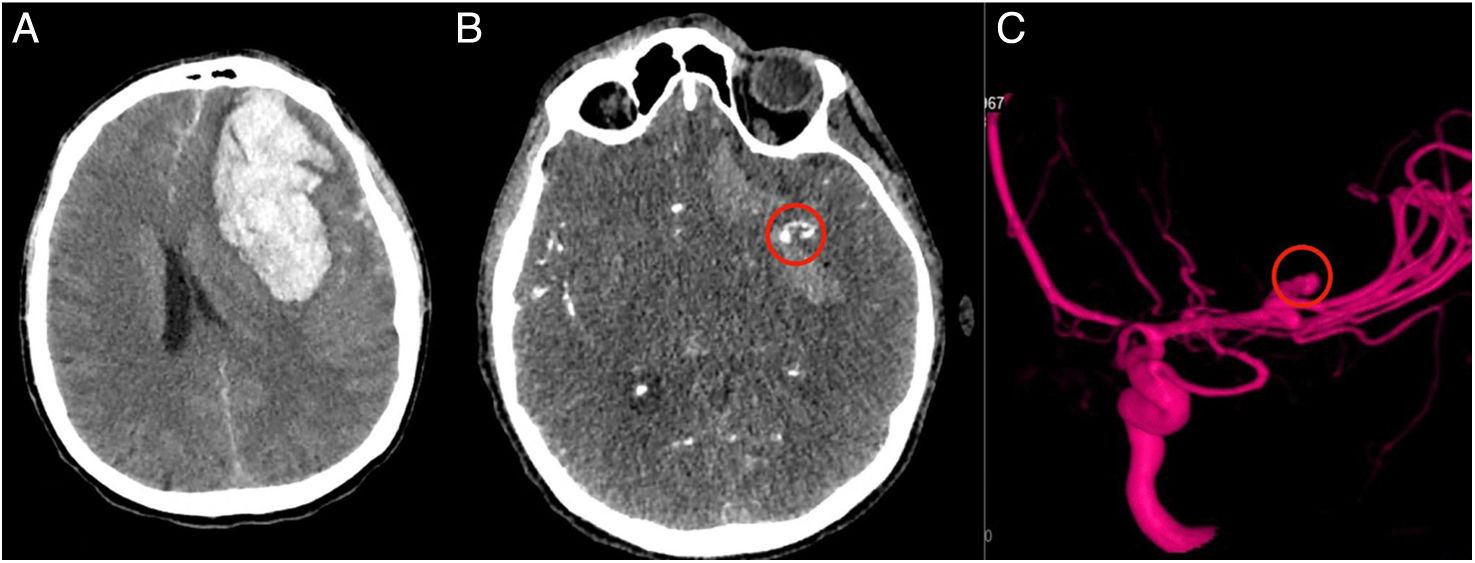
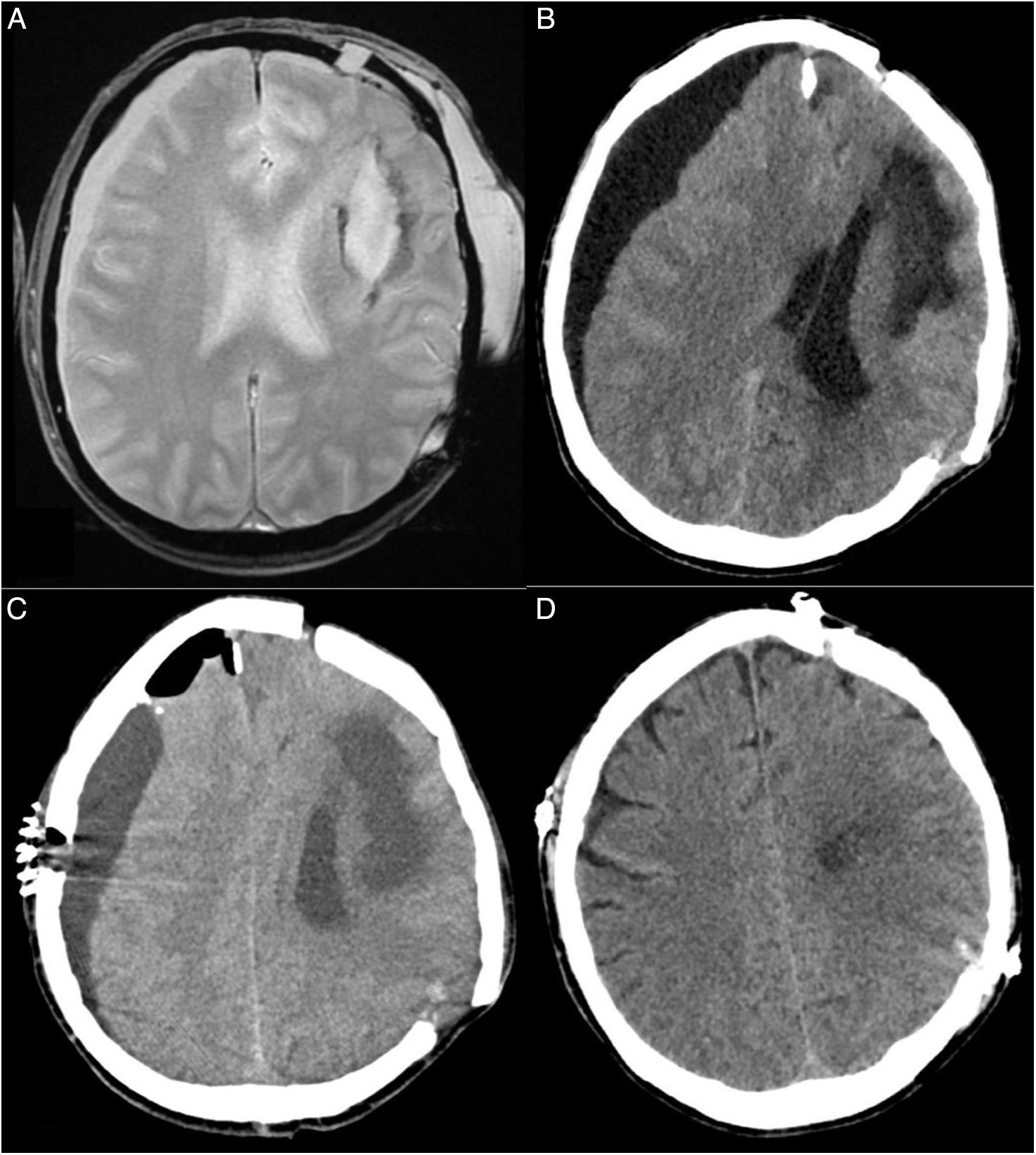
La craneotomía flotante es una técnica quirúrgica alternativa a la craniectomía descompresiva para tratar la hipertensión intracraneal refractaria. Este procedimiento tiene la ventaja de evitar la necesidad de una segunda cirugía para reponer el hueso, al tiempo que proporciona un buen control de la presión intracraneal. Sin embargo, no existe bibliografía consistente sobre sus complicaciones. En particular, no se ha descrito ningún caso de derrame subdural contralateral tras una craneotomía flotante. En este artículo presentamos el caso de un varón de 55 años que desarrolló un derrame subdural contralateral tras una craneotomía flotante por hipertensión intracraneal y cómo se manejó. Así pues, exploramos la bibliografía para comprender mejor la patogenia del derrame subdural contralateral, los tratamientos y las posibles estrategias de prevención.
Hinged craniotomy is an alternative surgical technique that can be used in place of decompressive craniectomy to treat refractory intracranial hypertension. This procedure has the advantage of avoiding the need for a second surgery to replace the bone, while giving a good control of intracranial pressure. However, there is no consistent literature about complications of hinged craniotomy. In particular, there are no reported cases of contralateral subdural effusion after hinged craniotomy. In this article we present a case of a 55-years-old man who developed contralateral subdural effusion after a hinged craniotomy for intracranial hypertension, and how we handled it. Therefore, we explored literature to better understand the pathogenesis of contralateral subdural effusion, treatments and possible prevention strategies.
Artículo

Si es la primera vez que accede a la web puede obtener sus claves de acceso poniéndose en contacto con Elsevier España en suscripciones@elsevier.com o a través de su teléfono de Atención al Cliente 902 88 87 40 si llama desde territorio español o del +34 932 418 800 (de 9 a 18h., GMT + 1) si lo hace desde el extranjero.
Si ya tiene sus datos de acceso, clique aquí.
Si olvidó su clave de acceso puede recuperarla clicando aquí y seleccionando la opción "He olvidado mi contraseña".