Neuronavigation in ventriculoscopy has been described in several papers. However, there are different ventriculoscopes and navigation systems. Because of these different combinations, it is difficult to find detailed navigation protocols for each ventriculoscope. We describe, step by step, a simple method to navigate both the trajectory to reach the ventricular system and the intraventricular work for the LOTTA ventriculoscope.
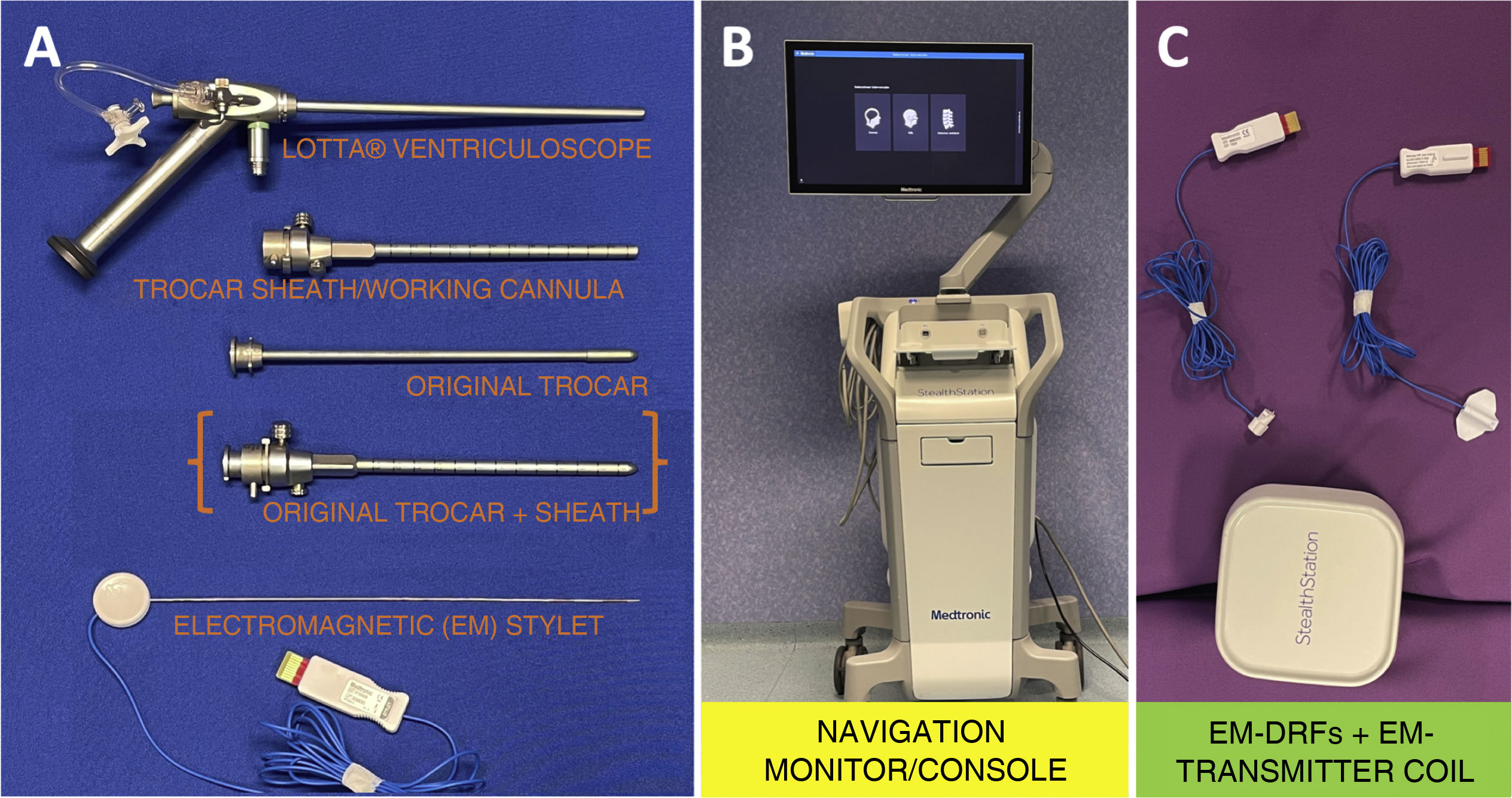
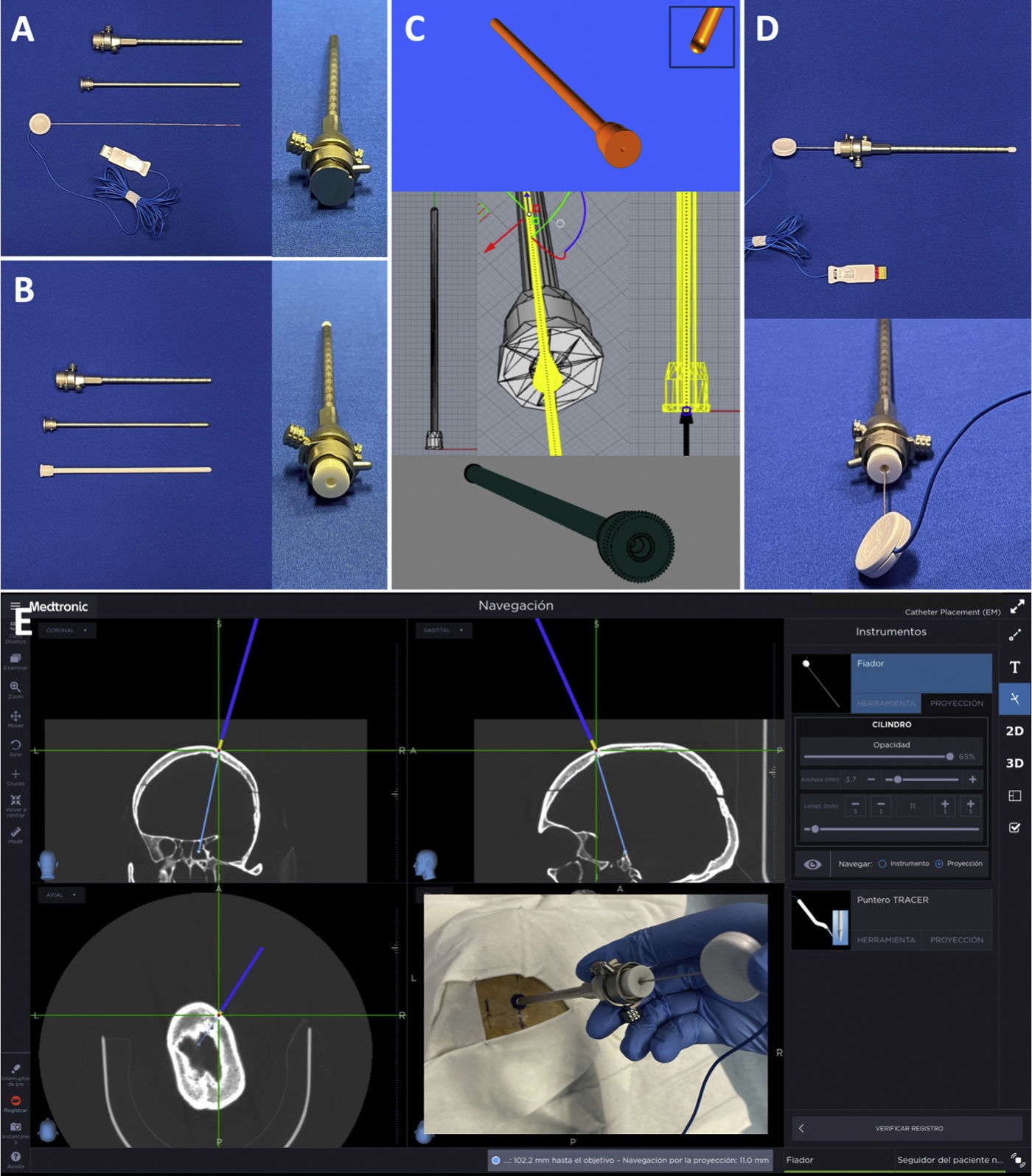
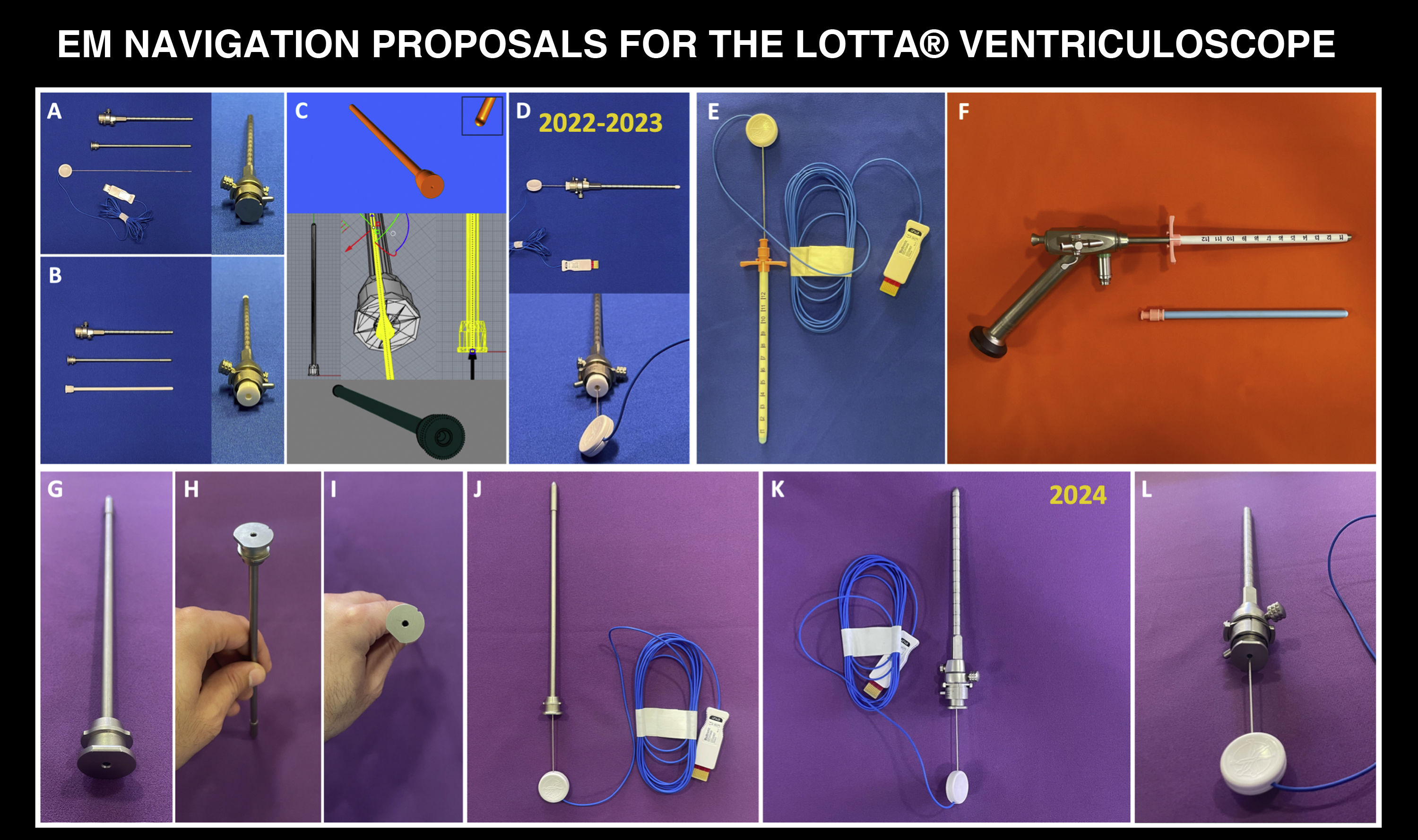
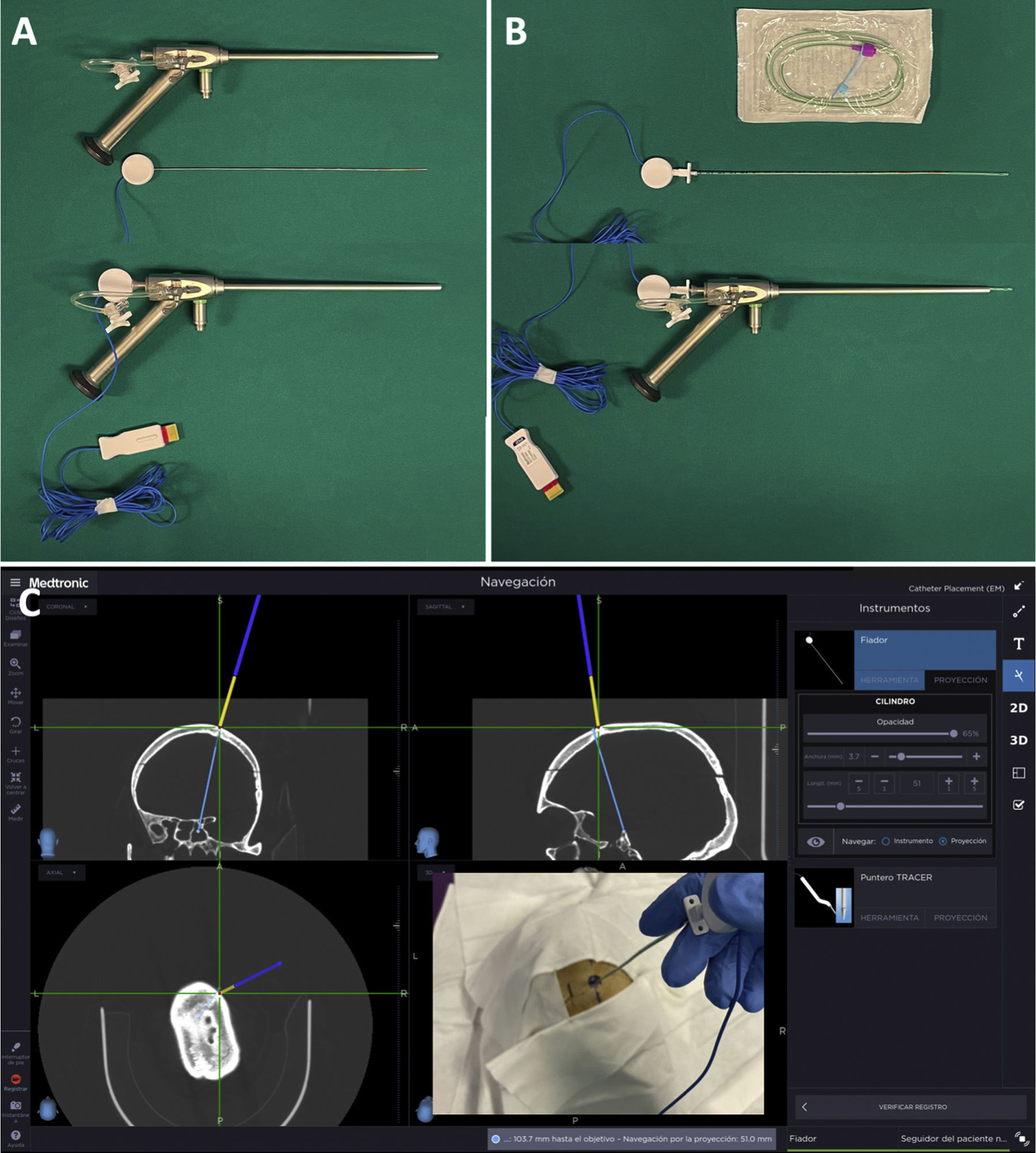
MethodsWe used a rigid ventriculoscope (LOTTA, KarlStorz) with an electromagnetic stylet (S8-StealthSystem, Medtronic) as the main navigation tool. The protocol is based on a 3D printed trocar or alternatively, on a modification of the original trocar for extraventricular phase navigation and a modified pediatric nasogastric tube for intraventricular phase navigation.
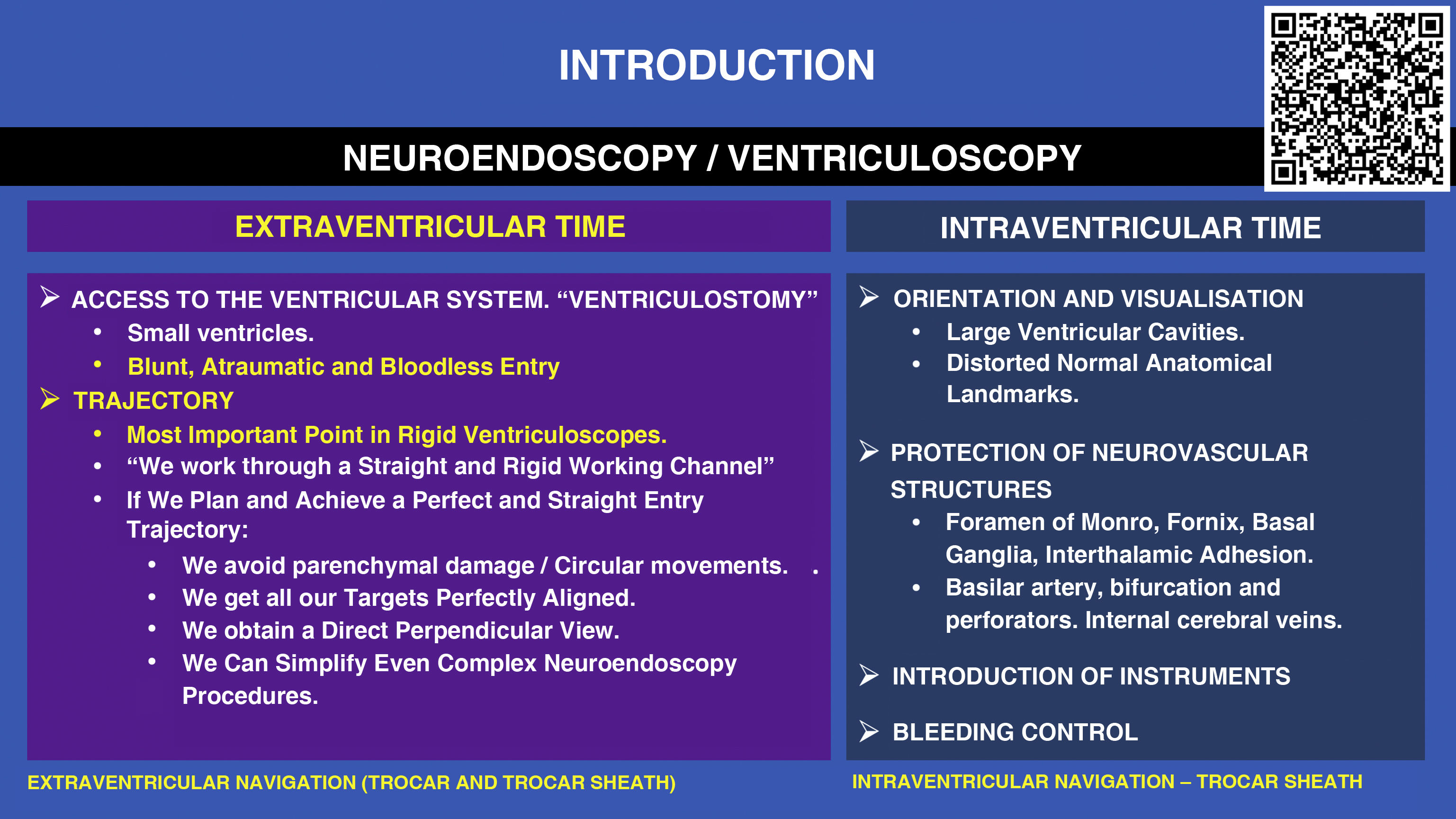
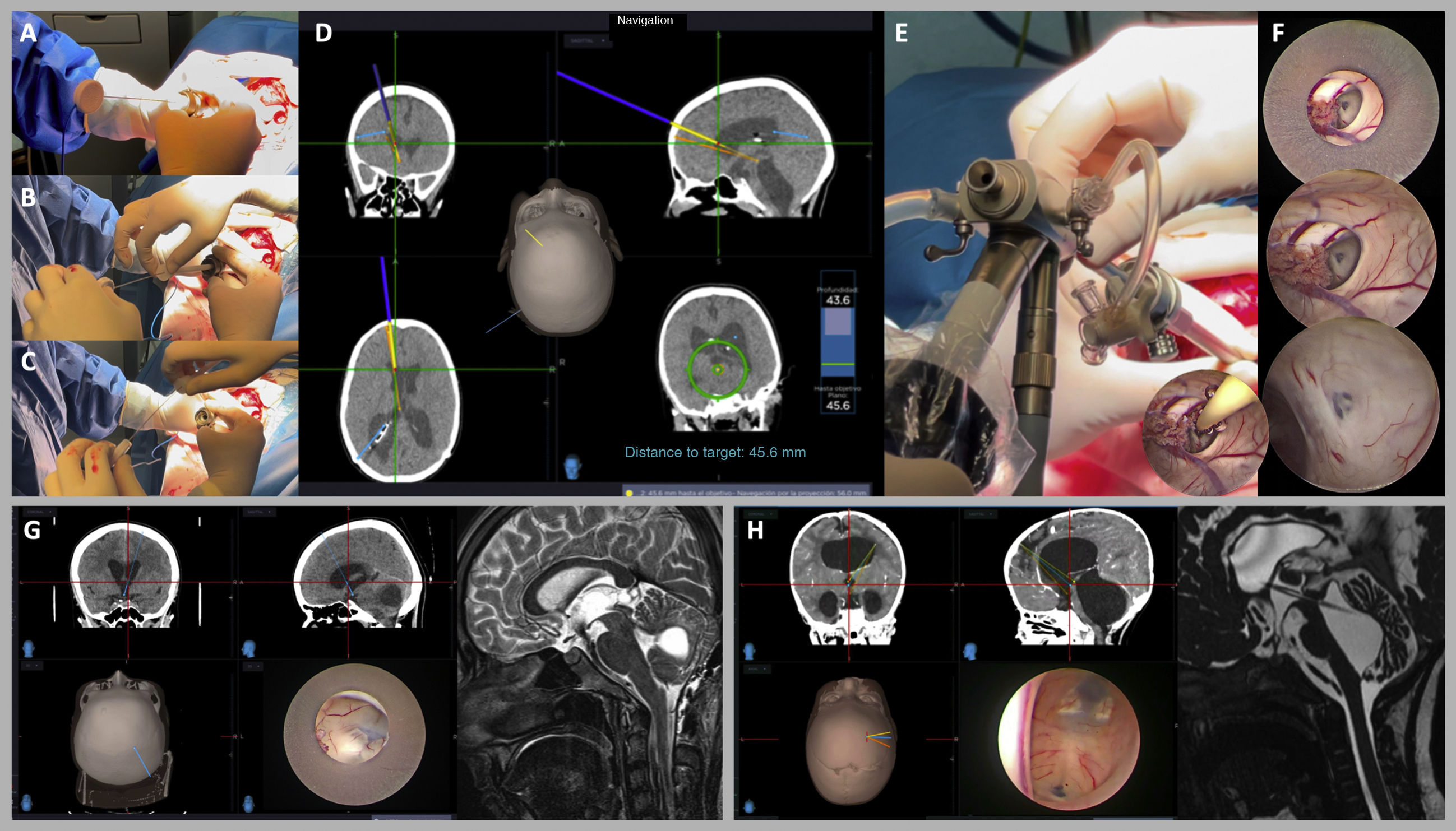
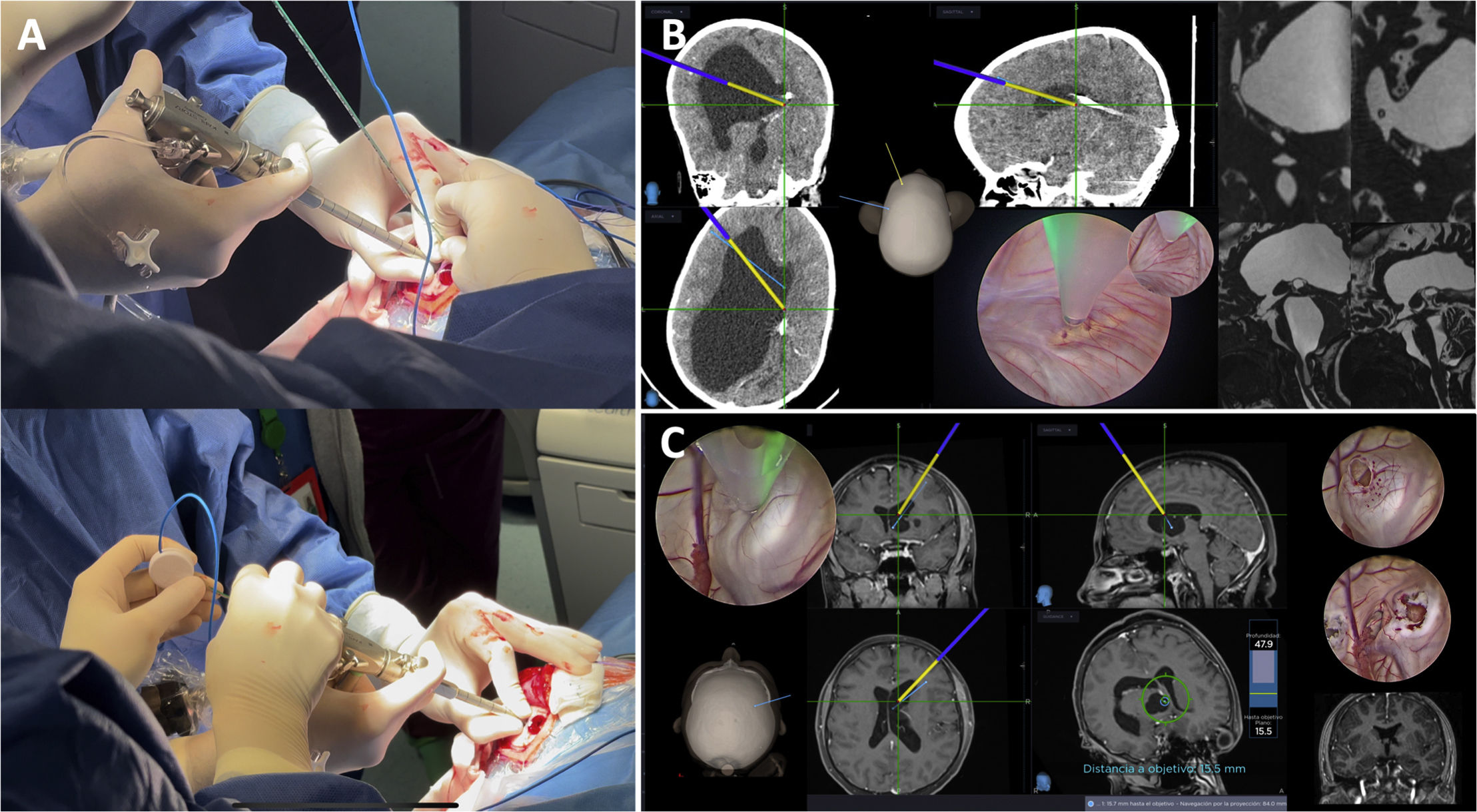
ResultsThe protocol can be set up in less than 10min. The extraventricular part is navigated by inserting the electromagnetic stylet inside the 3D printed trocar or inside the original modified trocar. Intraventricular navigation is performed by combining a modified pediatric nasogastric tube with the electromagnetic stylet inside the working channel of the endoscope. The most critical point is to obtain a blunt, bloodless approach to the ventricle and to achieve perfect alignment of all target structures by means of previously planned pure straight trajectories.
ConclusionsThis protocol is easy to set up, avoids rigid head fixation, bulky optical navigation accessories, while allows continuous navigation of both parts of the surgery. Since we have implemented this protocol, we have seen a significant improvement in both simple and complex neuroendoscopy procedures as the surgery is dramatically simplified.
La neuronavegación en ventriculoscopia se ha descrito en varios trabajos. Sin embargo, existen diferentes ventriculoscopios y sistemas de navegación. Debido a estas diferentes combinaciones, es difícil encontrar protocolos detallados de navegación para cada ventriculoscopio. Describimos, paso a paso, un método sencillo para navegar tanto la trayectoria hasta alcanzar el sistema ventricular, como el trabajo intraventricular para el ventriculoscopio LOTTA.
Material y métodosUtilizamos un ventriculoscopio rígido (LOTTA, KarlStorz) con un estilete electromagnético (S8-StealthSystem, Medtronic) como herramienta principal de navegación. El protocolo se basa en un trocar impreso en 3D o alternativamente, en una modificación del trócar original para la navegación de la fase extraventricular y en una sonda nasogástrica pediátrica modificada para la navegación de la fase intraventricular.
ResultadosEl protocolo puede configurarse en menos de 10 minutos. La parte extraventricular se navega introduciendo el estilete electromagnético dentro del trocar impreso en 3D o dentro del trócar original modificado. La navegación intraventricular se realiza combinando una sonda nasogástrica pediátrica modificada con el estilete electromagnético dentro del canal de trabajo del endoscopio. El punto más crítico consiste en obtener un acceso al ventrículo romo, exento de sangre y lograr una alineación perfecta de todas las estructuras diana mediante trayectorias rectas puras previamente planificadas.
ConclusionesEste protocolo es fácil de configurar, evita la fijación rígida de la cabeza, los voluminosos accesorios de navegación óptica, y a su vez permite la navegación continua de ambas partes de la cirugía. Desde que hemos implantado este protocolo, hemos observado una mejora significativa tanto en los procedimientos de neuroendoscopia sencillos como en los complejos ya que la cirugía se simplifica de forma drástica.
Article

If it is the first time you have accessed you can obtain your credentials by contacting Elsevier Spain in suscripciones@elsevier.com or by calling our Customer Service at902 88 87 40 if you are calling from Spain or at +34 932 418 800 (from 9 to 18h., GMT + 1) if you are calling outside of Spain.
If you already have your login data, please click here .
If you have forgotten your password you can you can recover it by clicking here and selecting the option ¿I have forgotten my password¿.