Mesial temporal lobe epilepsy with hippocampal sclerosis is the most common cause of refractory epilepsy, and the most common indication for surgery. Although effective, surgery fails in up to 40% of patients. The objective of our study was to establish a correlation between the different histological subtypes of mesial temporal lobe epilepsy with hippocampal sclerosis and the prognosis, seizures control, side effects and anticonvulsivant drug withdrawal in patients with refractory epilepsy.
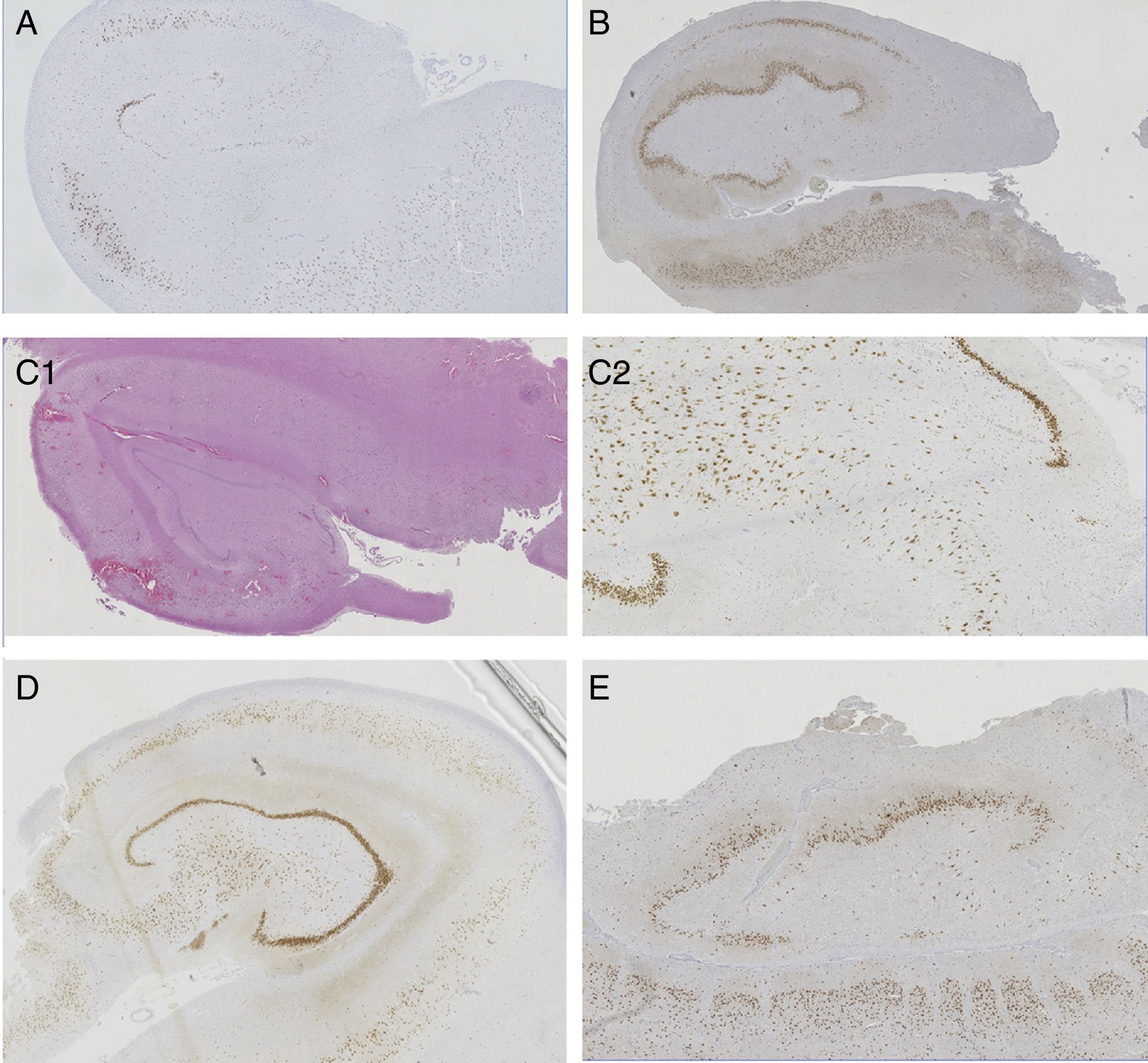
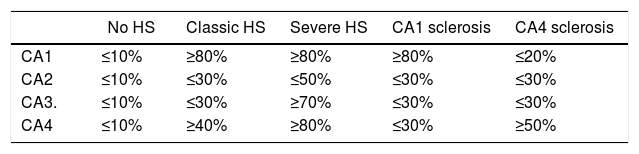
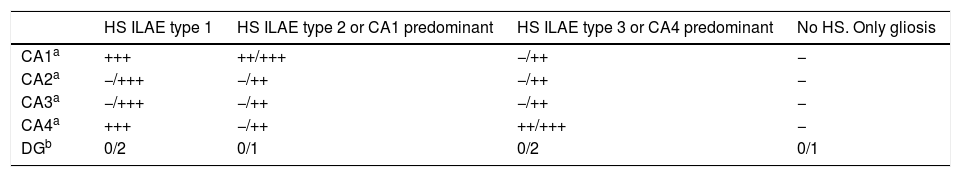
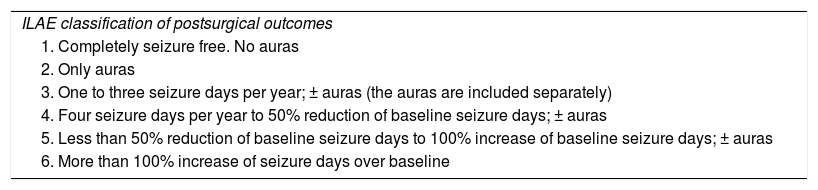
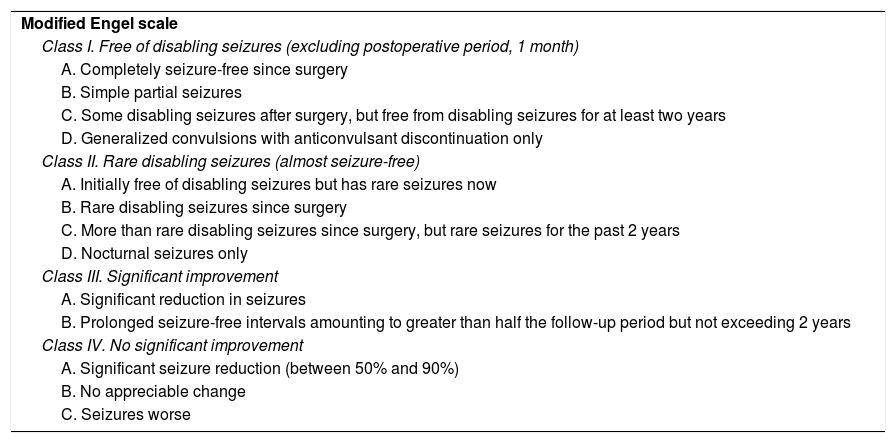
Patients and methodClinical histories and anatomopathological specimens of 228 patients with temporal epilepsy surgically obtained at our hospital between 1993 and 2014 were retrospectively analyzed. All patients underwent a standard preoperative evaluation and anterior temporal resection (modified from Spencer). The anatomopathological study included the standard hematoxylin–eosin and immunohistochemical protocol, with special interest in the assessment of neuronal loss with NeuN. Seizure control was assessed according to the scale of results of the ILAE and Engel. The mean follow-up was 8.6 years (2–19).
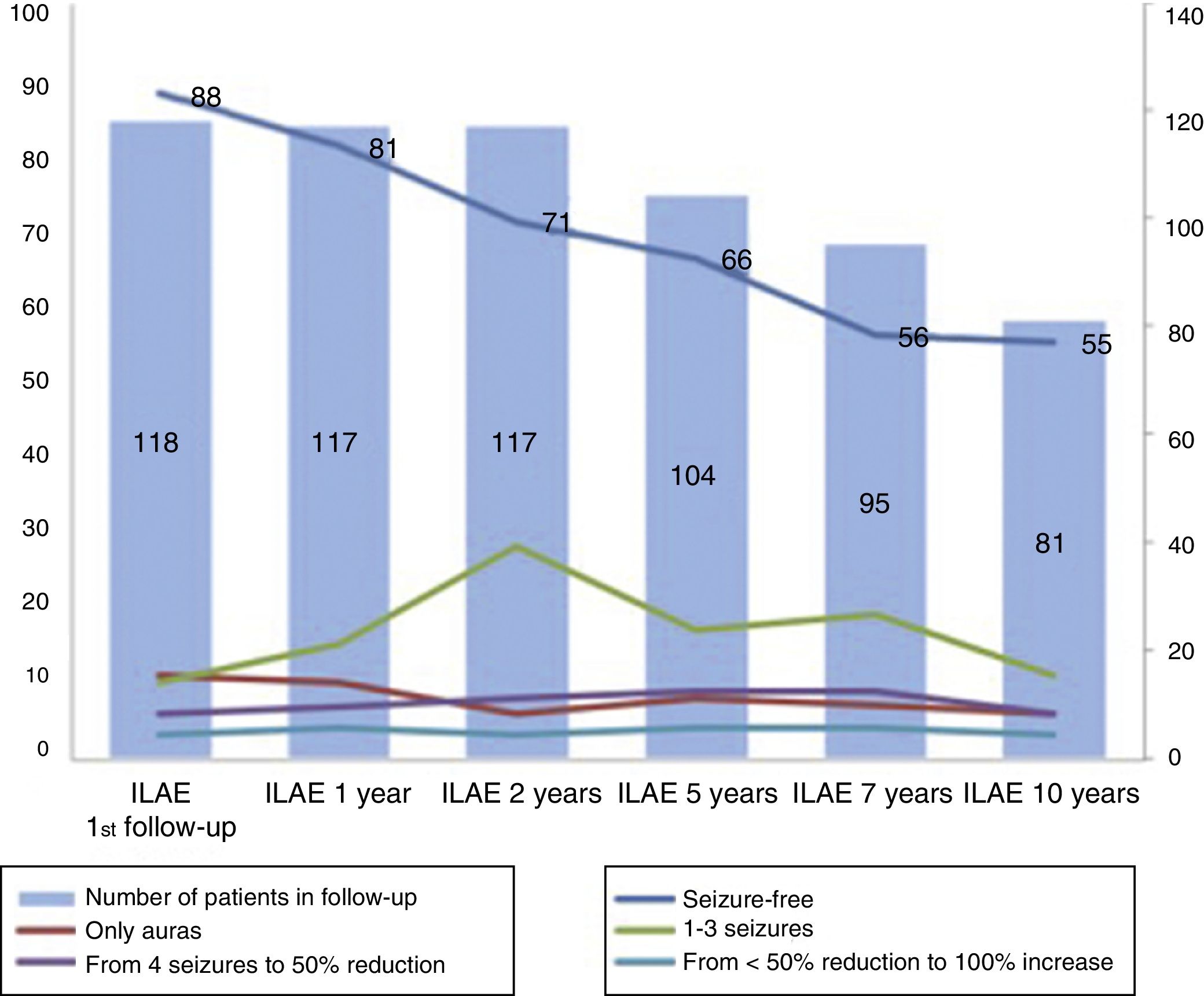
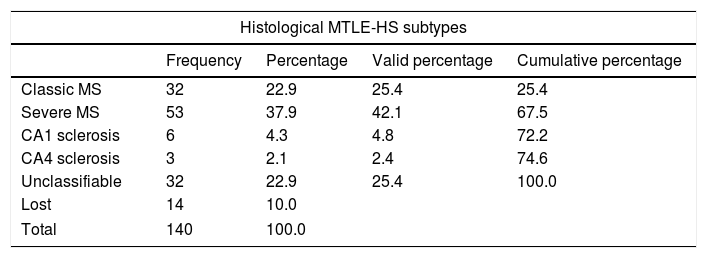
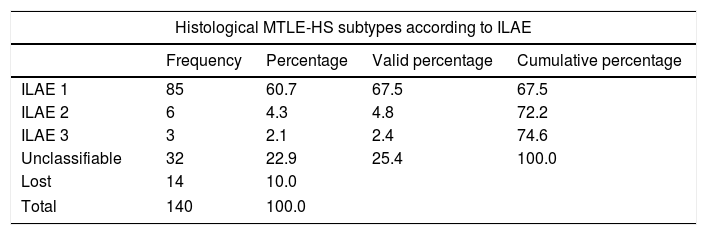
ResultsAt 10 years after the intervention, 67.9% of patients were seizure-free (ILAE 1) and as many as 77.5% of the patients were seizure-free (Engel 1) at the end of the follow-up. The probability of not having a seizure (ILAE 1) after surgery at 2 (p=0.042), 5 (p=0.001) and 7 years (p=0.22) was higher in classic and severe forms compared to isolated sclerosis CA1 and CA4 forms. Higher neuronal loss measured with the NeuN immunostain in CA1 was associated with better outcome in seizure management (multivariate analysis, p=0.08). The presence of a personal history of epilepsy was associated with greater neuronal loss in CA1 (p=0.028) and CA3 (p=0.034), and the presence of psychic auras was related with greater neuronal loss in CA3 (p=0.025). In our case, the probability of medication withdrawal was related to the presence of personal history (p=0.003) and, inversely, to neuronal loss in CA1 (p=0.036) and CA3 (p=0.038). The greatest impairment of verbal memory occurred in those patients with a lower neuronal loss in CA1 (p=0.023), CA2 (p=0.049) and CA3 (p=0.035).
ConclusionsThe results indicate that the classical and severe subtypes have a better prognosis in the control of seizures against the atypical forms, validating the clinical and prognostic utility of the classification of histological subtypes of hippocampal sclerosis from the ILAE. The value of the immunohistochemistry in the mesial temporal lobe epilepsy with hippocampal sclerosis has been demonstrated as a key element to determine the neuropsychological prognosis and seizure management of the patients after surgery.
La epilepsia temporal con esclerosis hipocampal es la causa más frecuente de epilepsia refractaria, y la indicación más común de cirugía. Aunque eficaz, la cirugía fracasa hasta en un 40% de los pacientes. El objetivo de nuestro trabajo es establecer una correlación entre los distintos subtipos histológicos de epilepsia temporal con esclerosis hipocampal y el pronóstico, control de crisis, efectos secundarios y retirada de fármacos anticomiciales en los pacientes con epilepsia resistente a fármacos intervenidos.
Pacientes y métodoSe analizaron de forma retrospectiva las historias clínicas y muestras anatomopatológicas de 228 pacientes con epilepsia temporal intervenidos en nuestro centro entre los años 1993 y 2014. Todos fueron sometidos a una evaluación prequirúrgica estándar e intervenidos mediante una resección temporal anterior (modificada de Spencer). El estudio anatomopatológico incluyó el protocolo de hematoxilina-eosina e inmunohistoquímico estándar, con especial interés en la valoración de pérdida neuronal con NeuN. El control de las crisis fue valorado de acuerdo a la escala de resultados de la ILAE y de Engel. El seguimiento medio fue de 8,6 años (2-19).
ResultadosA los 10 años tras la intervención, un 67,9% de los pacientes se encontraban libres de crisis (ILAE 1). Un 77,5% de los pacientes estaba libre de crisis (Engel 1) al final del seguimiento. La probabilidad de quedar sin crisis (ILAE 1) tras la cirugía a los 2 (p=0,042), 5 (p=0,001) y 7 (p=0,022) años fue mayor en las formas clásica y severa frente a las formas de esclerosis aislada CA1 y CA4. Una mayor pérdida neuronal medida con NeuN en CA1 se relacionó con un mejor resultado en el control de las crisis (análisis multivariante, p=0,08). La presencia de antecedentes personales desencadenantes de epilepsia se relacionó con una mayor pérdida neuronal en CA1 (p=0,028) y CA3 (p=0,034), y la presencia de auras psíquicas con una mayor pérdida de neuronas en CA3 (p=0,025). En nuestro caso, la probabilidad de dejar la medicación se relacionó con la presencia de antecedentes personales (p=0,003) y, de forma inversa, con la pérdida neuronal en CA1 (p=0,036) y CA3 (p=0,038). El mayor deterioro de memoria verbal ocurrió en aquellos pacientes con menor pérdida neuronal en CA1 (p=0,023), CA2 (p=0,049) y CA3 (p=0,035).
ConclusionesLos resultados señalan que los subtipos clásico y severo tienen un mejor pronóstico en el control de las crisis frente a las formas atípicas, validándose la utilidad clínica y pronóstica de la clasificación de consenso de los subtipos histológicos de esclerosis hipocampal de la ILAE. Se ha demostrado el valor de la inmunohistoquímica en la epilepsia temporal con esclerosis hipocampal como un elemento clave para determinar el pronóstico en el control de las crisis y neuropsicológico de los pacientes tras la cirugía.
Artículo

Si es la primera vez que accede a la web puede obtener sus claves de acceso poniéndose en contacto con Elsevier España en suscripciones@elsevier.com o a través de su teléfono de Atención al Cliente 902 88 87 40 si llama desde territorio español o del +34 932 418 800 (de 9 a 18h., GMT + 1) si lo hace desde el extranjero.
Si ya tiene sus datos de acceso, clique aquí.
Si olvidó su clave de acceso puede recuperarla clicando aquí y seleccionando la opción "He olvidado mi contraseña".
Comprando el artículo el PDF del mismo podrá ser descargado
Precio 19,34 €
Comprar ahora