The objective of the present study is to analyze urinary and sexual functions in females treated with ALIF and to describe possible complications not previously reported in the literature.
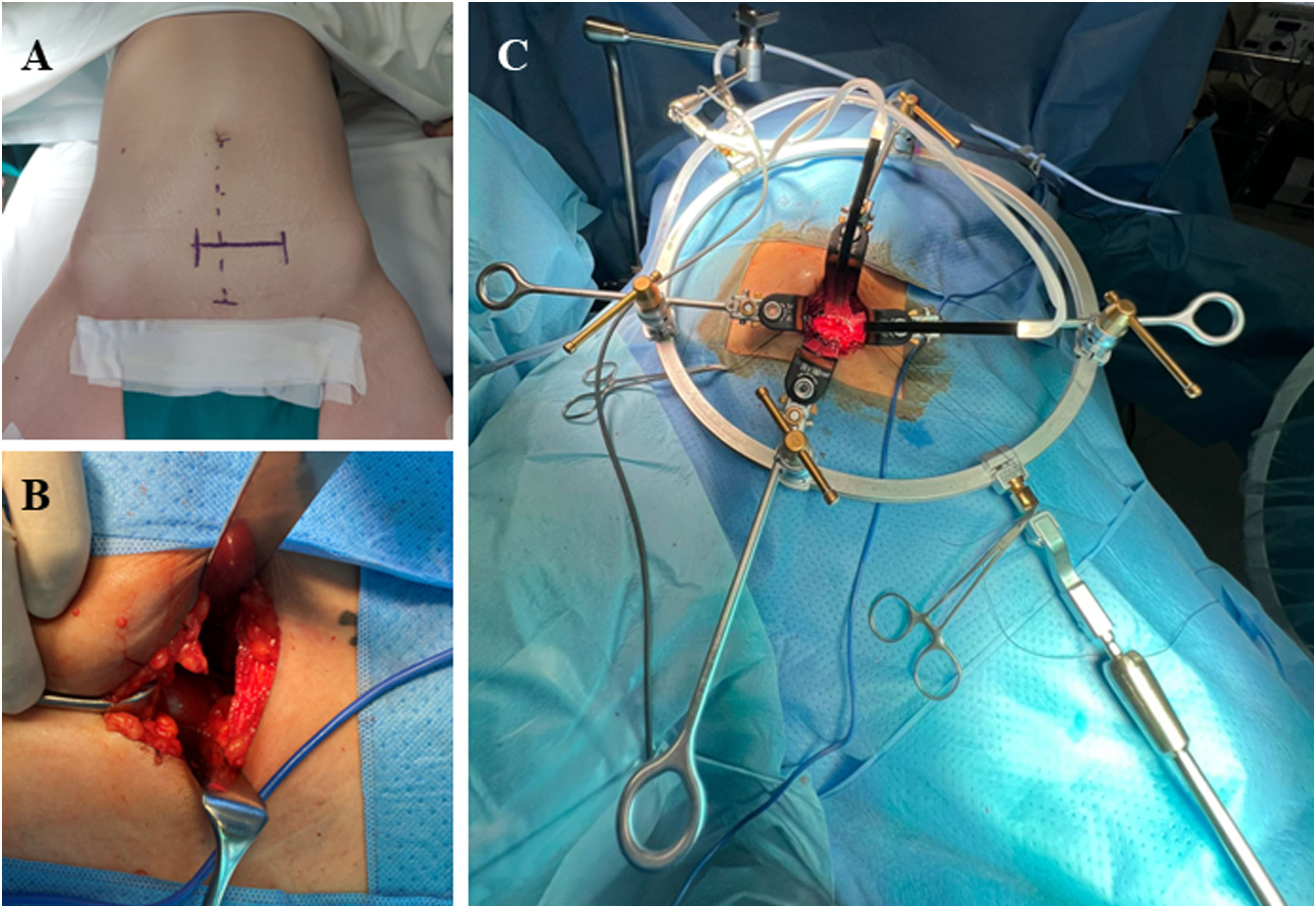
MethodsWe conducted a retrospective study of urinary and sexual functions in females treated with this technique in our hospital between 2019 and 2022. Inclusion criteria were: females treated with ALIF who provided informed consent.
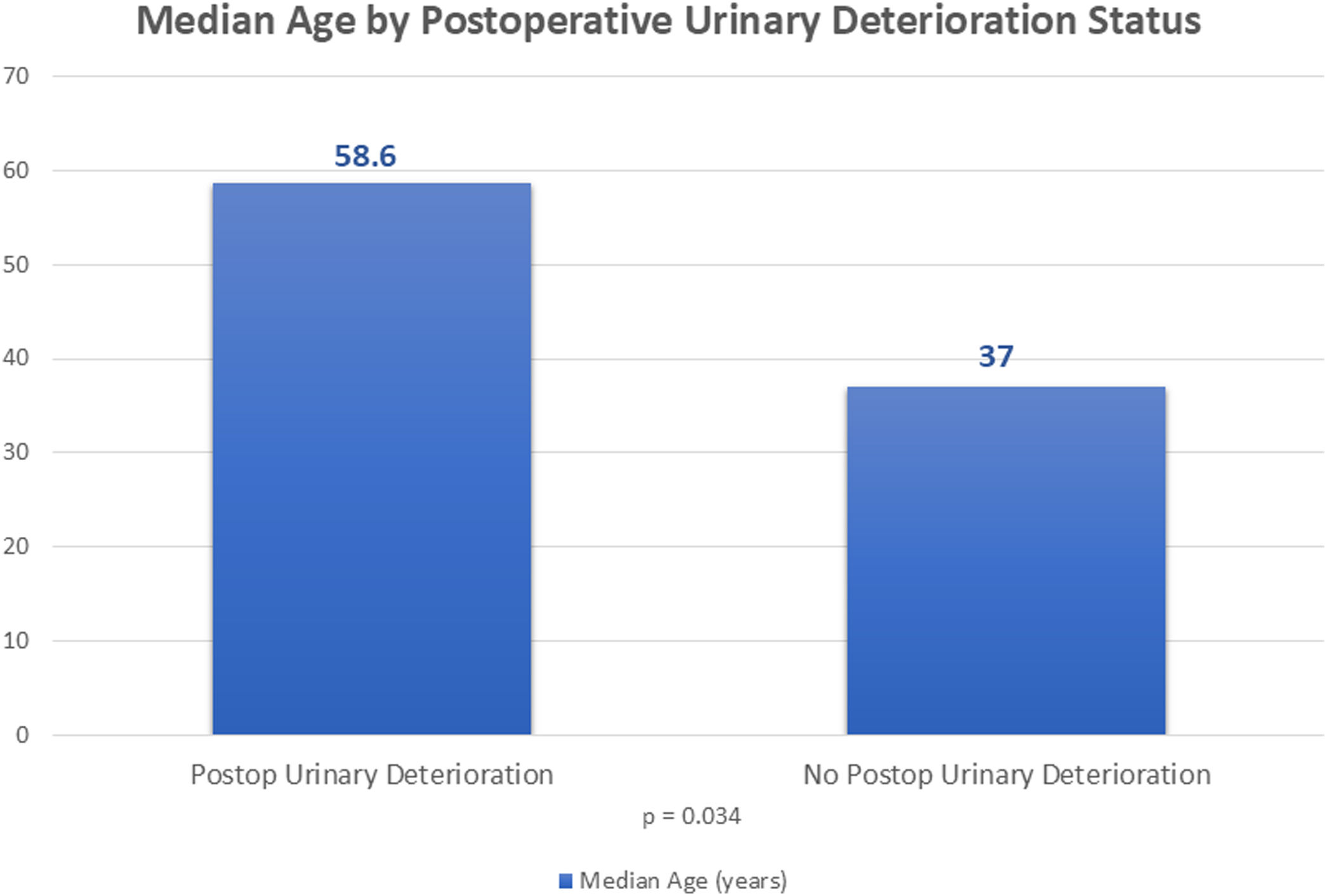
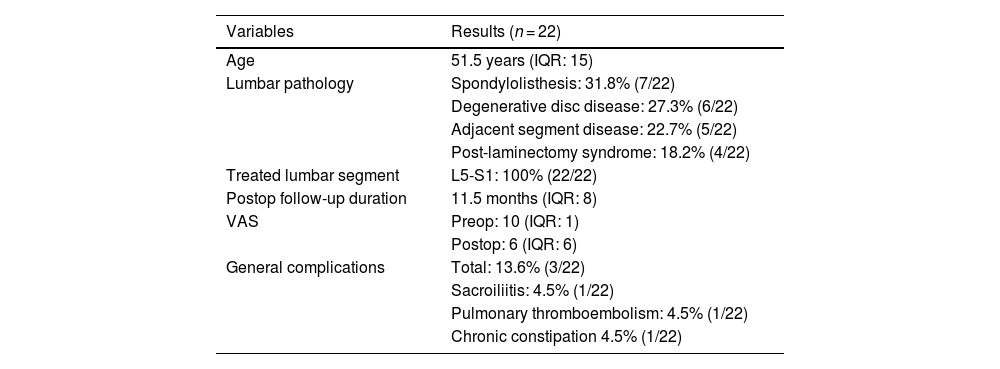
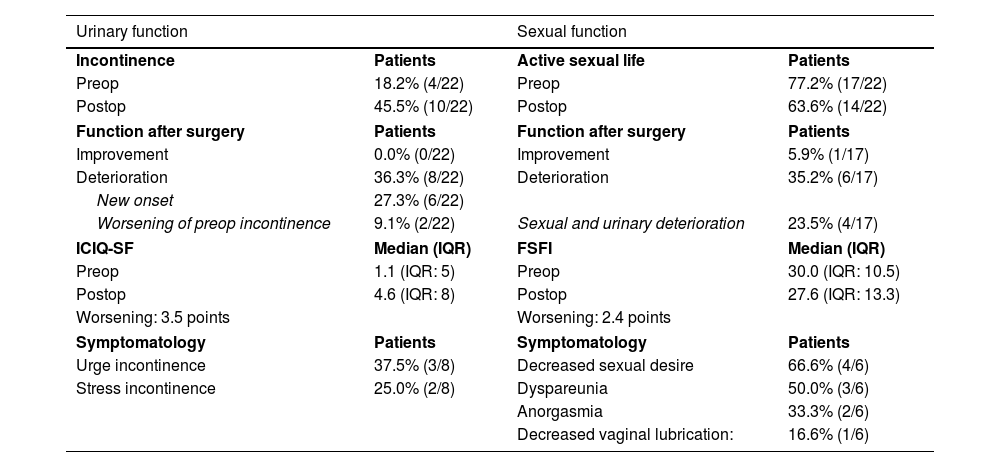
Results22 patients consented to participate. The median age was 51.5 years, the median follow-up was 11.5 months, and there was an improvement in low back pain of 4 points on the postoperative (postop) visual analogue scale (VAS). Overall, 36.3% of patients reported postoperative urinary deterioration, including 27.3% with new-onset urinary incontinence. The international consultation on incontinence questionnaire-short form score worsened by 3.5 points. 77.2% maintained an active sexual life; within this group, there was a worsening of 2.4 points in the postop female sexual function index and 35.2% described worsening in sexual function. We hypothesized that age, underlying lumbar pathology and changes in postoperative VAS scores could be confounding factors; however, only the relationship between age and postoperative urinary deterioration reached statistical significance (p = 0.034).
ConclusionsThe present study describes deterioration in urinary function in 36.3% and in sexual function in 35.2% after the procedure, findings also supported by specific scales. In view of the above, we cannot discount a possible gender bias in the literature. Despite that, we believe that ALIF is still an adequate technique, but studies of higher level of evidence should be conducted to improve the information process of our patients.
El objetivo del presente estudio es analizar las funciones urinarias y sexuales en mujeres tratadas con ALIF y detallar posibles complicaciones no descritas previamente en la literatura.
MétodosRealizamos un estudio retrospectivo sobre las funciones urinarias y sexuales en mujeres tratadas con esta técnica en nuestro hospital entre 2019 y 2022. Criterios de inclusión: mujeres tratadas mediante ALIF previo consentimiento informado.
Resultados22 pacientes consintieron participar. La mediana de edad fue de 51.5 años, el seguimiento medio fue de 11.5 meses y hubo una mejoría en el dolor lumbar de 4 puntos en la escala analógica visual postoperatoria (VAS). En general, el 36.3% de las pacientes reportó deterioro urinario postoperatorio, incluyendo un 27.3% con nueva aparición de incontinencia urinaria. La puntuación del international consultation on incontinence questionnaire-short form score empeoró en 3.5 puntos. El 77.2% presentaba una vida sexual activa previamente a la cirugía; dentro de este grupo, hubo un empeoramiento de 2.4 puntos en el índice de función sexual femenina postoperatorio y el 35.2% describió un deterioro en la función sexual. Hipotetizamos que la edad, la patología lumbar subyacente y los cambios en las puntuaciones de VAS postoperatorios podrían ser factores de confusión; sin embargo, solo la relación entre la edad y el deterioro urinario postoperatorio alcanzó significación estadística (p = 0.034).
ConclusionesEl presente estudio describe un deterioro en la función urinaria en el 36.3% y en la función sexual en el 35.2% después del procedimiento, hallazgos respaldados por escalas específicas. En vista de lo anterior, no podemos descartar un posible sesgo de género en la literatura. A pesar de ello, creemos que el ALIF sigue siendo una técnica adecuada, pero deben realizarse estudios de mayor nivel de evidencia para mejorar el proceso de información a nuestras pacientes.
Article

If it is the first time you have accessed you can obtain your credentials by contacting Elsevier Spain in suscripciones@elsevier.com or by calling our Customer Service at902 88 87 40 if you are calling from Spain or at +34 932 418 800 (from 9 to 18h., GMT + 1) if you are calling outside of Spain.
If you already have your login data, please click here .
If you have forgotten your password you can you can recover it by clicking here and selecting the option ¿I have forgotten my password¿.