Spontaneous subarachnoid haemorrhage is a rare cause of stroke, but it causes great socioeconomic impact and high morbidity and mortality.
The aim of this study is to describe the clinical profile and evolution of a series of patients with SAH admitted to a tertiary hospital, as well as the diagnostic and therapeutic management.
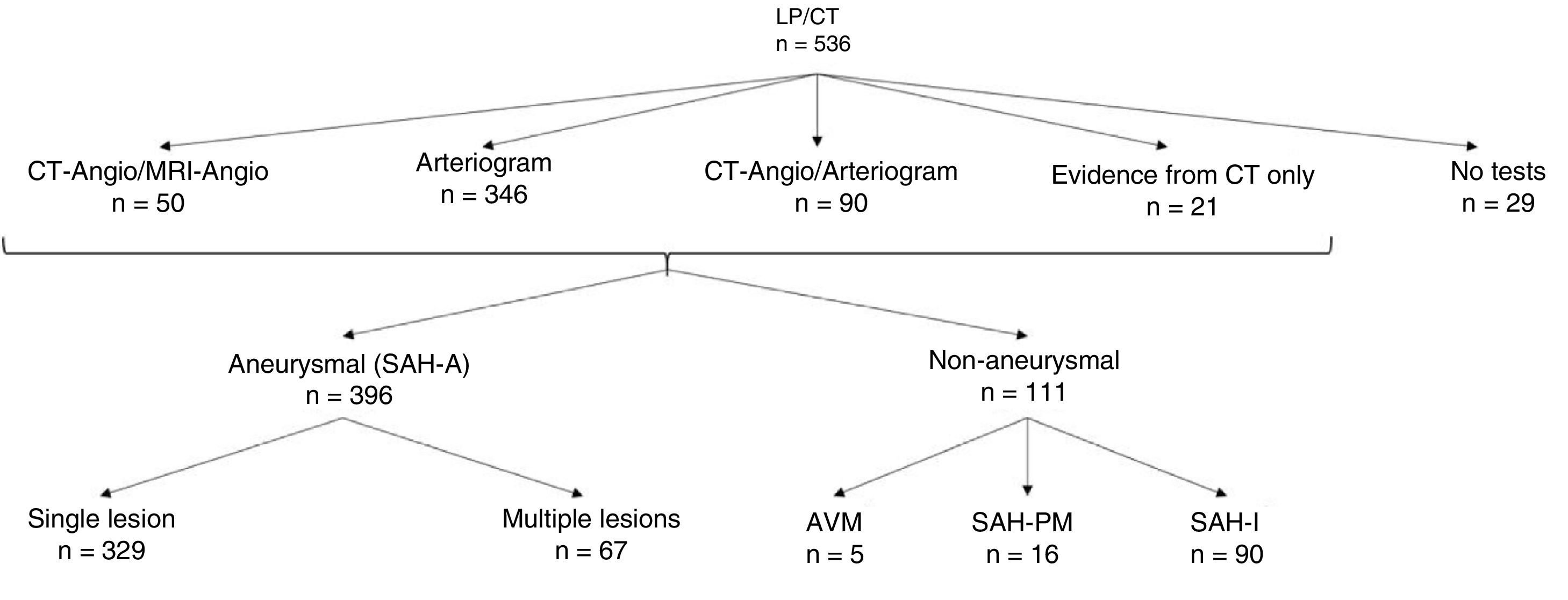
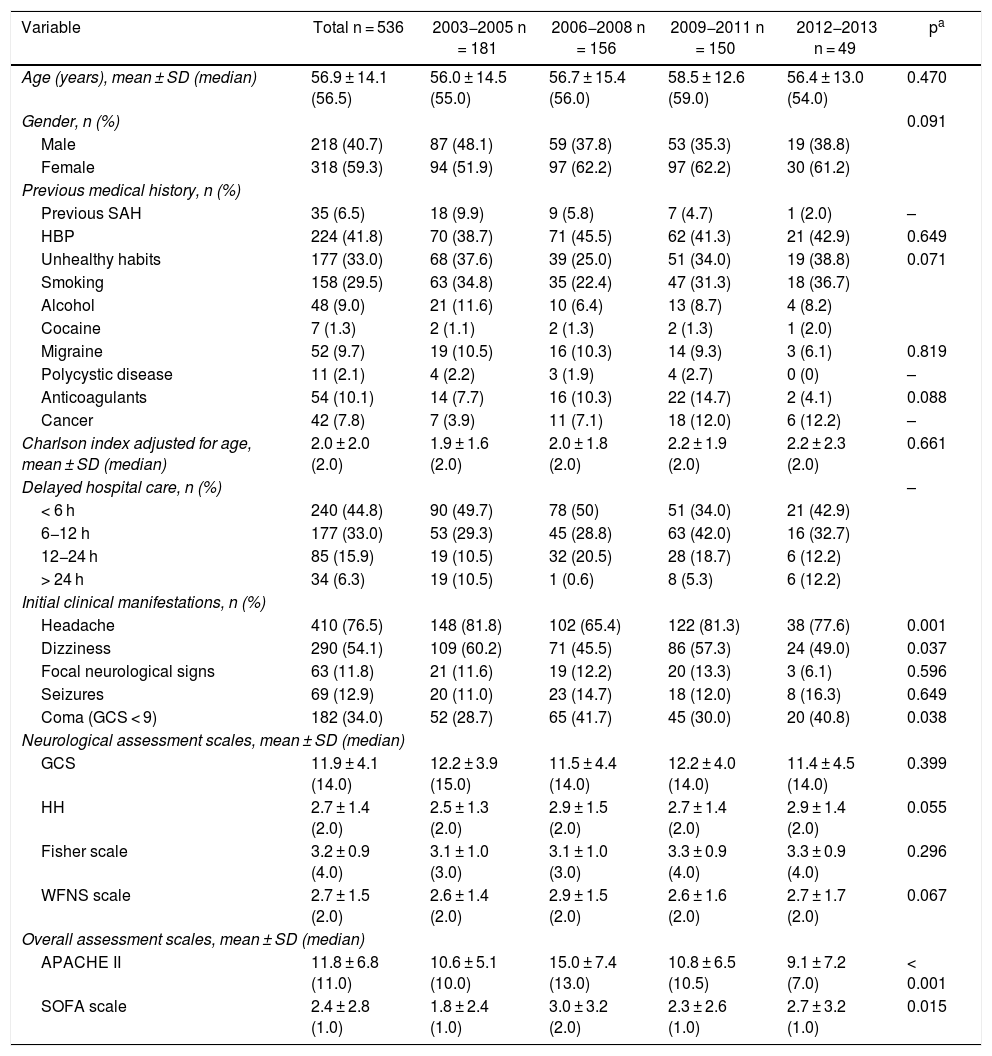
Material and methodsRetrospective study of 536 patients diagnosed with SAH admitted to the ICU of the Hospital Universitario de A Coruña between 2003 and 2013 (Age: 56.9 ± 14.1 years, female/male ratio: 1.5:1). Demographic characteristics, risk factors, aetiologies and clinical signs, prognostic scales, diagnostic tests and treatment were collected. A comparative analysis was made between the general series and subgroups of patients with aneurysmal (SAH-A) and idiopathic (SAH-I) subarachnoid haemorrhage.
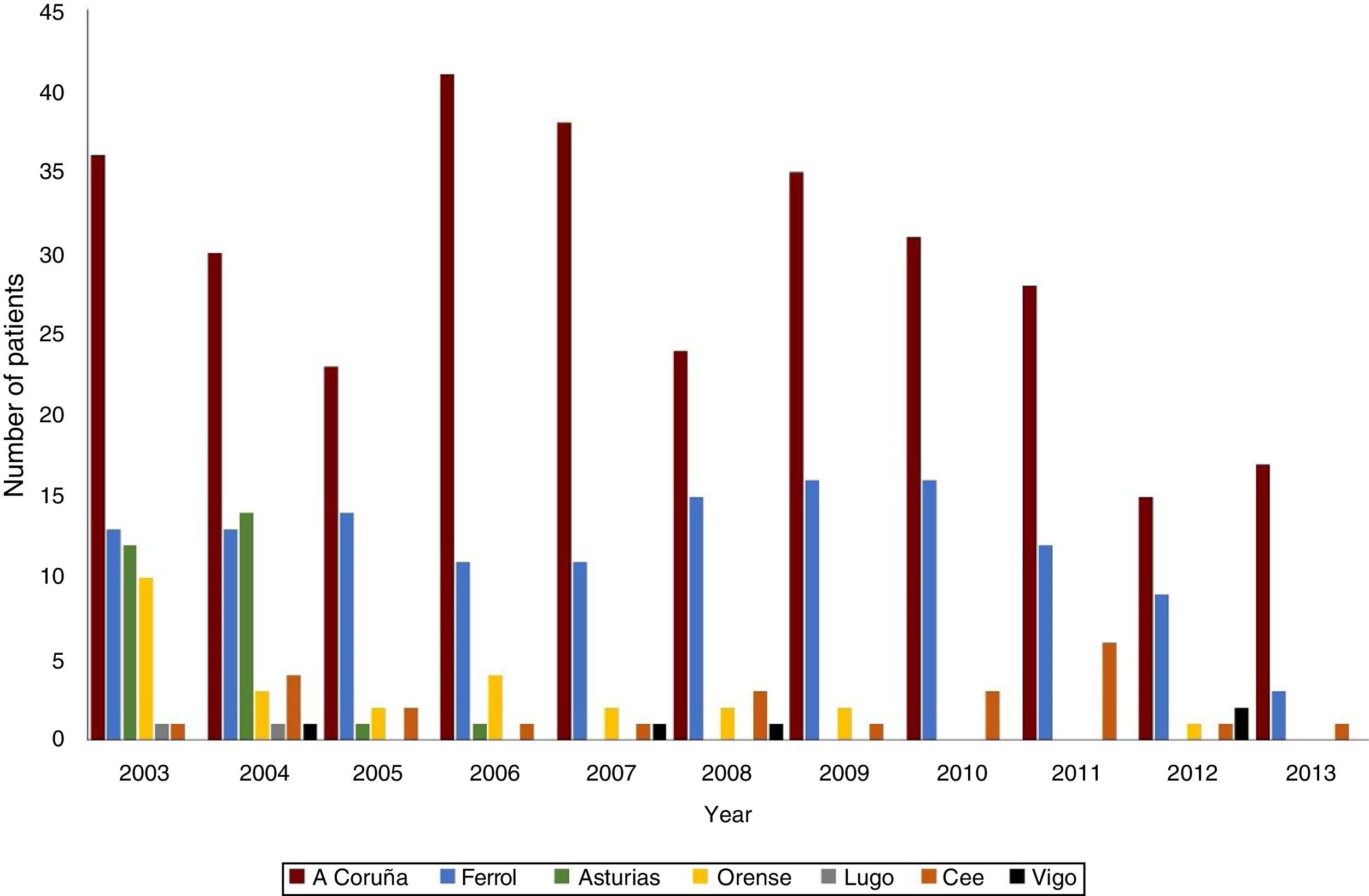
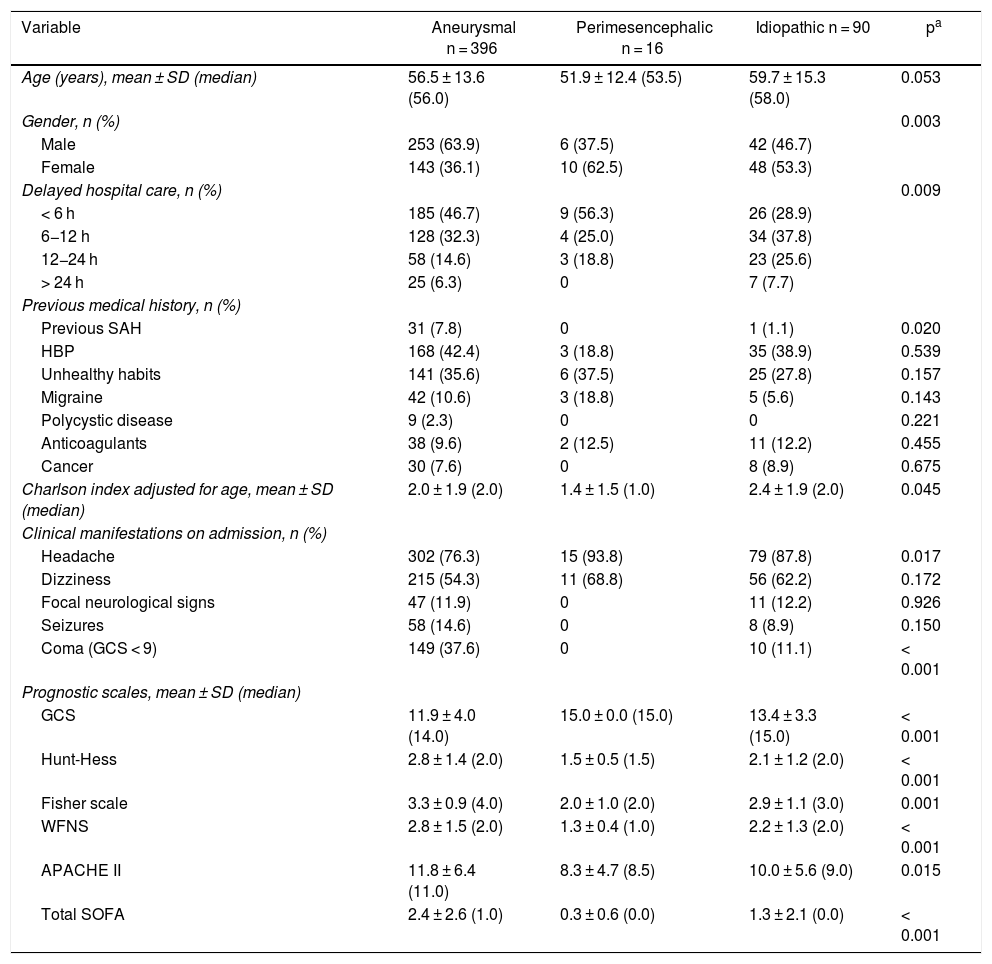
ResultsThere were 49.0 ± 15.1 patients/year (2013 incidence: 4.3/100,000 inhabitants). 60.3% presented Glasgow Coma Scale (GCS) 14-15, with scarce symptomatology (Hunt-Hess I-II 61.9%, World Federation Neurosurgeons Scale I-II 60.4%). 50.7% presented Fisher IV.
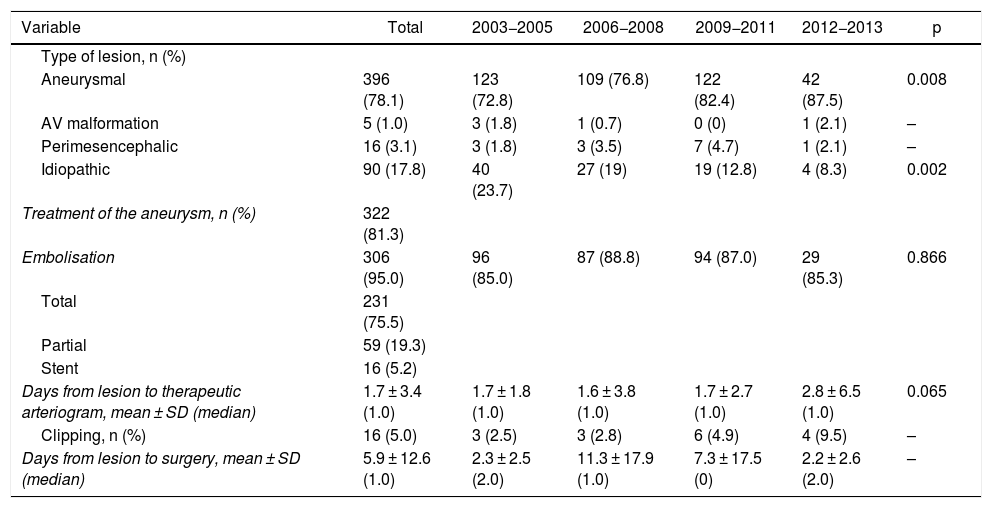
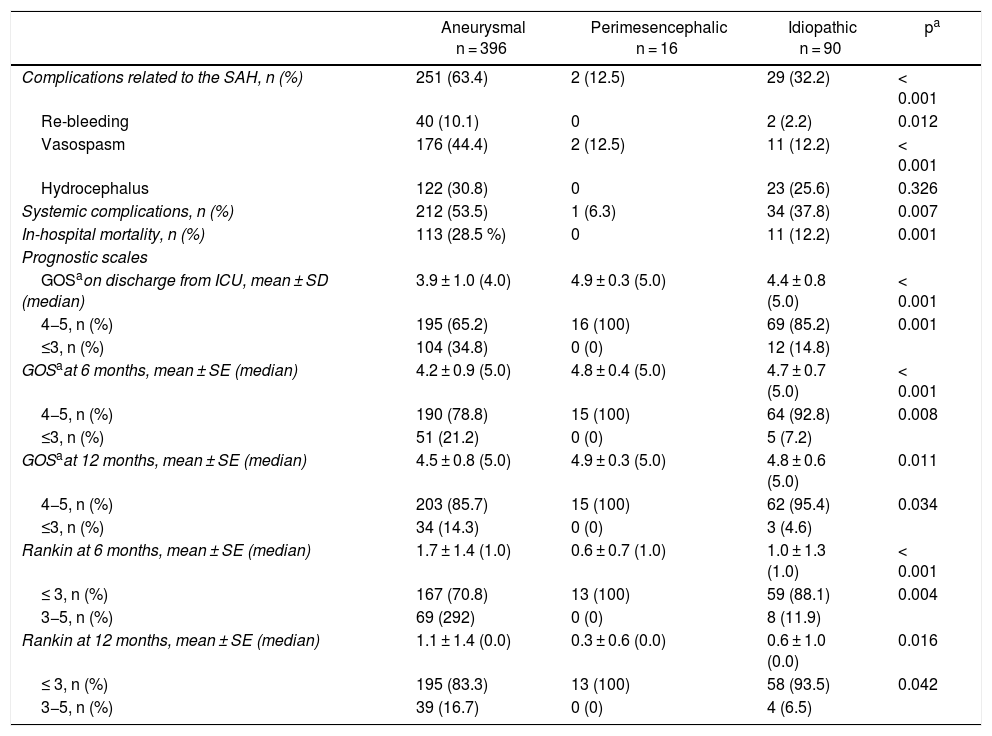
SAH-A was diagnosed in 78.3% (n = 396); perimesencephalic subarachnoid haemorrhage (SAH-PM) in 3.2%; and SAH-I in 17.9%. During the study period there was an increase in the prevalence of aneurysms, causing an increased number of surgeries in recent years. Both SAH-A and SAH-I presented greater severity upon admission. Patients with SAH-A had higher percentage of complications and mortality, with lesser degree of independence at 6 and 12 months.
ConclusionsThe incidence of SAH appears to have decreased in recent years, with SAH-I comprising 17.9% of the cases. Patients with SAH-I have better prognosis and lower risk of complications, highlighting the benignity of SAH-PM.
La hemorragia subaracnoidea espontánea es una causa poco frecuente de ictus que ocasiona gran impacto socioeconómico y elevada morbimortalidad.
El objetivo de este estudio es describir el perfil clínico y evolución de una serie de pacientes con HSA ingresados en un hospital terciario, así como el manejo diagnóstico-terapéutico.
Material y métodosEstudio retrospectivo de 536 pacientes diagnosticados de HSA ingresados en la Unidad de Cuidados Intensivos del Hospital Universitario de A Coruña de 2003–2013 (edad: 56,9 ± 14,1 años, ratio mujer/hombre:1,5:1). Se recogieron características demográficas, factores de riesgo, etiología y clínica, escalas pronósticas, pruebas diagnósticas y tratamiento. Se realizó un análisis comparativo entre la serie general y subgrupos de pacientes con HSA aneurismática (HSA-A) e idiopática (HSA-I).
ResultadosSe registraron 49,0 ± 15,1 pacientes/año (incidencia 2013:4,3/100.000 habitantes). 60,3% presentaban Glasgow Coma Scale 14-15, con escasa sintomatología (Hunt-Hess (H-H) I-II 61,9%; World Federation Neurosurgeons Scale (WFNS) I-II 60,4%). 50,7% presentaban Fisher IV. En 78,3%(n = 396) se diagnosticó HSA-A, 3,2% presentaban sangrado perimesencefálico (HSA-PM) y HSA-I 17,9%. Durante el periodo de estudio se registró aumento de la prevalencia de aneurismas, incrementándose en los últimos años la cirugía. Tanto la HSA-A como HSA-I presentaban mayor gravedad al ingreso. Los pacientes con HSA-A presentaron mayor porcentaje de complicaciones y mortalidad, con menor grado de independencia a 6 y 12 meses.
ConclusionesLa incidencia de HSA tiende a descender en los últimos años, representando la HSA-I el 17,9% de los casos. Los pacientes con HSA-I tienen mejor pronóstico y menor riesgo de complicaciones, destacando la benignidad de la HSA-PM.
Article

If it is the first time you have accessed you can obtain your credentials by contacting Elsevier Spain in suscripciones@elsevier.com or by calling our Customer Service at902 88 87 40 if you are calling from Spain or at +34 932 418 800 (from 9 to 18h., GMT + 1) if you are calling outside of Spain.
If you already have your login data, please click here .
If you have forgotten your password you can you can recover it by clicking here and selecting the option ¿I have forgotten my password¿.