Endoscopic transsphenoidal surgery (ETSS) is the preferred approach for most pituitary adenomas. However, transcranial microsurgery remains relevant for giant adenomas with complex features. This study presents long-term outcomes and complications in a single-surgeon series of patients with giant pituitary adenomas who underwent transcranial resection.
Material and methodsThis retrospective study analyzed 29 patients with giant pituitary adenomas (≥4 cm) who underwent transcranial surgery between 2009 and 2018 at Bursa Uludağ University Faculty of Medicine. Inclusion criteria were: a minimum tumor diameter of 4 cm, histologically confirmed pituitary adenoma, tumor resection via a transcranial approach, regular postoperative follow-up, and a minimum follow-up of 60 months. Data collected included patient demographics, clinical presentation, tumor characteristics, surgical details, extent of resection, and long-term outcomes (minimum 60 months follow-up).
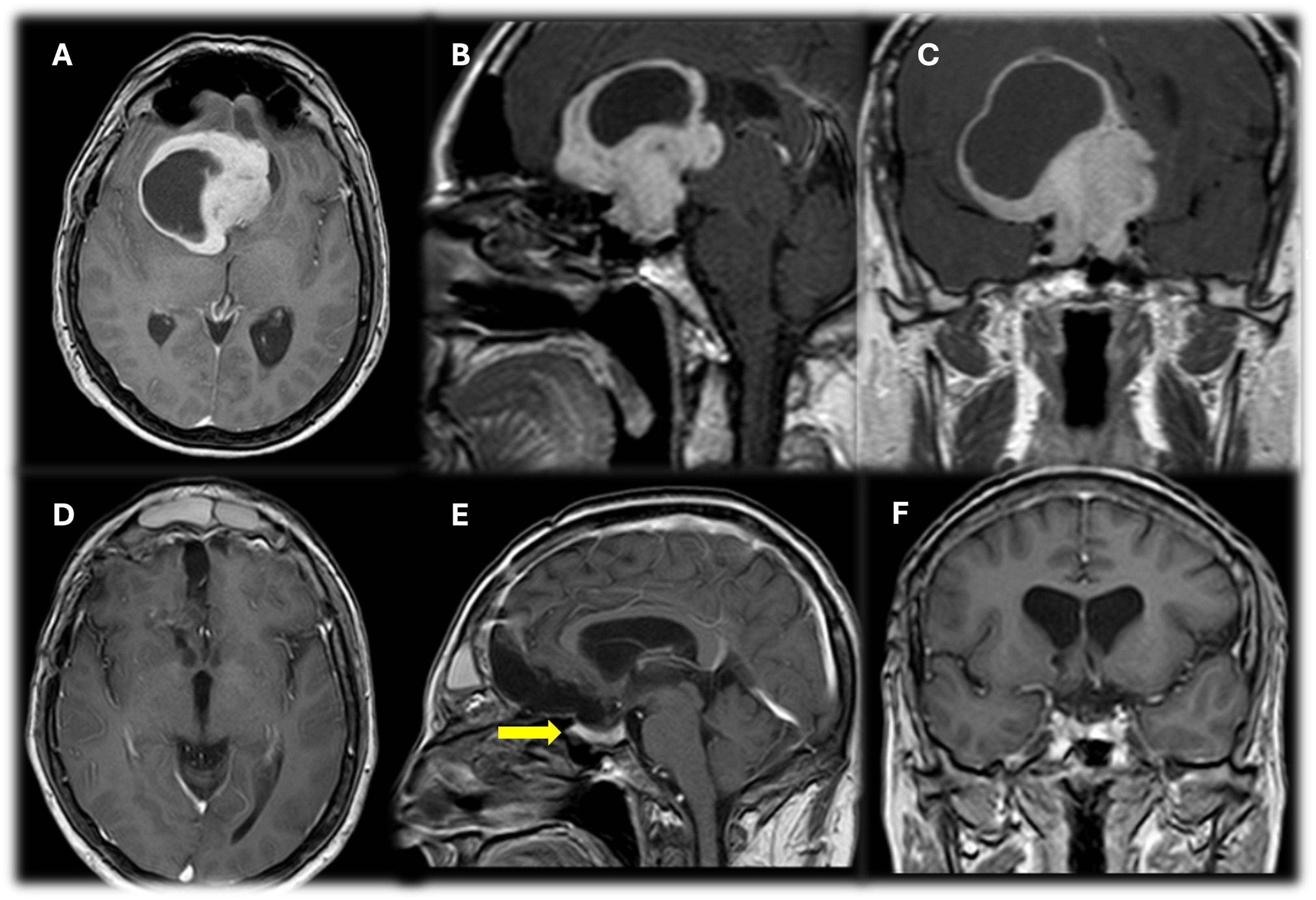
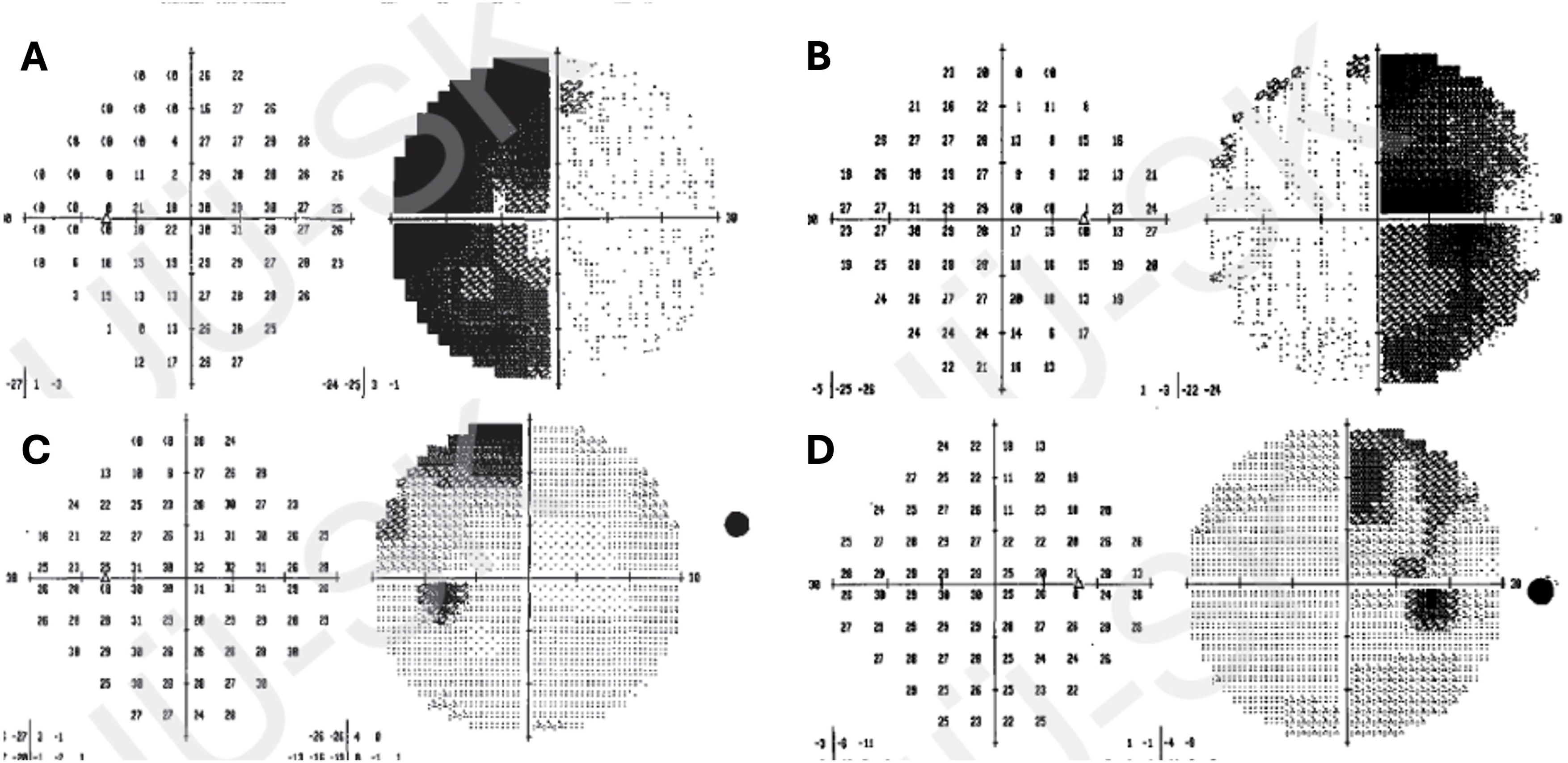
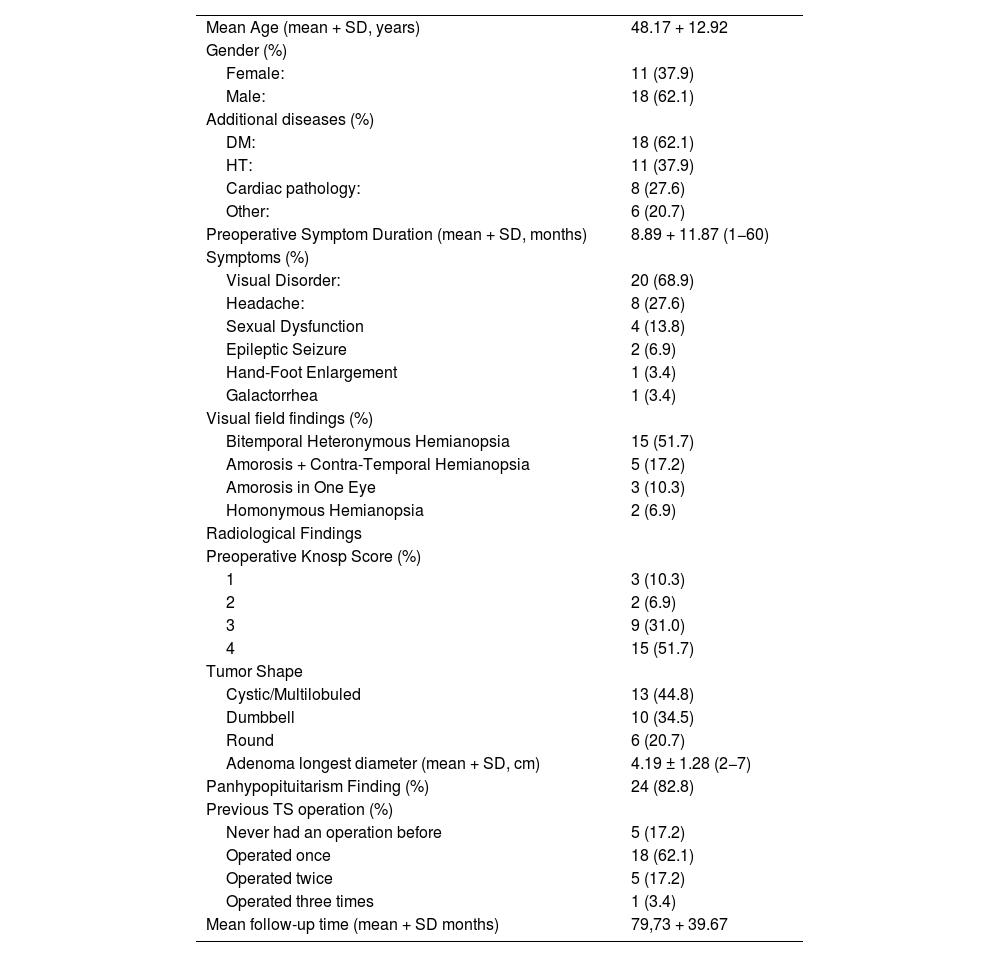
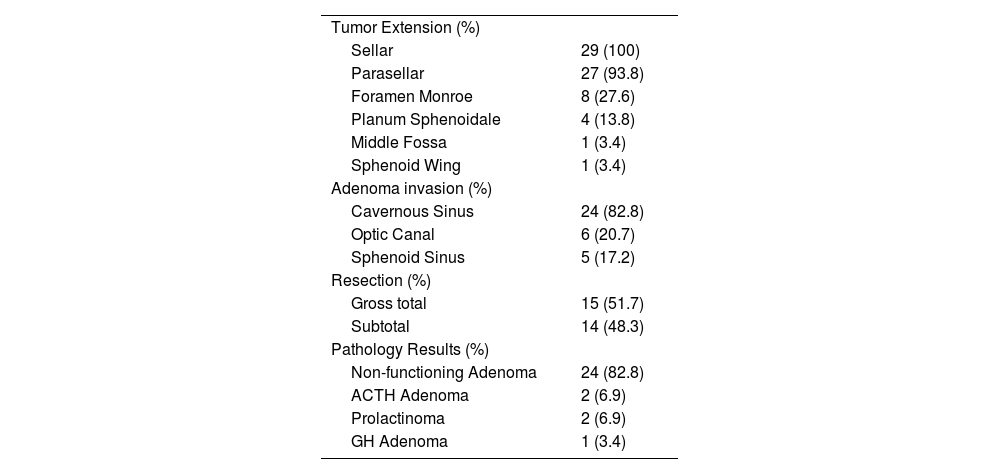
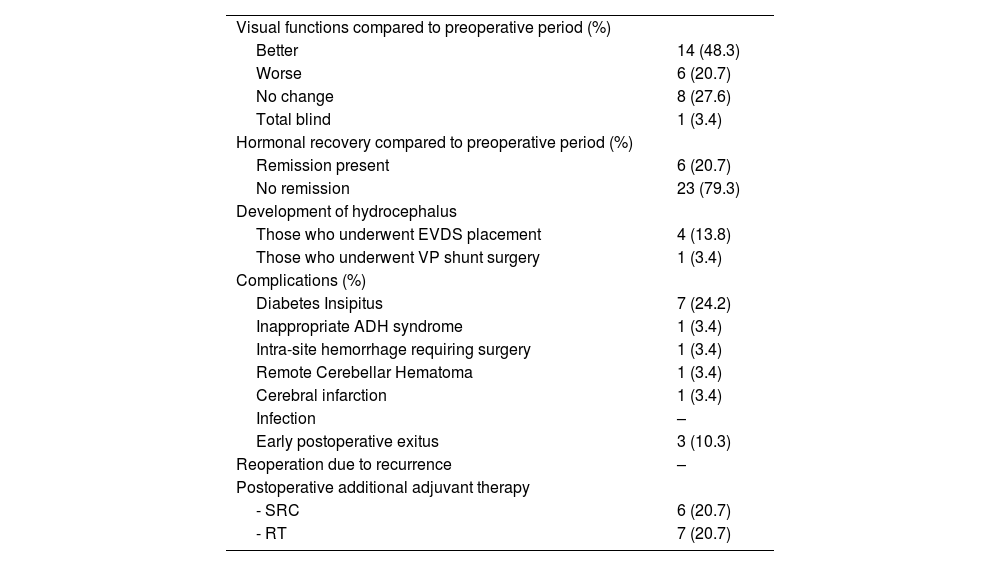
ResultsThe mean patient age was 48.17 ± 12.92 years. Vision loss was the most common presenting symptom (n = 20). Gross total resection (GTR) was achieved in 51.7% (n = 15) and subtotal resection (STR) in 48.3% (n = 14). Postoperative improvement in visual function was observed in 48.3% (n = 14), while 20.7% (n = 6) experienced deterioration. Endocrinological remission occurred in 20.7% (n = 6). Complications included diabetes insipidus (24.13%, n = 7), cerebrovascular events (10.34%, n = 3), and mortality (17.24%, n = 5).
ConclusionsTranscranial surgery for giant pituitary adenomas can achieve favorable outcomes in terms of tumor control and visual function improvement. However, it is associated with a risk of complications, including endocrinological and cerebrovascular events. Careful patient selection, meticulous surgical technique, and close postoperative monitoring are essential for optimizing outcomes. Transcranial microsurgery remains an important tool in the armamentarium of neurosurgeons managing complex giant pituitary adenomas.
La cirugía endoscópica transesfenoidal (ETSS) es el enfoque preferido para la mayoría de los adenomas hipofisarios. Sin embargo, la microcirugía transcraneal sigue siendo relevante para adenomas gigantes con características complejas. Este estudio presenta los resultados a largo plazo y las complicaciones en una serie de pacientes con adenomas hipofisarios gigantes que fueron sometidos a resección transcraneal por un único cirujano.
Material y métodosEste estudio retrospectivo analizó a 29 pacientes con adenomas hipofisarios gigantes (≥4 cm) que se sometieron a cirugía transcraneal entre 2009 y 2018 en la Facultad de Medicina de la Universidad de Bursa Uludağ. Los criterios de inclusión fueron: un diámetro mínimo del tumor de 4 cm, adenoma hipofisario confirmado histológicamente, resección del tumor mediante un enfoque transcraneal, seguimiento postoperatorio regular y un seguimiento mínimo de 60 meses. Los datos recopilados incluyeron demografía de los pacientes, presentación clínica, características del tumor, detalles quirúrgicos, extensión de la resección y resultados a largo plazo (seguimiento mínimo de 60 meses).
ResultadosLa edad media de los pacientes fue de 48,17 ± 12,92 años. La pérdida de visión fue el síntoma más común (n = 20). Se logró una resección total macroscópica (RTM) en el 51,7% (n = 15) y una resección subtotal (RST) en el 48,3% (n = 14). La mejoría de la función visual postoperatoria se observó en el 48,3% (n = 14), mientras que el 20,7% (n = 6) experimentó deterioro. La remisión endocrinológica ocurrió en el 20,7% (n = 6). Las complicaciones incluyeron diabetes insípida (24,13%, n = 7), eventos cerebrovasculares (10,34%, n = 3) y mortalidad (17,24%, n = 5).
ConclusionesLa cirugía transcraneal para adenomas hipofisarios gigantes puede lograr resultados favorables en términos de control tumoral y mejoría de la función visual. Sin embargo, está asociada con un riesgo de complicaciones, incluyendo eventos endocrinológicos y cerebrovasculares. La selección cuidadosa de los pacientes, una técnica quirúrgica meticulosa y un estrecho seguimiento postoperatorio son esenciales para optimizar los resultados. La microcirugía transcraneal sigue siendo una herramienta importante en el arsenal de los neurocirujanos que manejan adenomas hipofisarios gigantes complejos.
Article

If it is the first time you have accessed you can obtain your credentials by contacting Elsevier Spain in suscripciones@elsevier.com or by calling our Customer Service at902 88 87 40 if you are calling from Spain or at +34 932 418 800 (from 9 to 18h., GMT + 1) if you are calling outside of Spain.
If you already have your login data, please click here .
If you have forgotten your password you can you can recover it by clicking here and selecting the option ¿I have forgotten my password¿.