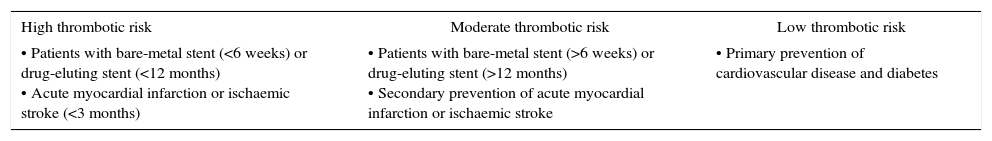
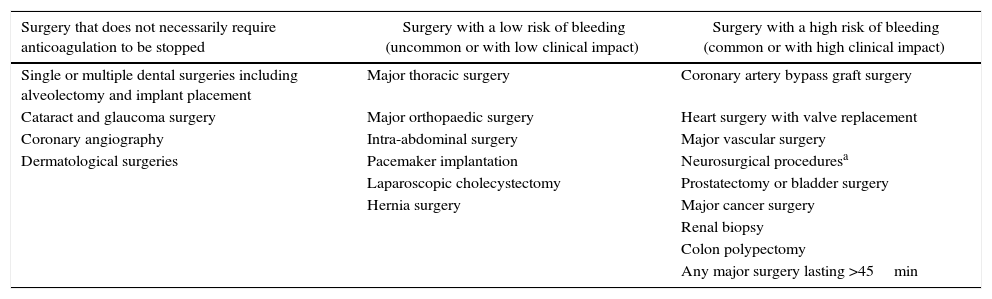
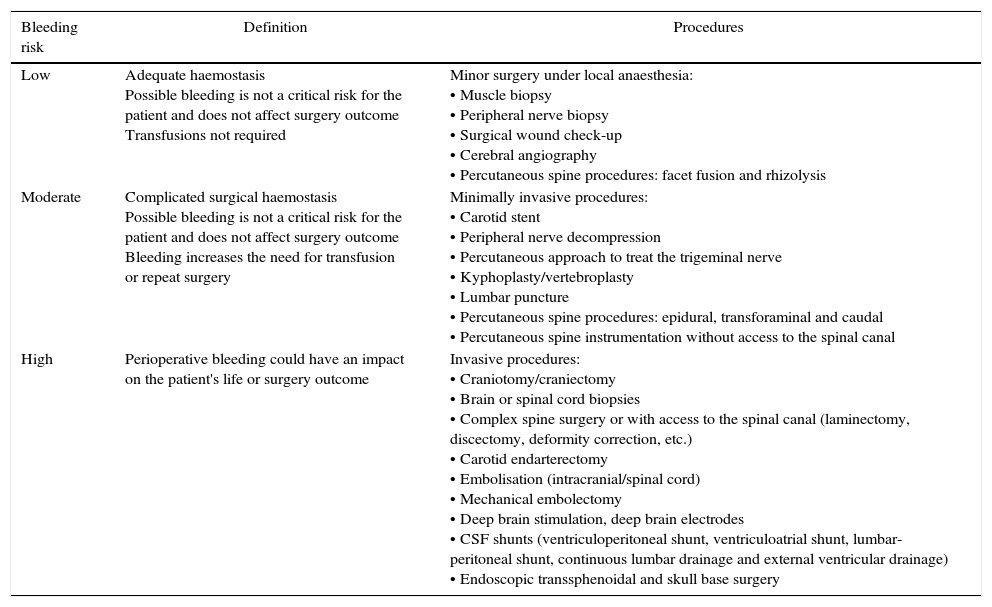
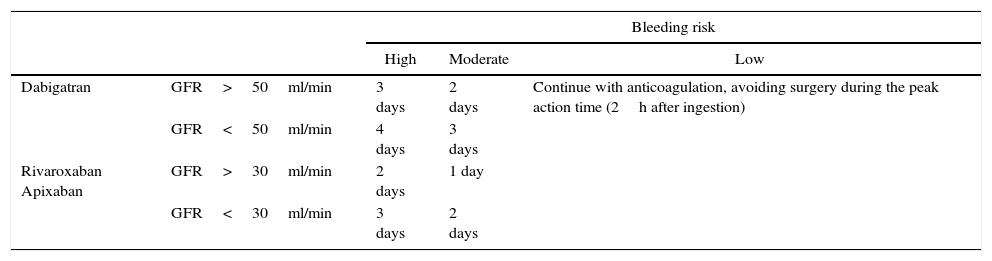
The use of antithrombotic medication (antiplatelet and/or anticoagulant therapy) is widespread. Currently, the management of neurosurgical patients receiving this type of therapy continues to be a problem of special importance.
Patients receiving antithrombotic treatment may need neurosurgical care because of bleeding secondary to such treatment, non-haemorrhagic neurosurgical lesions requiring urgent attention, or simply elective neurosurgical procedures.
In addition, the consequences of reintroducing early (bleeding or rebleeding) or late (thrombotic or thromboembolic) anticoagulation can be devastating.
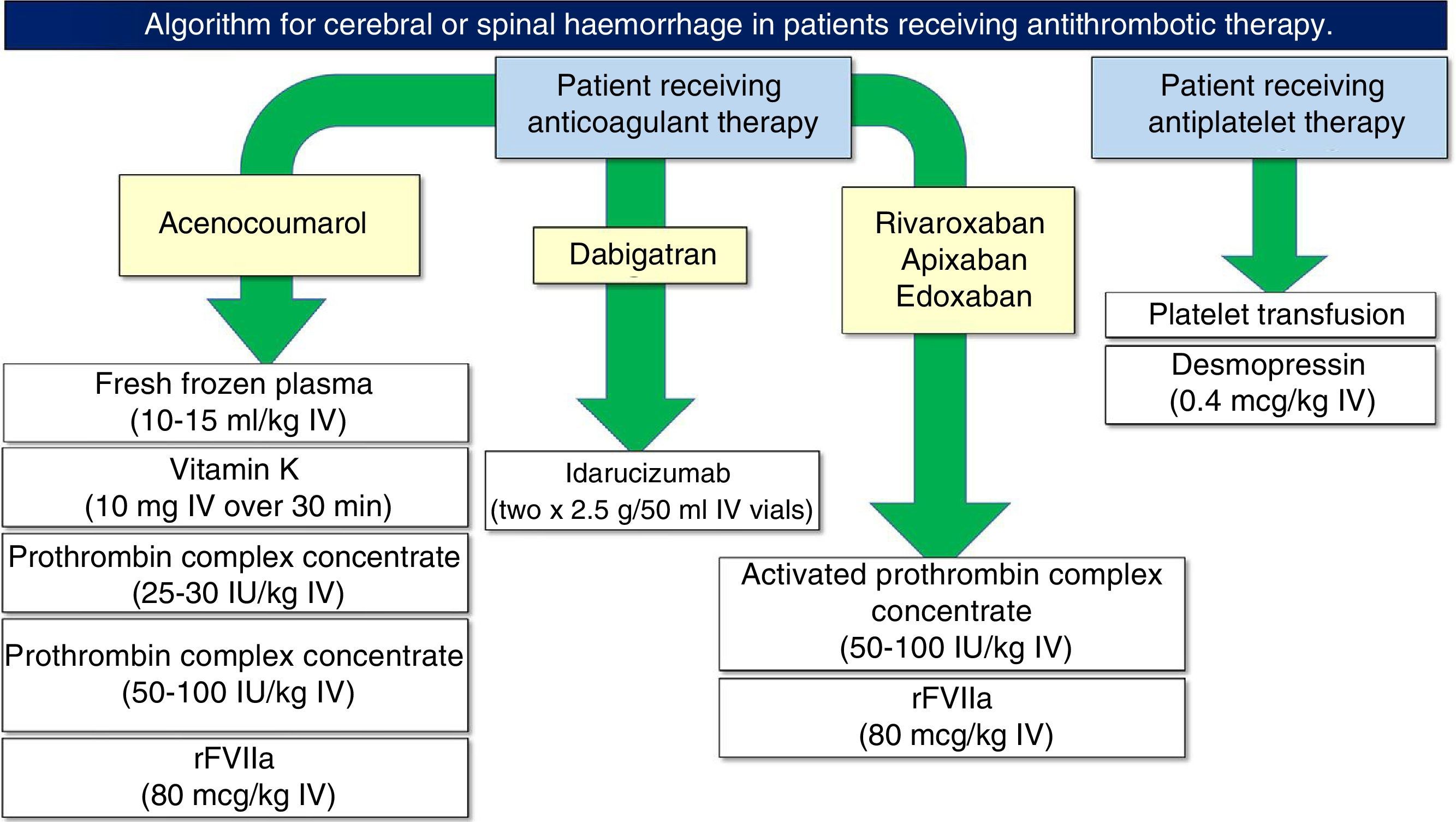
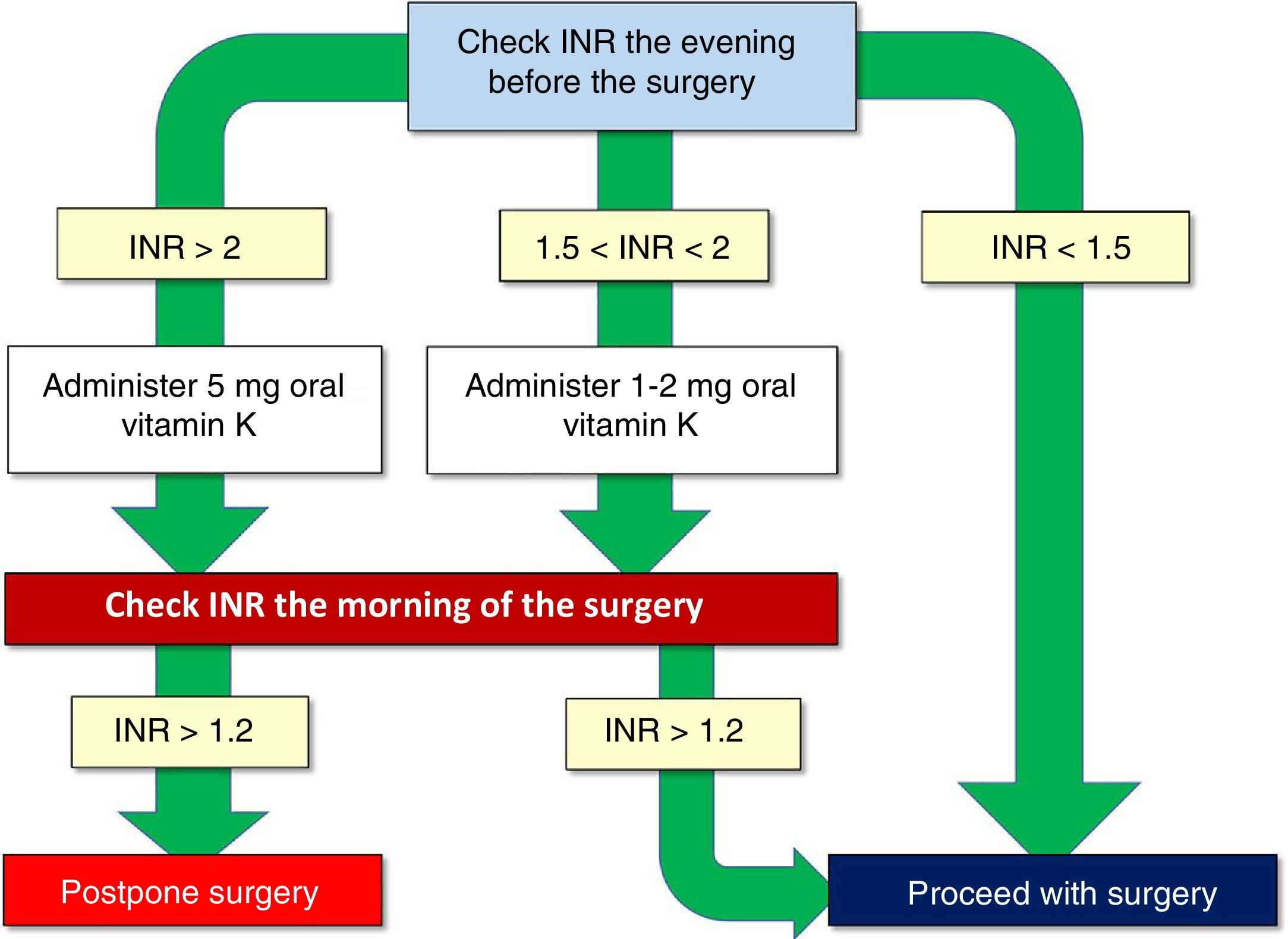
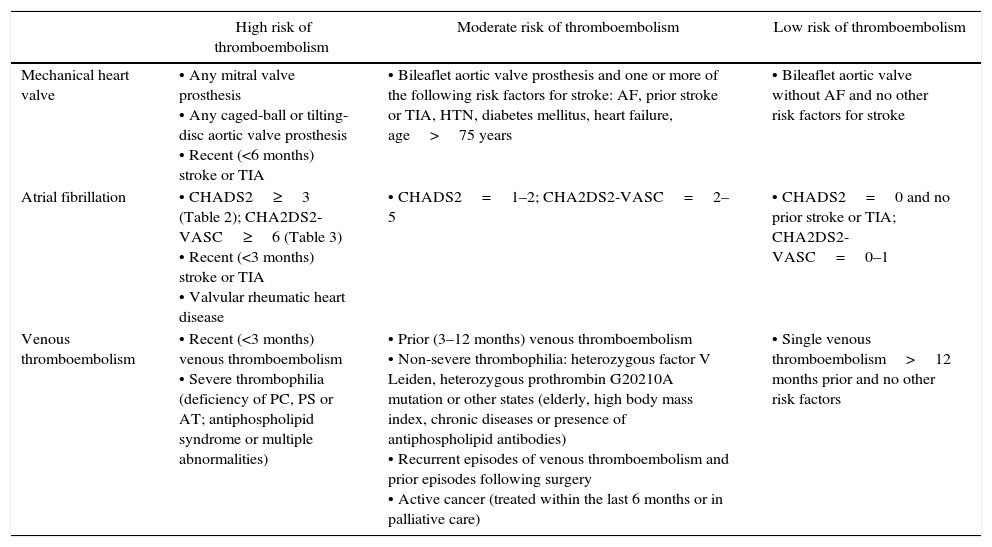
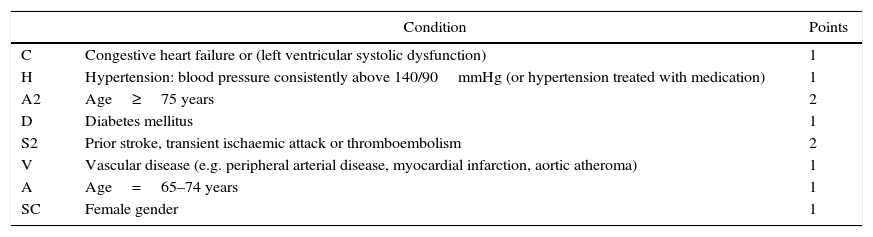
In this paper we present the antithrombotic treatment consensus protocol during the perioperative and periprocedural period, both in emergent surgery and in elective neurosurgical procedures.
El uso de medicación antitrombótica (antiagregante y/o anticoagulante) se encuentra ampliamente extendido. El manejo de los pacientes neuroquirúrgicos que reciben este tipo de terapia continúa siendo, a día de hoy, un problema de especial importancia.
Los pacientes en tratamiento antitrombótico pueden necesitar atención neuroquirúrgica bien por presentar sangrados secundarios a dicho tratamiento, lesiones neuroquirúrgicas no hemorrágicas pero que precisen intervención urgente, o simplemente procedimientos neuroquirúrgicos electivos.
Además, las consecuencias de la reintroducción de la anticoagulación temprana (sangrado o resangrado) o tardía (trombóticas o tromboembólicas) pueden ser devastadoras.
En este documento presentamos el protocolo de consenso en el tratamiento antitrombótico durante el periodo perioperatorio y periprocedimiento, tanto en cirugía emergente como en procedimientos electivos de neurocirugía.
Article

If it is the first time you have accessed you can obtain your credentials by contacting Elsevier Spain in suscripciones@elsevier.com or by calling our Customer Service at902 88 87 40 if you are calling from Spain or at +34 932 418 800 (from 9 to 18h., GMT + 1) if you are calling outside of Spain.
If you already have your login data, please click here .
If you have forgotten your password you can you can recover it by clicking here and selecting the option ¿I have forgotten my password¿.