Traumatic atlanto-occipital dislocation (AOD) is a life-threatening injury. Although traumatic brain injury (TBI) is associated with increased mortality in AOD patients, a detailed individual analysis of these patients is lacking in the literature.
MethodsPatients ≥16 years old who were diagnosed of AOD with concomitant severe TBI from 2010 to 2020 were included in this retrospective study. We examined the epidemiology, injury mechanisms, associated injuries, and outcomes of these patients.
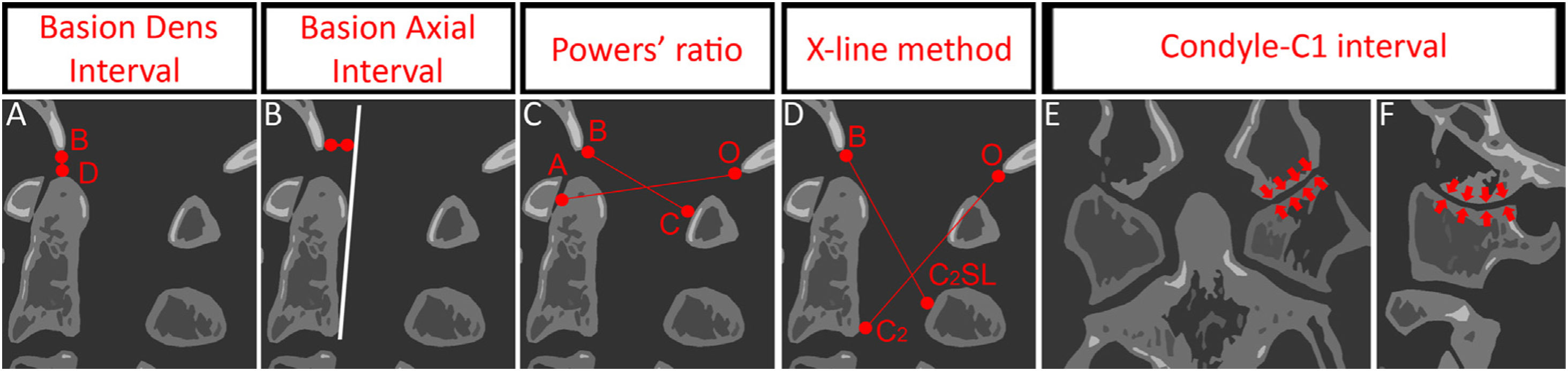
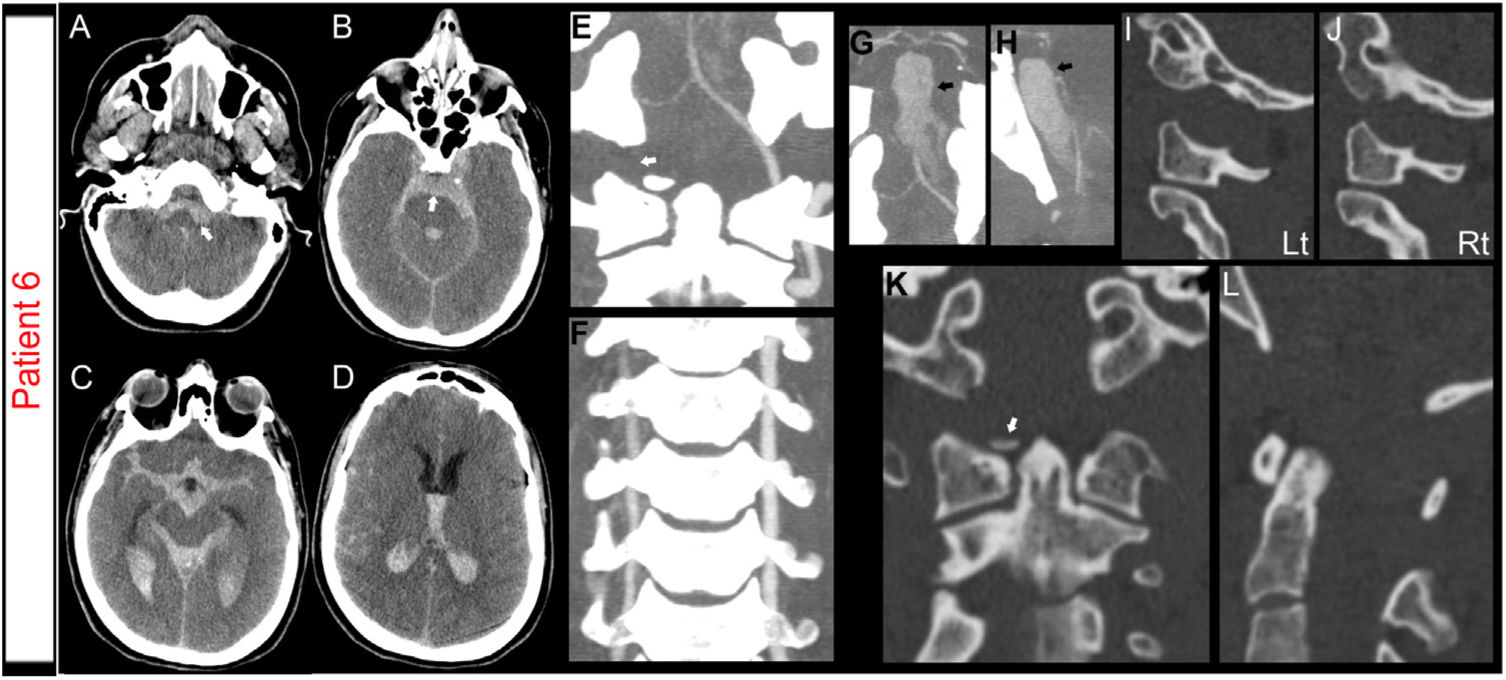
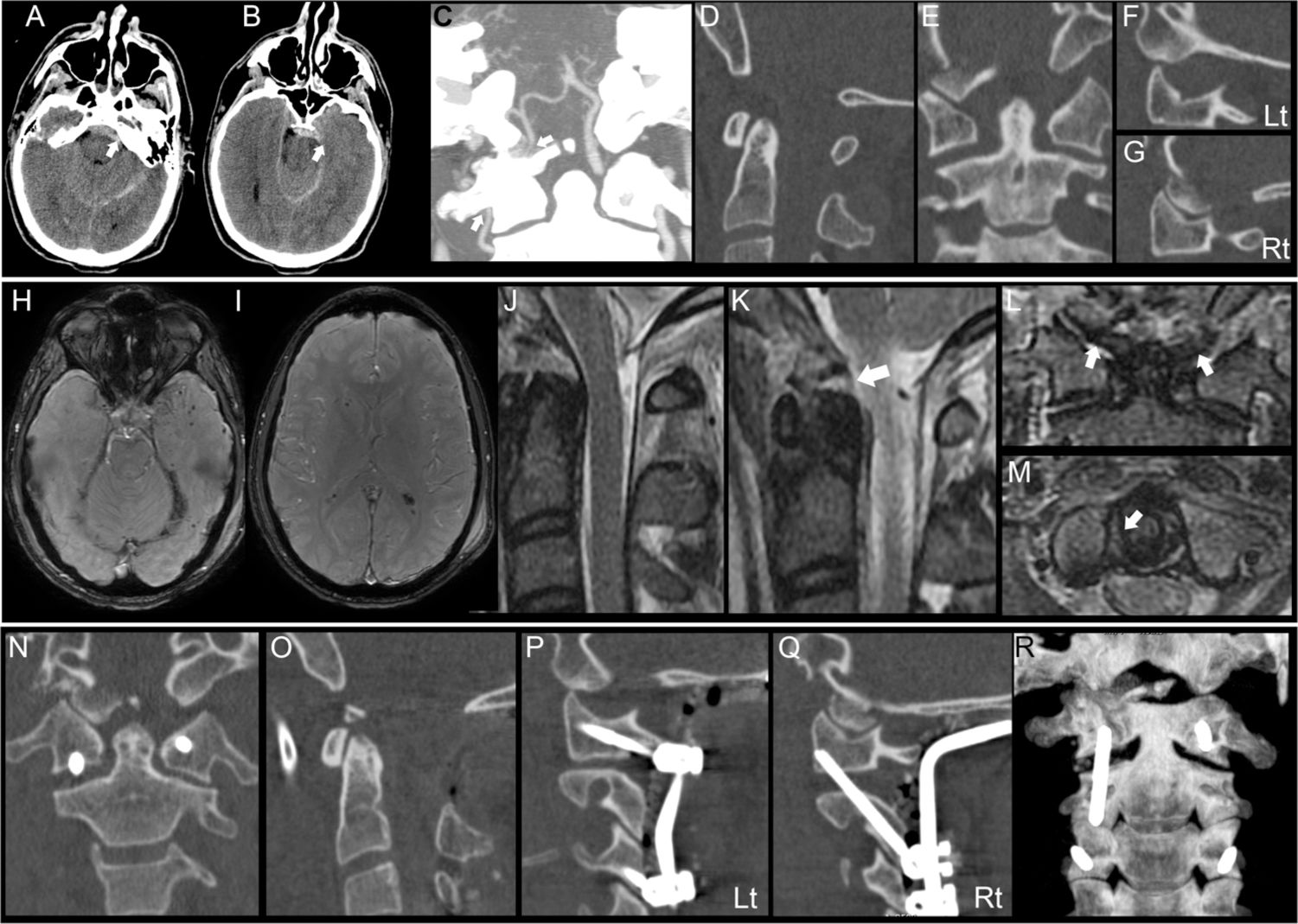
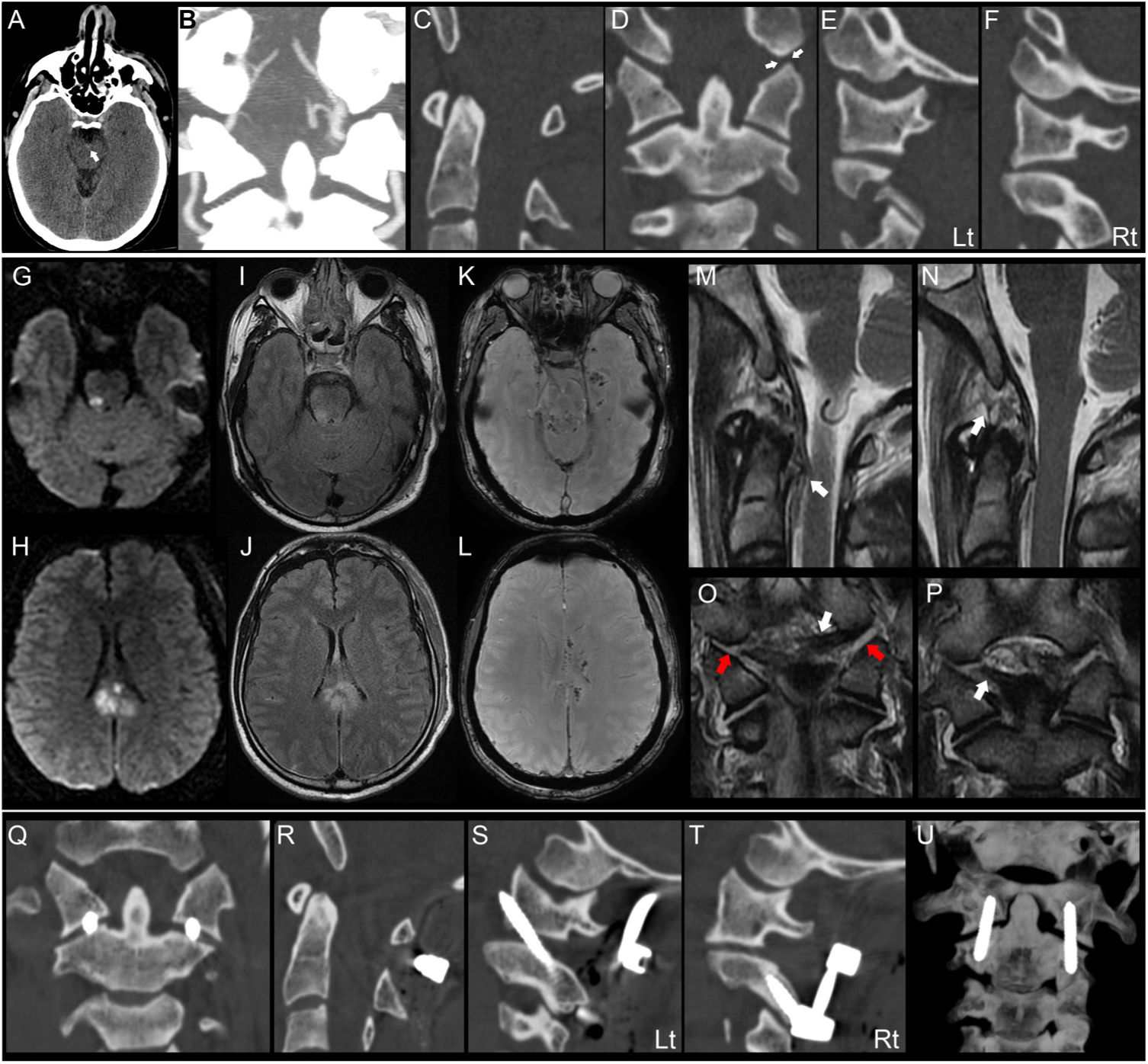
ResultsEight patients were included. Six patients died before any intervention could be performed, and two patients underwent an occipito-cervical fixation, showing a notorious neurologic improvement on follow-up. Cardiorespiratory arrest (CRA) was a strong predictor of subsequent death. CT signs of diffuse axonal injury (DAI) were present in most patients and were confirmed by magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) in survivors. Although TBI was not the main cause of death, it was responsible for the delayed neurological improvement and deferred stabilization. The average sensitivity of the different used methodologies for AOD diagnosis ranged from 0.50 to 1.00, being the Basion Dens Interval (BDI) and the Condyle-C1 interval (CCI) sum the most reliable criteria. Non-survivors tended to show greater distraction measurements. The high incidence of condylar avulsion fractures suggests that their visualization on the initial CT study should heighten the suspicion for AOD.
ConclusionsOur data suggest that patients with AOD and concomitant severe TBI might be salvageable patients. In those who survive beyond the first hospital days and show neurological improvement, surgical treatment should be performed as they can achieve an important neurologic recovery.
La luxación atlantooccipital (AOD) traumática es una lesión potencialmente mortal. Aunque el traumatismo craneoencefálico (TCE) se asocia con un aumento de la mortalidad en los pacientes con AOD, no existe en la literatura un análisis individual detallado de estos pacientes.
MétodosEn este estudio retrospectivo se incluyeron pacientes mayores de 16 años que fueron diagnosticados de AOD con TCE grave concomitante durante el periodo 2010-2020. Estudiamos la epidemiología, los mecanismos lesionales, así como las lesiones asociadas y los resultados de estos pacientes.
ResultadosSe incluyeron ocho pacientes. Seis pacientes fallecieron antes de que se pudiera realizar cualquier intervención y dos pacientes fueron sometidos a una fijación occipitocervical, mostrando una notoria mejoría neurológica durante el seguimiento. La parada cardiorrespiratoria fue un predictor de muerte. En la TC inicial, signos de lesión axonal difusa estaban presentes en la mayoría de los pacientes y se confirmaron mediante imágenes de resonancia magnética en los supervivientes. Aunque el TCE no fue la principal causa de muerte, fue responsable de una mejoría neurológica tardía y por ello una estabilización diferida. La sensibilidad de las diferentes metodologías utilizadas para el diagnóstico de AOD osciló entre 0,50 y 1,00, siendo el intervalo Basion Dens y la suma del intervalo Condylo-C1 los criterios más fiables. Además, los no supervivientes presentaban mayores medidas de distracción. La alta incidencia de fracturas de cóndilo por avulsión sugiere que su visualización en el estudio de TC inicial debería aumentar la sospecha de AOD.
ConclusionesNuestros datos sugieren que los pacientes con AOD y TCE grave concomitante podrían ser pacientes salvables. En aquellos que sobreviven más allá de los primeros días de hospitalización y presentan mejoría neurológica, se debe considerar realizar un tratamiento quirúrgico ya que pueden lograr una importante recuperación neurológica.
Article

If it is the first time you have accessed you can obtain your credentials by contacting Elsevier Spain in suscripciones@elsevier.com or by calling our Customer Service at902 88 87 40 if you are calling from Spain or at +34 932 418 800 (from 9 to 18h., GMT + 1) if you are calling outside of Spain.
If you already have your login data, please click here .
If you have forgotten your password you can you can recover it by clicking here and selecting the option ¿I have forgotten my password¿.