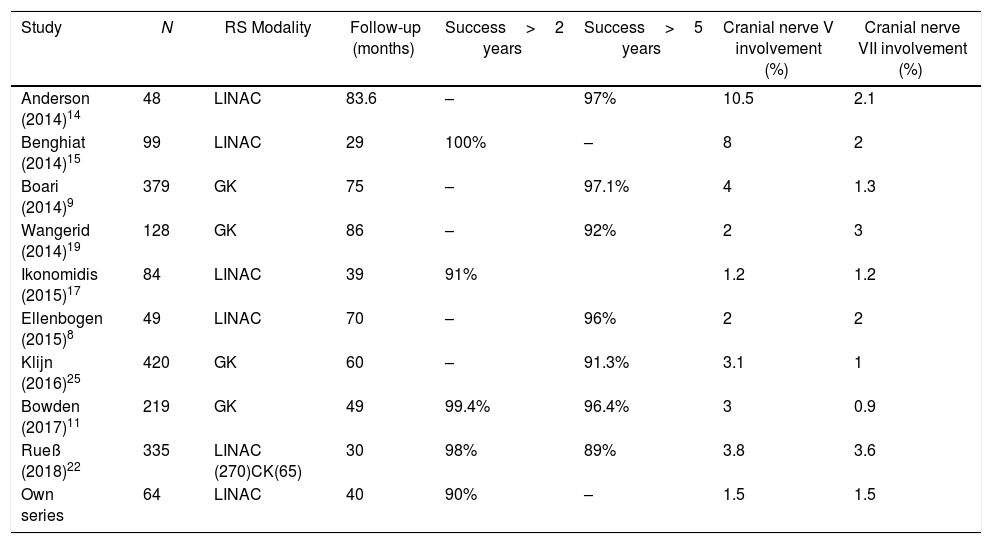
ResultsThe mean age at treatment was 53 years, 56% were women. Ninety-eight percent of the patients had hearing loss, 71% with grade III according to the Gardner–Robertson Classification. The mean volume at treatment was 2.92cc and the mean follow-up, 40.95 months. The overall therapeutic success was 90%, reaching 100% at 12 and 24 months, and 86% after 36 months of follow-up. The radiological result was significantly related to the initial tumour volume (p<0.037). In 20 patients there was evidence of transient tumour growth compatible with pseudoprogression. Acute complications were present in 37.5%, and transitory complications in 50%. Chronic complications were found in 20%, with 84% being permanent. The rate of acute complications was lower in patients with regression (p<0.016). Chronic complications were more frequent in the 41–60 year old age group (p<0.040).
ConclusionsIn our study, the overall tumour control was in accordance with other published series. The radiological result significantly related to the tumour volume at the commencement of treatment. The rate of acute complications was lower in patients with regression.
Los objetivos del estudio fueron evaluar la respuesta tumoral en una serie de pacientes con schwannoma vestibular (SV) tratados con radiocirugía (RC) mediante acelerador lineal de electrones (LINAC), describir las complicaciones y analizar las variables relacionadas con la respuesta al tratamiento.
Material y métodosEstudio descriptivo retrospectivo de 64 pacientes tratados entre 2010-2016 con seguimiento mínimo de un año, excluyendo pacientes con neurofibromatosis. Se evaluaron parámetros clínico-radiológicos. El tratamiento se realizó mediante RC-LINAC. La dosis prescrita fue de 12Gy al 90% de isodosis.
ResultadosLa edad media al tratamiento fue de 53 años, 56% mujeres. El 98% de los pacientes presentaban hipoacusia, el 71% grado iii según la clasificación Gardner-Robertson. El volumen medio al tratamiento fue de 2,92cc, y la media de seguimiento 40,95 meses. El éxito terapéutico global fue del 90% siendo del 100% a los 12 y 24 meses y del 86% a partir de los 36 meses de seguimiento. El resultado radiológico se relacionaba con el volumen tumoral inicial (p<0,037). En 20 pacientes se evidenció un crecimiento tumoral transitorio compatible con seudoprogresión. El 37,5% tuvieron complicaciones agudas siendo transitorias el 50%. Se recogieron complicaciones crónicas en el 20%, siendo permanentes en el 84%. La tasa de complicaciones agudas era menor en pacientes con regresión (p<0,016). Las complicaciones crónicas fueron más frecuentes en el grupo de 41-60 años (p<0,040).
ConclusionesEn nuestra serie, el control tumoral global obtenido es acorde con otras series publicadas. El resultado radiológico estaba relacionado con el volumen tumoral inicial al tratamiento. La tasa de complicaciones agudas fue menor en pacientes con regresión.
Article

If it is the first time you have accessed you can obtain your credentials by contacting Elsevier Spain in suscripciones@elsevier.com or by calling our Customer Service at902 88 87 40 if you are calling from Spain or at +34 932 418 800 (from 9 to 18h., GMT + 1) if you are calling outside of Spain.
If you already have your login data, please click here .
If you have forgotten your password you can you can recover it by clicking here and selecting the option ¿I have forgotten my password¿.