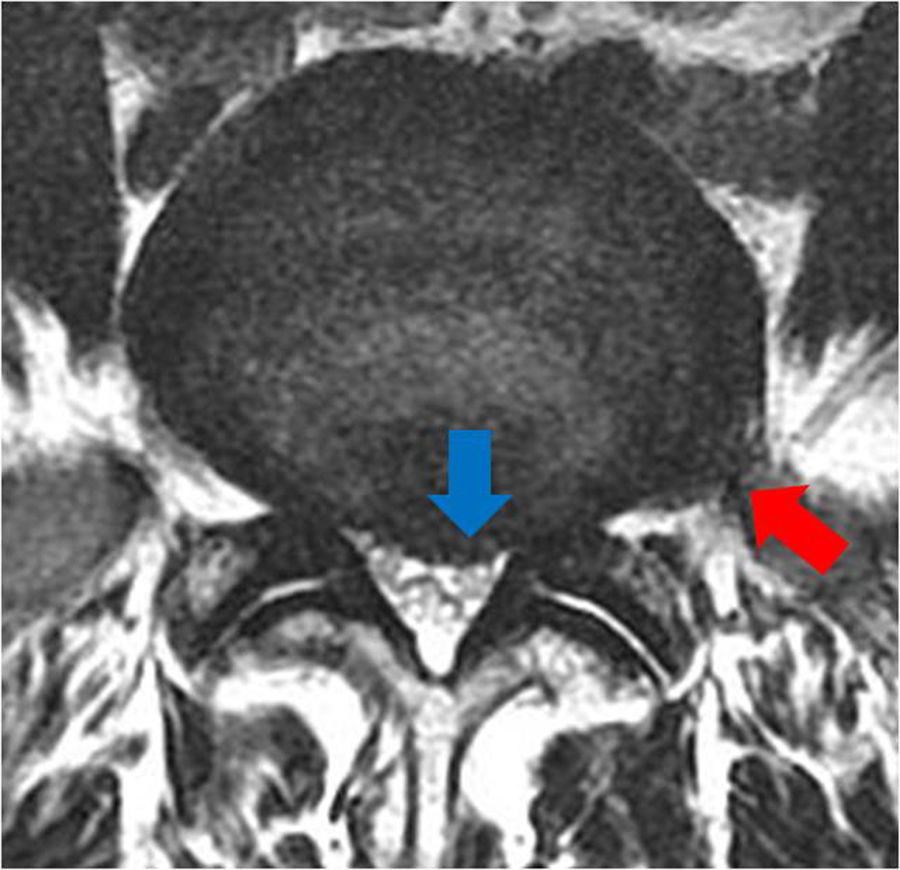
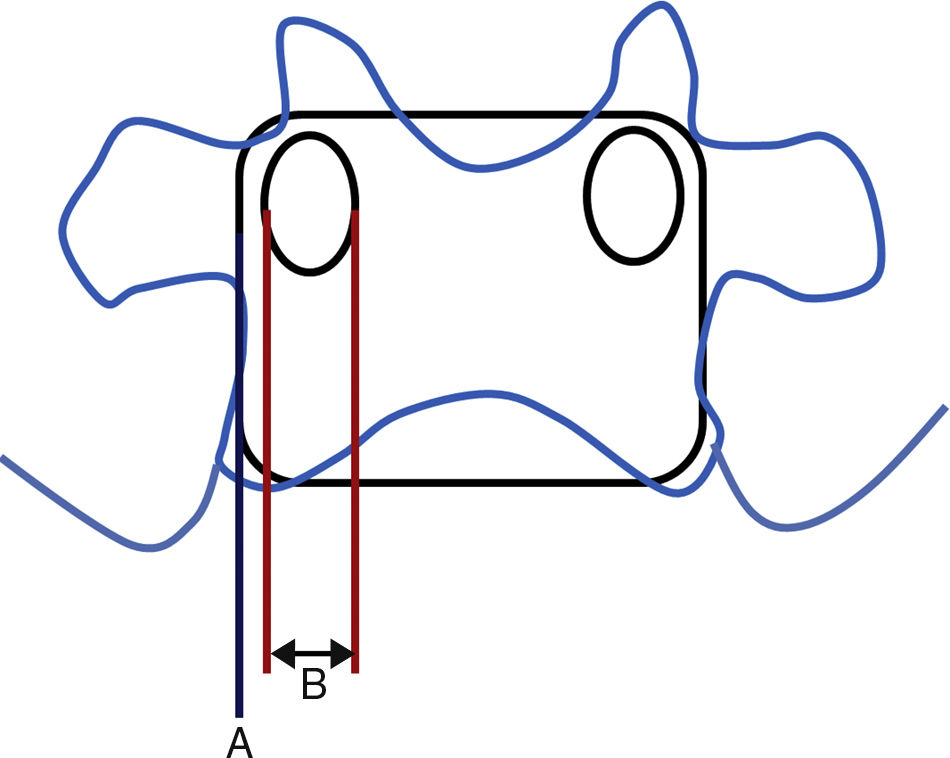
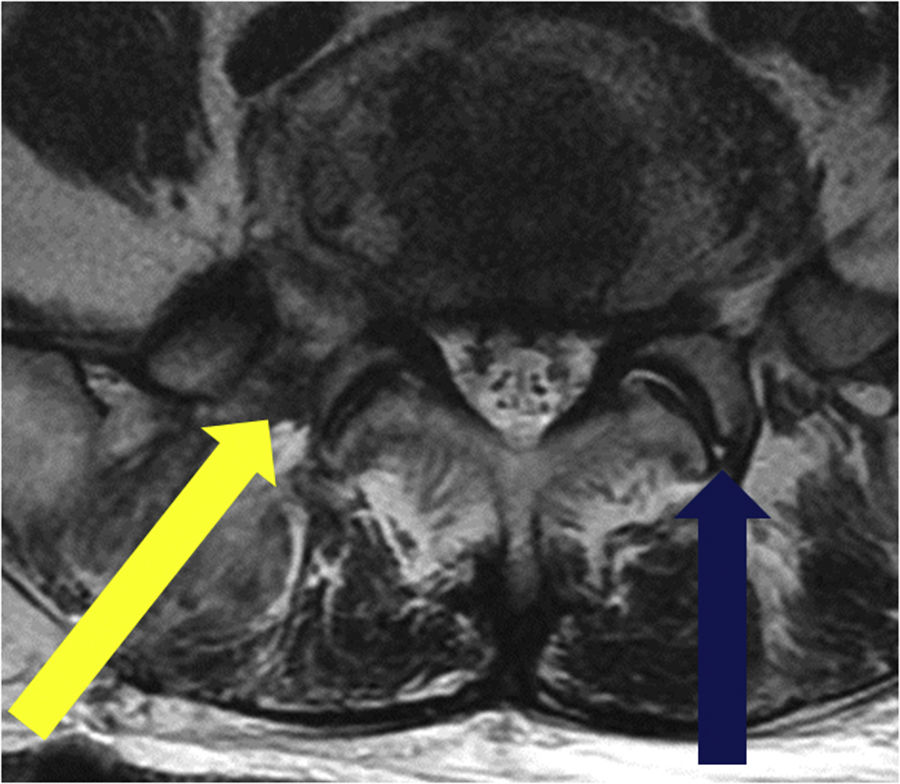
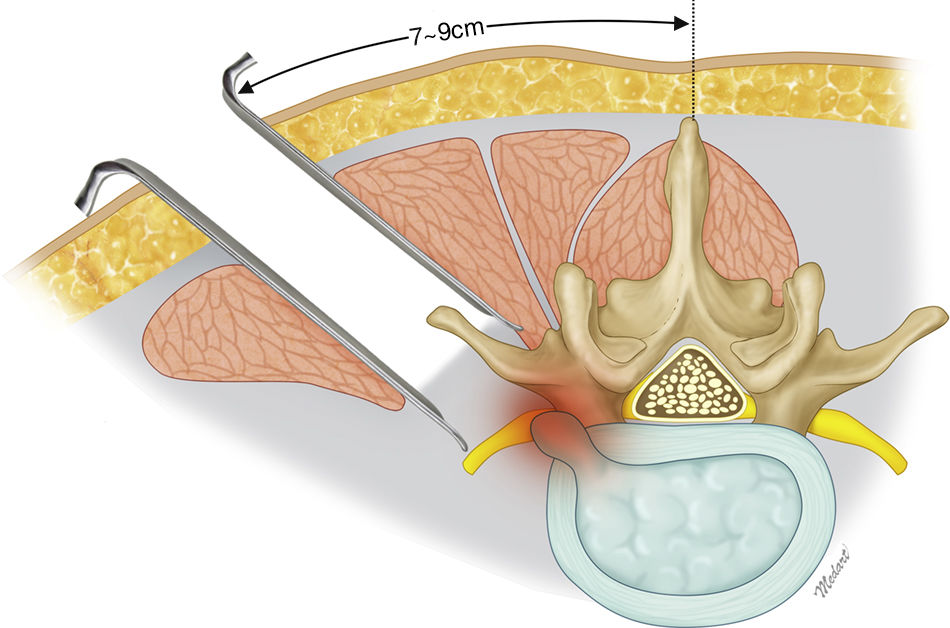
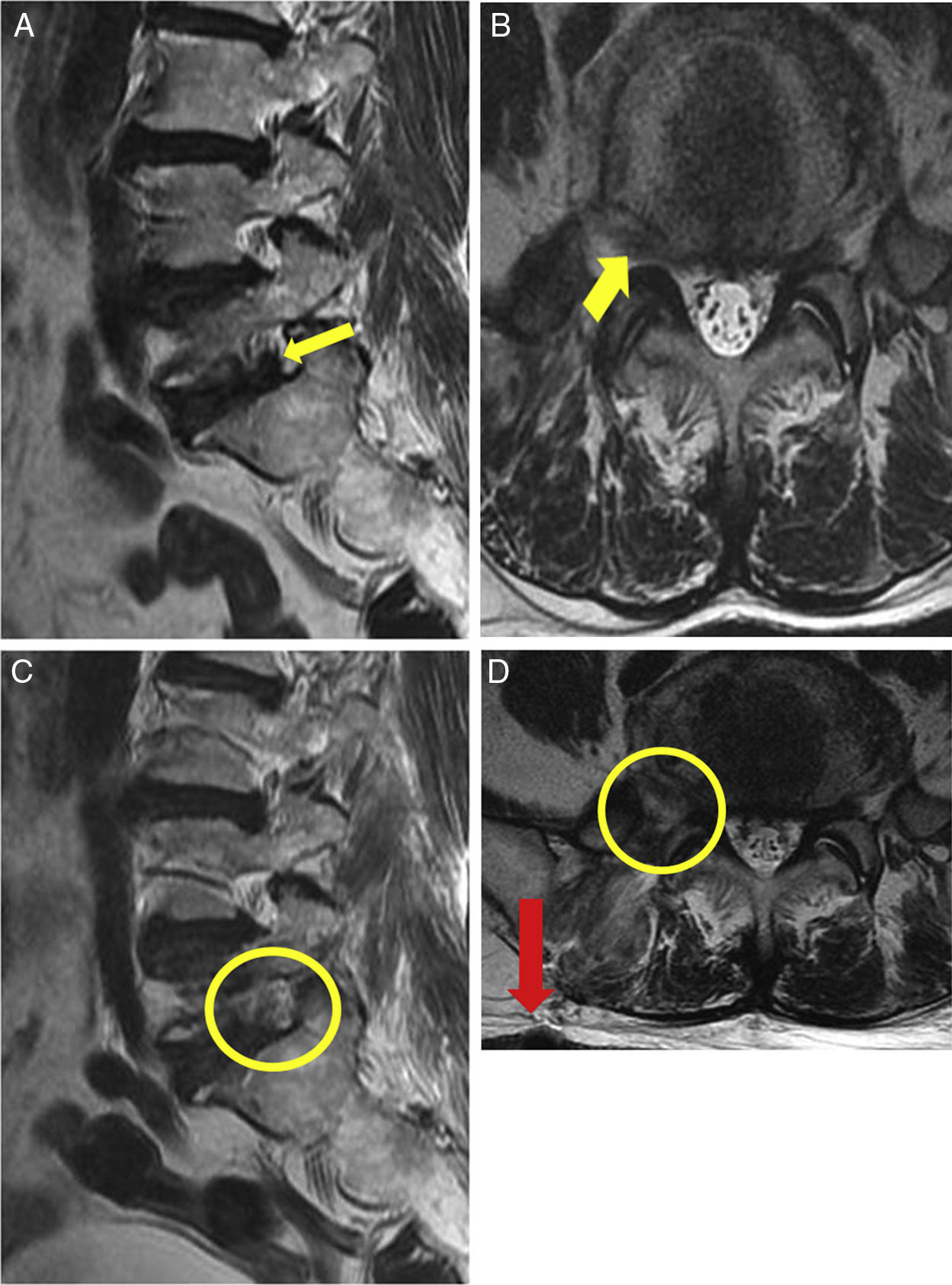
There are several approaches for double disc herniation consisting of an intracanal and foraminal lesion. Of several approaches, we introduced extreme lateral and interlaminar approach (ELIA). And we aimed to compare the approach with the conventional combined interlaminar and paraisthmic approach (CIPA).
Patients and methodsThe authors reviewed the medical charts of patients who underwent a procedure for a double disc herniation at the lumbosacral level between March 2012 and February 2016 and patients who underwent CIPA or ELIA were selected. For preoperative testing, simple X-ray, computed tomography (CT), and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) scans were performed. For postoperative outcomes, the Korean version of the Oswestry Disability Index (K-ODI) and Numeric Rating Scale (NRS) at one, two, and three months post-operation were checked.
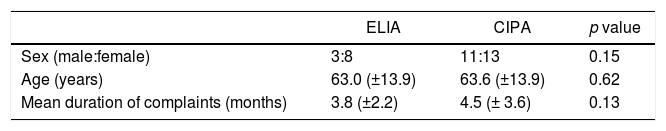
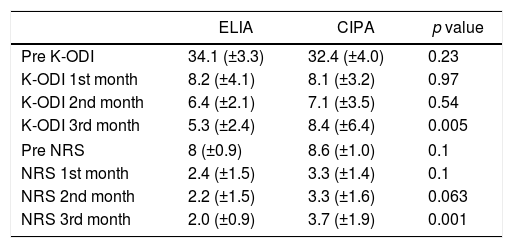
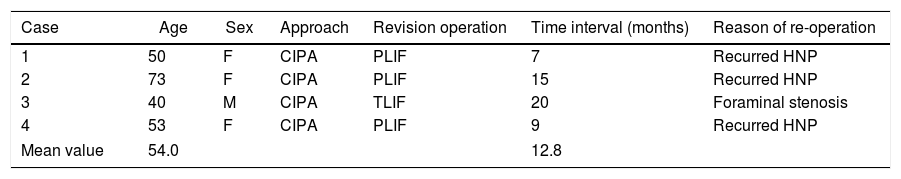
ResultsEleven patients were given ELIA and twenty-four patients were involved in CIPA. The mean pre K-ODI was 34.1 (±13.9) and 32.4 (±4.0) at each group. 1st, 2nd and 3rd month post-operative K-ODI was 8.2 (±4.1), 6.4 (±2.1) and 5.3 (±2.4) in ELIA and 8.1 (±3.2), 7.1 (±3.5) and 8.4 (±6.4) in CIPA. Post-operative 3rd month K-ODI showed significant difference between two groups (p: 0.005). The mean pre NRS was 8 (±0.9) and 8.6 (±1.0). 1st, 2nd and 3rd month post-operative NRS was 2.4 (±1.5), 2.2 (±1.5) and 2.0 (±0.9) in ELIA and 3.3 (±1.4), 3.3 (±1.6) and 3.7 (±1.9). Post-operative 3rd month NRS showed significant difference between two groups as well (p: 0.001). There were four (19.0%) recurrence cases in CIPA patients group, otherwise there was no recurrence case in ELIA group.
ConclusionsIn the treatment of L5-S1 double disc herniation, the ELIA surgical approach showed better outcomes than the CIPA surgical approach did with respect to pain and K-ODI during a mid-term follow-up examination conducted three months post-operation.
Existen varios tipos de abordajes para la hernia discal doble formada por una lesión intracanal y foraminal. Hemos elegido el Abordaje Extremo Lateral e Interlaminar (ELIA, por su sigla en inglés) con el objetivo de compararlo con el Abordaje Interlaminar y Paraístmico Convencional combinado (CIPA, por su sigla en inglés).
Pacientes y MétodosLos autores revisaron los cuadros médicos de pacientes que se vieron sometidos a un procedimiento para una hernia discal doble a nivel lumbosacro entre marzo del 2012 y febrero del 2016, y se seleccionaron los pacientes que se sometieron a CIPA o a ELIA. Como pruebas preoperatorias, se realizaron radiografías simples, tomografías computarizadas (CT, por su sigla en inglés), y escaneos de imágenes de resonancia magnética (MRI, por su sigla en inglés). Para resultados postoperatorios, se revisó la versión coreana del Índice de Discapacidad Owestry (K-ODI, por su sigla en inglés) y la Escala de Estimación Numérica (NRS, por su sigla en inglés) a intervalos postoperatorios de uno, dos y tres meses.
ResultadosOnce pacientes fueron sometidos a ELIA y veinticuatro pacientes a CIPA. La media antes de K-ODI fue 34,1 (±13,9) y 32,4 (±4,0) en cada grupo. El resultado K-ODI para el 1°, 2° y 3° mes postoperatorio fue de 8,2 (±4,1), 6,4 (±2,1) y 5,3 (±2,4) en ELIA y 8,1 (±3,2), 7,1 (±3,5) y 8,4 (±6,4) en CIPA. El resultado postoperatorio K-ODI del 3° mes mostró una diferencia significativa entre los dos grupos (p: 0,005). La media antes del NRS fue de 8 (±0,9) y 8,6 (±1,0). El resultado del NRS del 1°, 2° y 3° mes postoperatorio fue de 2,4 (±1,5), 2,2 (±1,5) y 2,0 (±0,9) en ELIA y 3,3 (±1,4), 3,3 (±1,6) y 3,7 (±1,9). El resultado del NRS para el 3° mes postoperatorio también mostró una diferencia significativa entre los dos grupos (p: 0,001). Hubo cuatro casos de recurrencia en el grupo de pacientes sometidos a CIPA (19,0%), mientras que, por el contrario, no existió recurrencia en el grupo de pacientes sometidos a ELIA.
ConclusionesEn el tratamiento de hernia discal doble L5-S1, el abordaje quirúrgico ELIA mostró mejores resultados que el abordaje quirúrgico CIPA con respecto a dolor y resultados de K-ODI durante los exámenes de seguimiento a intermedio conducidos durante los tres meses posteriores a la cirugía.
Article

If it is the first time you have accessed you can obtain your credentials by contacting Elsevier Spain in suscripciones@elsevier.com or by calling our Customer Service at902 88 87 40 if you are calling from Spain or at +34 932 418 800 (from 9 to 18h., GMT + 1) if you are calling outside of Spain.
If you already have your login data, please click here .
If you have forgotten your password you can you can recover it by clicking here and selecting the option ¿I have forgotten my password¿.