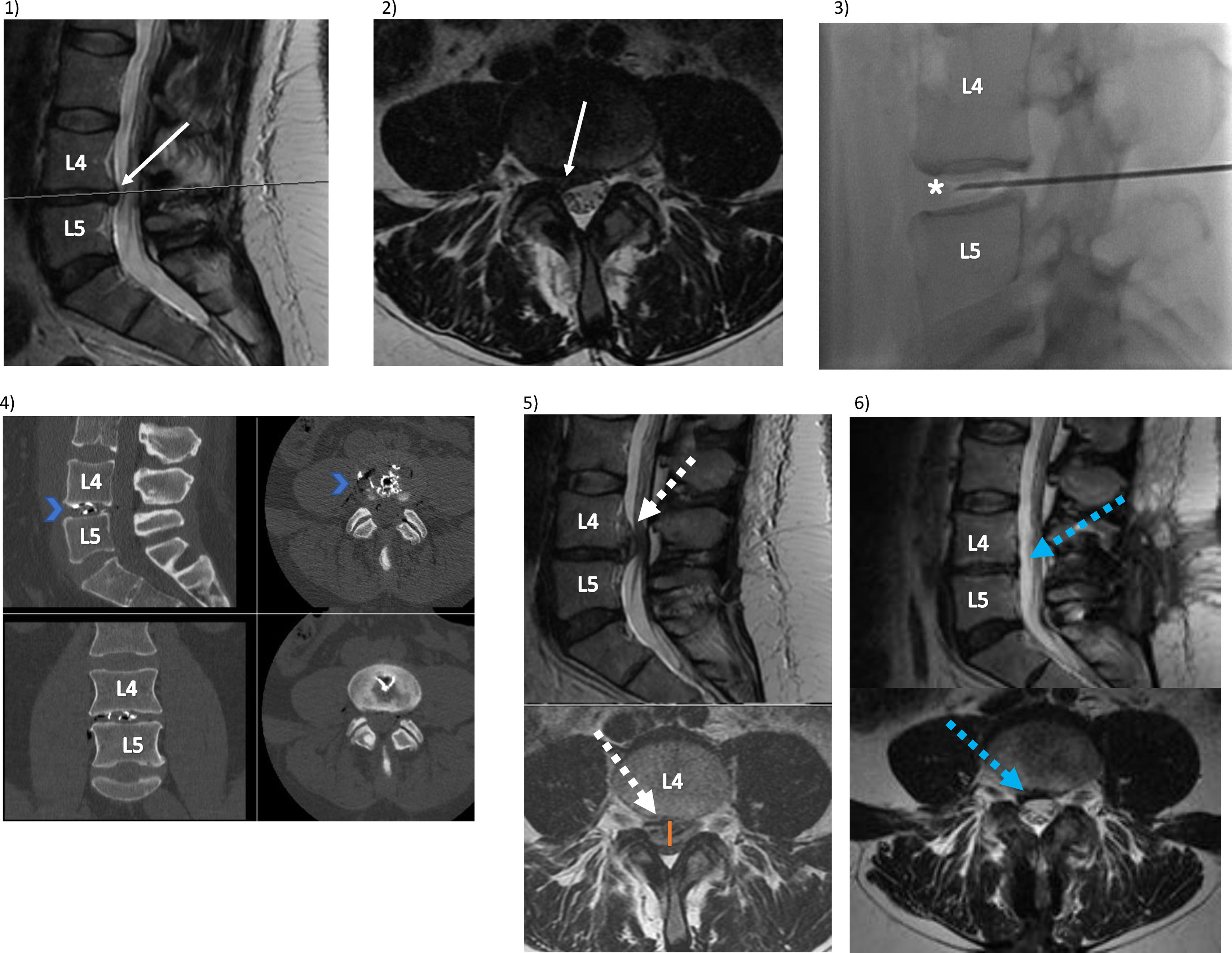
Sciatica due to a lumbar disc herniation is a frequent symptom, between 13% and 40% of the general population will experience an episode of sciatica during their lives. Different techniques exist to treat this condition. Among them the percutaneous intradiscal Discogel®. In all the series of patients reviewed treated with Discogel®, so far, there is not any case reported with disc extrusion and significant neurological damage. We present a case of a foot drop, caused by a disc herniation after percutaneous treatment with Discogel®. We hypothesize that the pathogenic mechanism would be the increased intradiscal volume and pressure post-puncture and annulus fibrosus damage, which could produce the disc extrusion.
The extrusion of Discogel® material is possible. To the best of our knowledge, this is the first reported case of this complication with this product.
La ciática secundaria a una hernia discal lumbar es un síntoma frecuente; entre el 13% y el 40% de la población general experimentará un episodio de ciática durante sus vidas. Se han desarrollado diferentes técnicas para tratar esta dolencia. Entre ellas, el Discogel® intradiscal percutáneo. En todas las series revisadas de pacientes tratados con Discogel®, hasta el momento, no se ha informado ningún caso de extrusión discal ni daño neurológico importante. Presentamos un caso de pie caído, causado por una hernia de disco posterior al tratamiento percutáneo con Discogel®. Nuestro mecanismo teórico es el aumento del volumen y la presión intradiscal más el daño del anillo fibroso pospunción que podría producir una extrusión discal. La extrusión del material Discogel® es posible. Hasta donde sabemos, este es el primer caso reportado de esta complicación con este producto.
Artículo

Si es la primera vez que accede a la web puede obtener sus claves de acceso poniéndose en contacto con Elsevier España en suscripciones@elsevier.com o a través de su teléfono de Atención al Cliente 902 88 87 40 si llama desde territorio español o del +34 932 418 800 (de 9 a 18h., GMT + 1) si lo hace desde el extranjero.
Si ya tiene sus datos de acceso, clique aquí.
Si olvidó su clave de acceso puede recuperarla clicando aquí y seleccionando la opción "He olvidado mi contraseña".