Pudendal nerve entrapment (PNE) is rare, and mostly affects women, with men accounting for only 1/3 of cases. The European guidelines advocate surgical decompression in select PNE cases. We aim to evaluate surgical outcomes in a group of male patients diagnosed with PNE who underwent laparoscopic decompression surgery supported by intraoperative neurophysiological monitoring (pIOM).
Material and methodsThis retrospective and multicentric study included 138 patients with suspected PNE syndrome. The diagnosis of PNE was established based on neurophysiological tests and response to pudendal nerve block. Patients who experienced symptom relief following the nerve block underwent laparoscopic pudendal nerve decompression surgery, with pIOM utilized during the procedure. Symptom progression was tracked over a 12-month follow-up period.
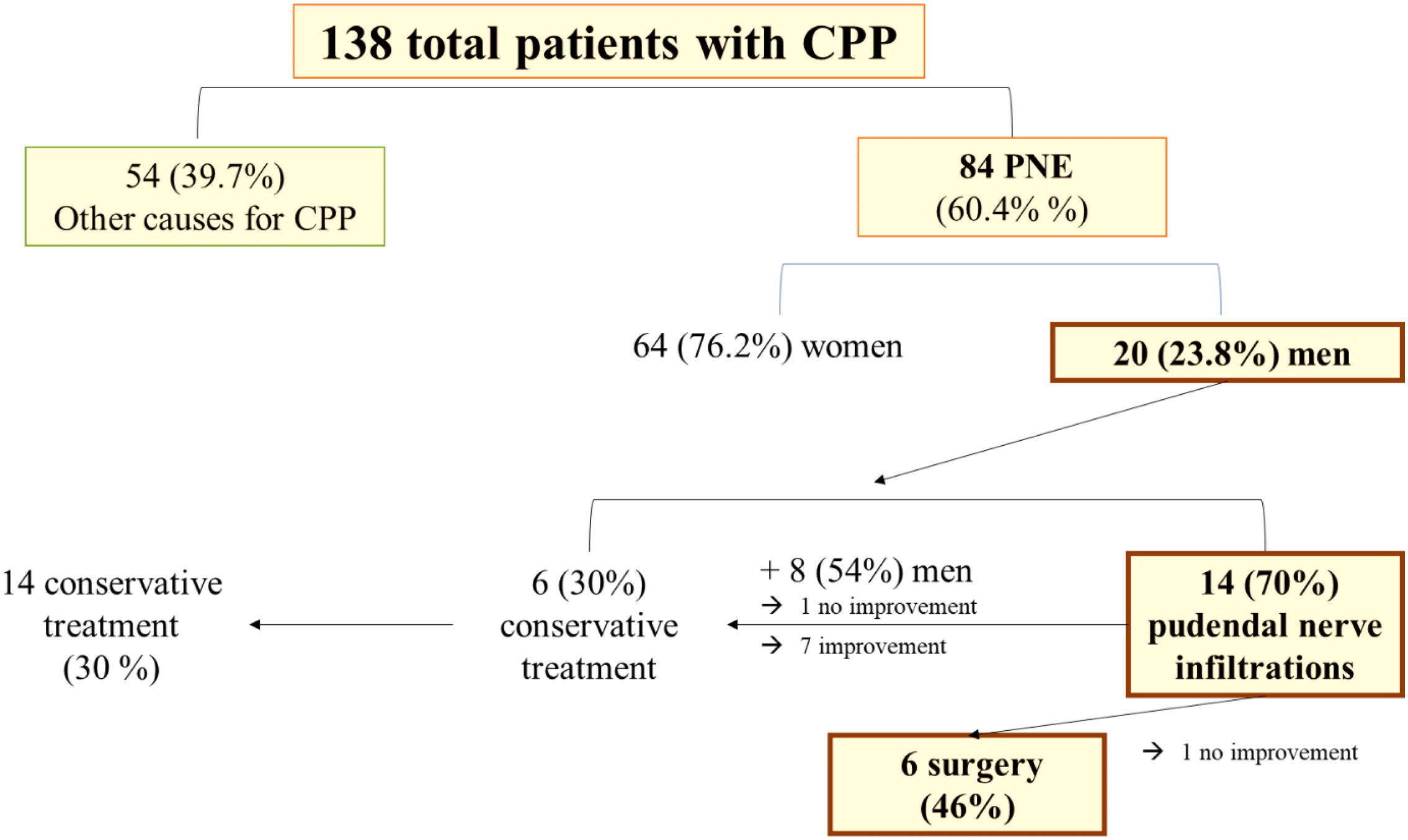
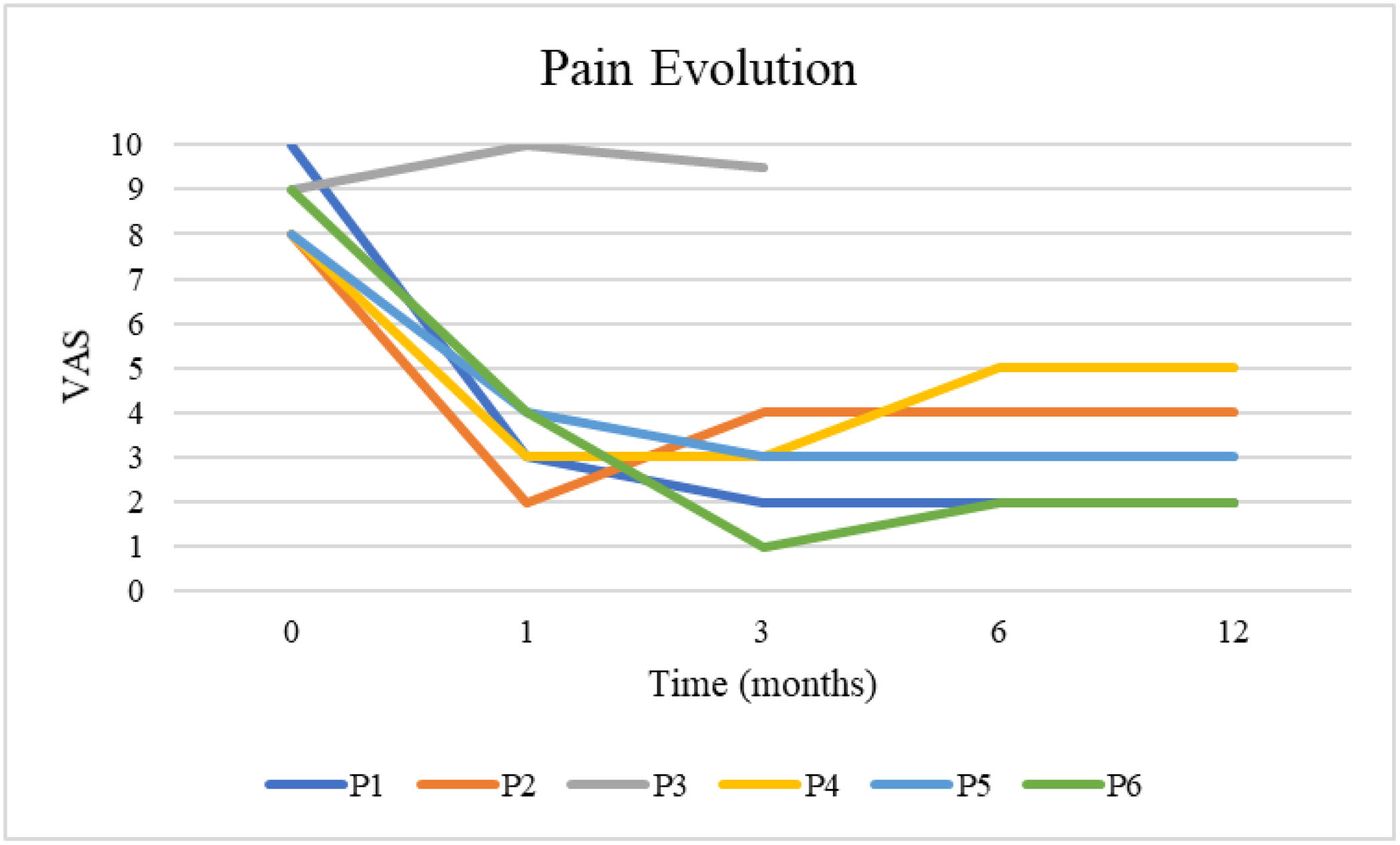
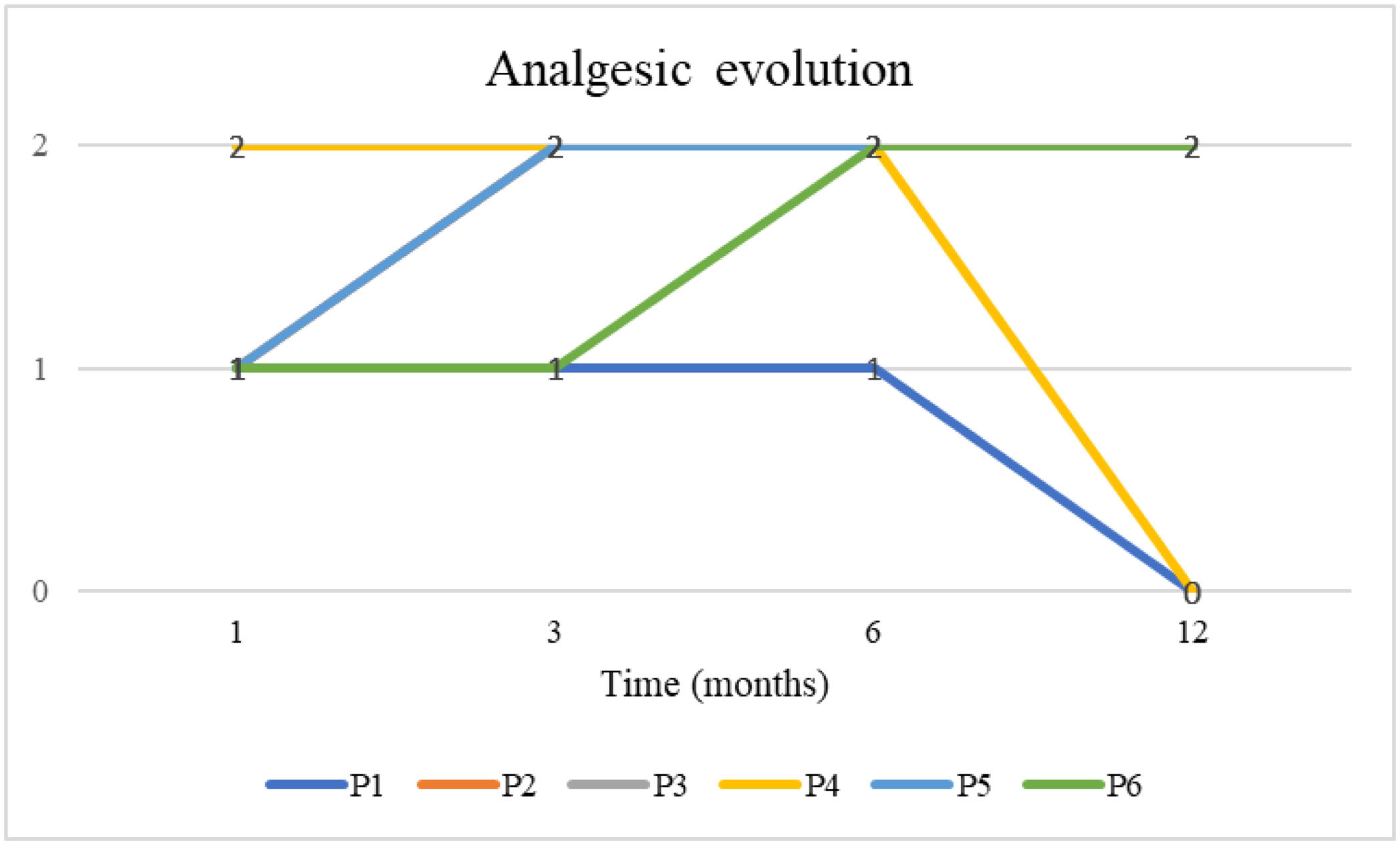
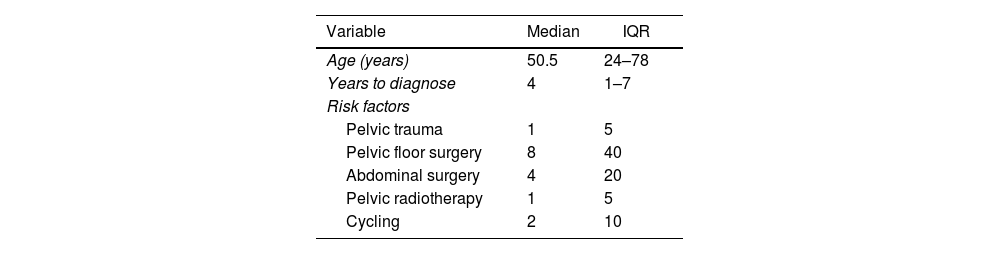
ResultsA total of 84 (60%) were diagnosed with PNE. Of these, 20 (24%) were male, with 14 (70%) receiving pudendal nerve infiltration. Six men (46%) later underwent laparoscopic pudendal nerve decompression surgery with pIOM. At the 12-month follow-up, five patients (83%) reported significant pain reduction, while one (17%) noted no improvement. Visual Analog Scale ranged between 2 and 5. Bladder dysfunction resolved in 2 of the 3. Two patients ceased all medications by the 12-month mark. In terms of satisfaction, four patients expressed complete satisfaction, one reported partial satisfaction, and one did not provide feedback.
ConclusionLaparoscopic PNE decompression surgery, combined with pIOM is an effective intervention for male PNE patients with significant pain relief and enhanced quality of life. Further research is needed to validate these results and refine the criteria for patient selection.
El atrapamiento del nervio pudendo (ANP) es poco frecuente y afecta principalmente a mujeres, representando los hombres solo 1/3 de los casos. Las guías europeas recomiendan la descompresión quirúrgica en casos seleccionados de ANP. Nuestro objetivo es evaluar los resultados quirúrgicos en un grupo de pacientes varones diagnosticados de ANP que fueron sometidos a cirugía de descompresión laparoscópica con monitorización neurofisiológica intraoperatoria (pIOM).
Material y métodosEste estudio retrospectivo y multicéntrico incluyó a 138 pacientes con sospecha de síndrome de ANP. El diagnóstico se estableció mediante pruebas neurofisiológicas y respuesta al bloqueo del nervio pudendo. Los pacientes que experimentaron alivio de los síntomas tras el bloqueo nervioso fueron sometidos a descompresión laparoscópica del nervio pudendo con pIOM durante el procedimiento. La evolución de los síntomas se siguió durante un período de 12meses.
ResultadosUn total de 84 pacientes (60%) fueron diagnosticados con ANP. De estos, 20 (24%) eran varones, y 14 (70%) recibieron infiltración del nervio pudendo. Seis hombres (46%) se sometieron posteriormente a cirugía de descompresión laparoscópica del nervio pudendo con pIOM. En el seguimiento a los 12meses, cinco pacientes (83%) informaron una reducción significativa del dolor, mientras que uno (17%) no presentó mejoría. La escala analógica visual osciló entre 2 y 5. La disfunción vesical se resolvió en 2 de los 3 casos. Dos pacientes dejaron de tomar medicación al cabo de 12meses. En términos de satisfacción, cuatro pacientes expresaron una satisfacción completa, uno reportó una satisfacción parcial y uno no proporcionó respuesta.
ConclusiónLa cirugía de descompresión laparoscópica del ANP combinada con pIOM es una intervención eficaz en pacientes varones con ANP, proporcionando un alivio significativo del dolor y una mejora en la calidad de vida. Se requieren más estudios para validar estos resultados y perfeccionar los criterios de selección de pacientes.
Article

If it is the first time you have accessed you can obtain your credentials by contacting Elsevier Spain in suscripciones@elsevier.com or by calling our Customer Service at902 88 87 40 if you are calling from Spain or at +34 932 418 800 (from 9 to 18h., GMT + 1) if you are calling outside of Spain.
If you already have your login data, please click here .
If you have forgotten your password you can you can recover it by clicking here and selecting the option ¿I have forgotten my password¿.