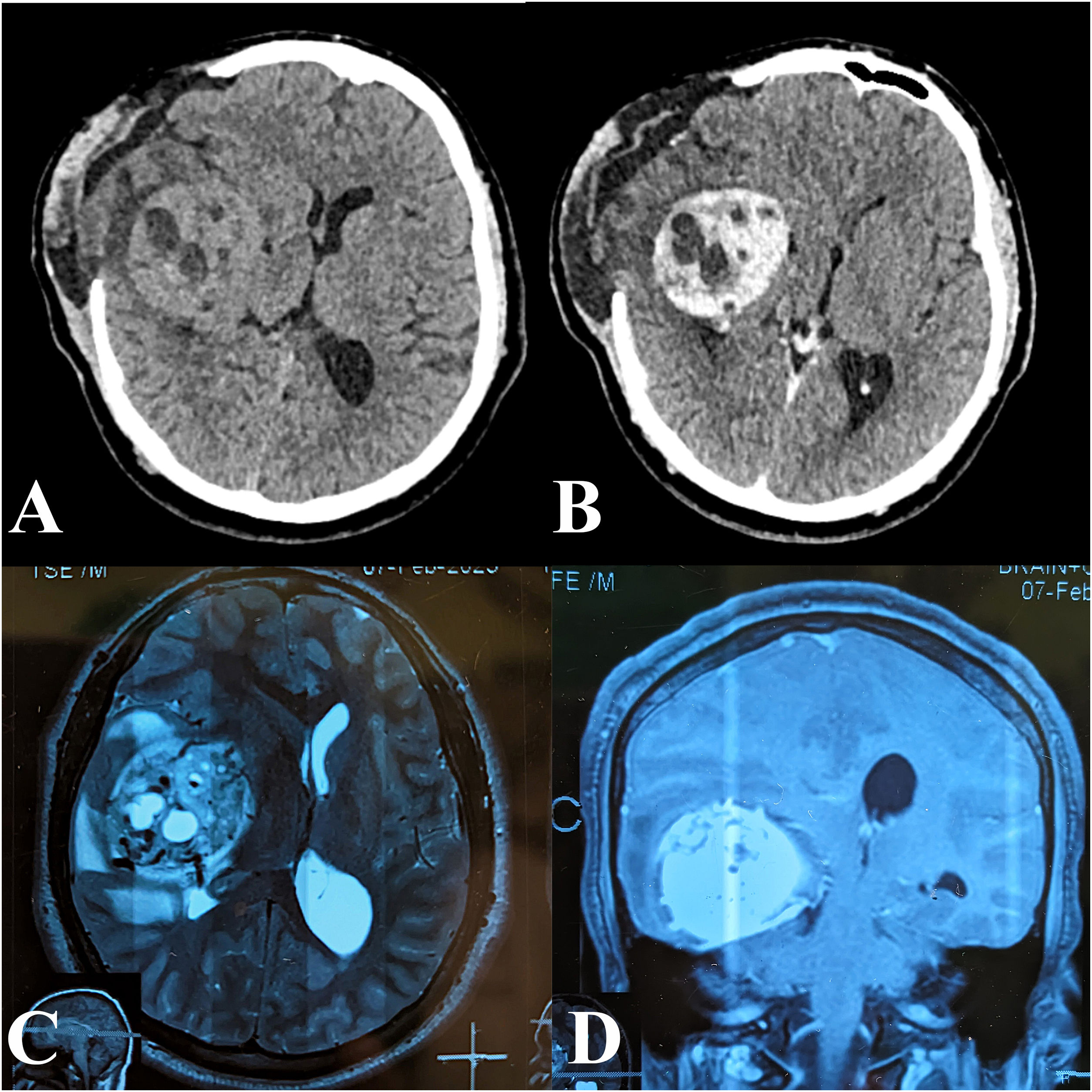
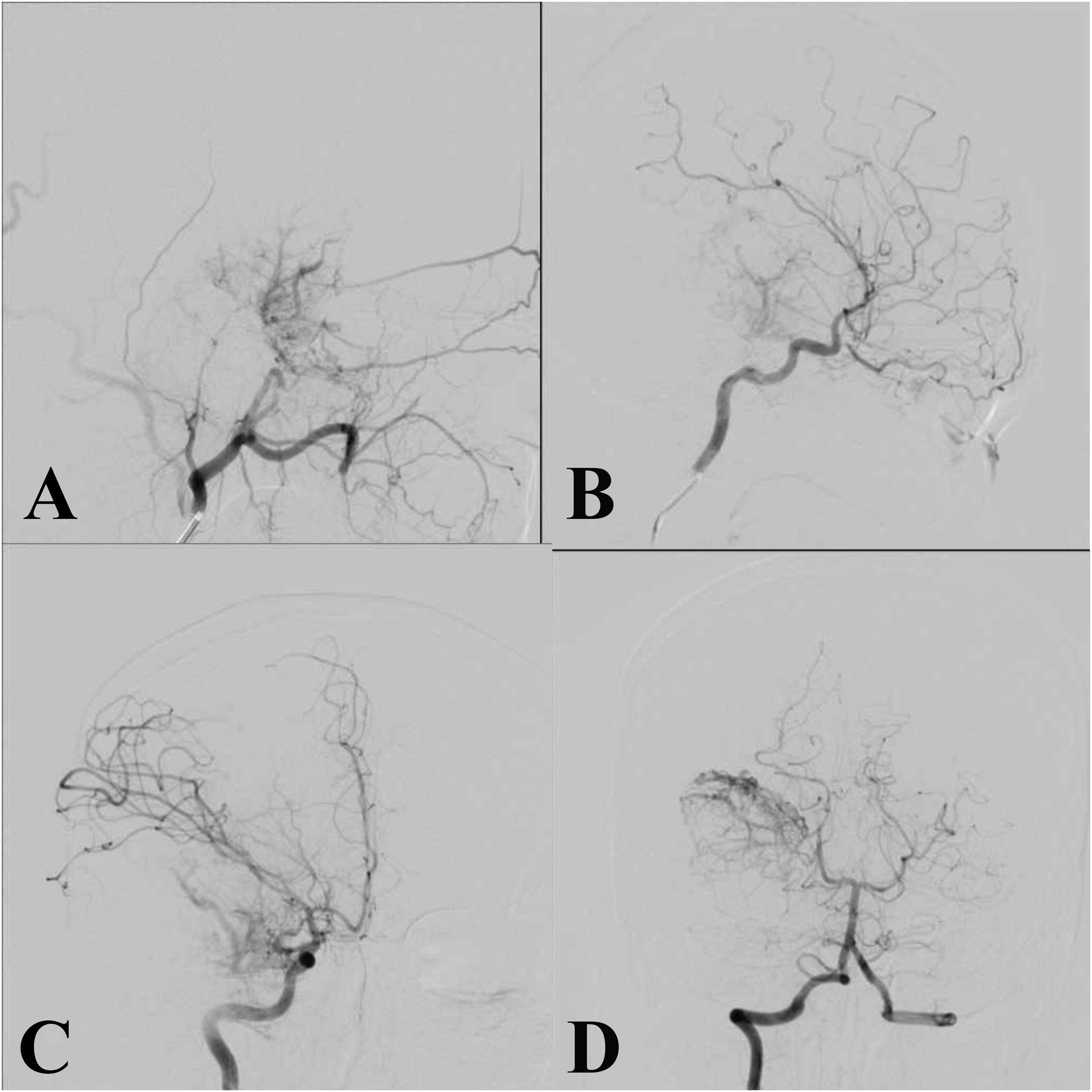
Solitary fibrous tumors (SFTs) are rare intracranial neoplasms that are highly vascular, making surgical resection challenging due to significant intraoperative blood loss. Preoperative embolization is commonly performed via the transarterial route; however, this approach has limitations, including difficulty in accessing multiple feeders, prolonged procedural time, and the risk of embolic material reflux into the intracranial circulation.
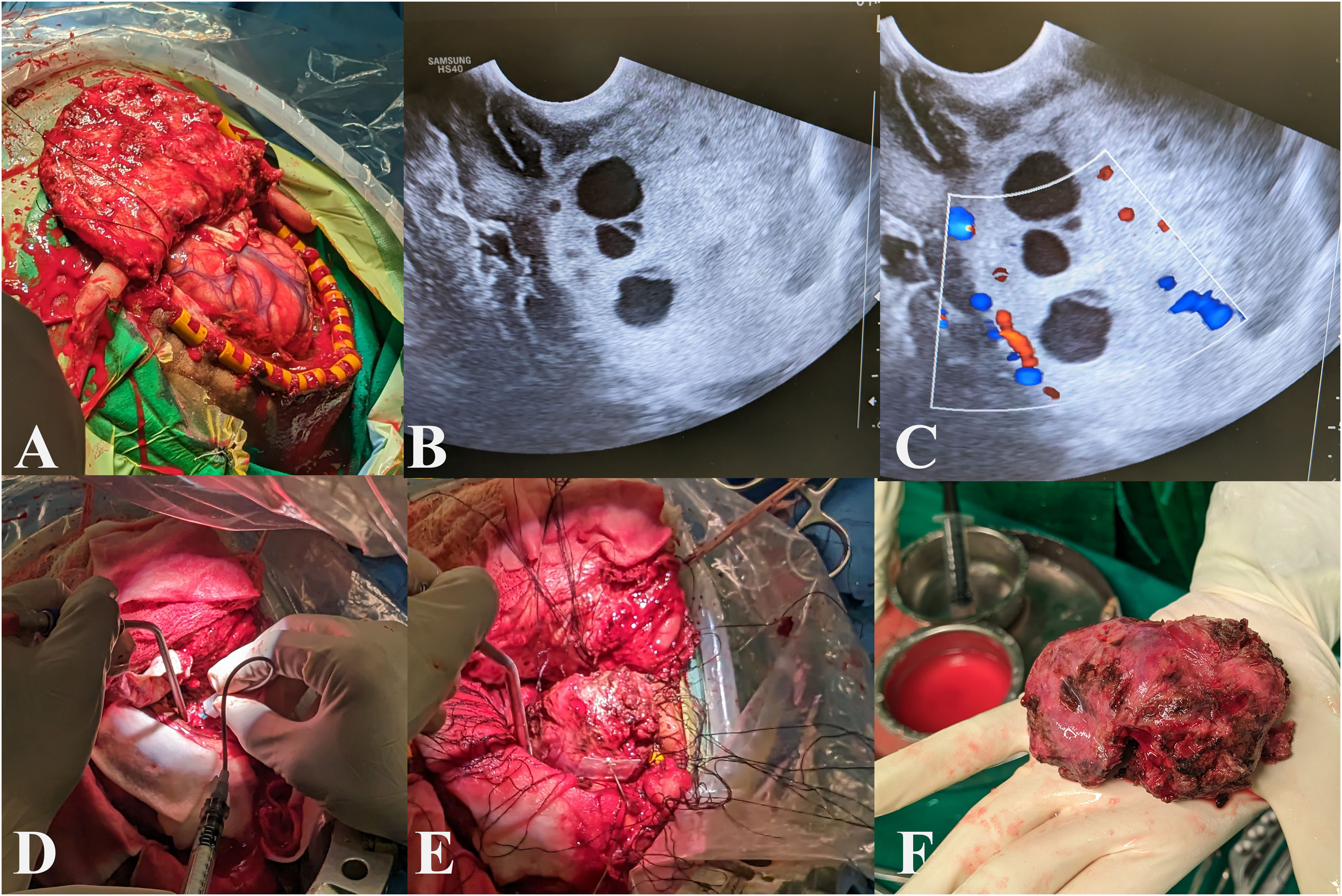
Here, we report the case of a 19-year-old male with a large intracranial SFT, initially treated with transarterial embolization using polyvinyl alcohol (PVA) particles, which failed to achieve proper devascularization of the tumor. Consequently, direct puncture embolization using the SQUID 12 agent was performed. Following successful embolization, complete tumor resection was achieved with significantly reduced intraoperative blood loss and no postoperative neurological deficits.
This case highlights the effectiveness of direct puncture embolization as a viable alternative to traditional transarterial approaches for managing highly vascular intracranial tumors.
Los tumores fibrosos solitarios (TFS) son neoplasias intracraneales raras que presentan una gran vascularización, lo que dificulta la resección quirúrgica debido a la importante pérdida de sangre intraoperatoria. La embolización preoperatoria se realiza habitualmente por vía transarterial; sin embargo, este abordaje tiene limitaciones, como la dificultad para acceder a múltiples vías de alimentación, el tiempo prolongado del procedimiento y el riesgo de reflujo de material embólico hacia la circulación intracraneal.
En este artículo, informamos del caso de un varón de 19 años con un gran TFS intracraneal, tratado inicialmente con embolización transarterial utilizando partículas de alcohol polivinílico (PVA), que no logró una desvascularización adecuada del tumor. En consecuencia, se realizó una embolización por punción directa utilizando el agente SQUID 12. Tras una embolización exitosa, se logró la resección completa del tumor con una pérdida de sangre intraoperatoria significativamente reducida y sin déficits neurológicos posoperatorios.
Este caso destaca la eficacia de la embolización por punción directa como una alternativa viable a los abordajes transarteriales tradicionales para el tratamiento de tumores intracraneales altamente vascularizados.
Article

If it is the first time you have accessed you can obtain your credentials by contacting Elsevier Spain in suscripciones@elsevier.com or by calling our Customer Service at902 88 87 40 if you are calling from Spain or at +34 932 418 800 (from 9 to 18h., GMT + 1) if you are calling outside of Spain.
If you already have your login data, please click here .
If you have forgotten your password you can you can recover it by clicking here and selecting the option ¿I have forgotten my password¿.