Improved shunt survival and a better understanding of factors related to failure in paediatric hydrocephalus still pose a challenge for neurosurgeons, in order to avoid morbidity and mortality, as well as the economic impact of repeated revision surgeries. For these reasons, an analysis is performed on the factors related to the first shunt failure in the long-term follow-up of a series in a single centre.
MethodsA retrospective review was conducted on 166 hydrocephalic paediatric patients shunted for the first time between 2000 and 2014. An analysis was made of the statistical relationships between first shunt failure and the demographic, aetiological, surgical and clinical variables.
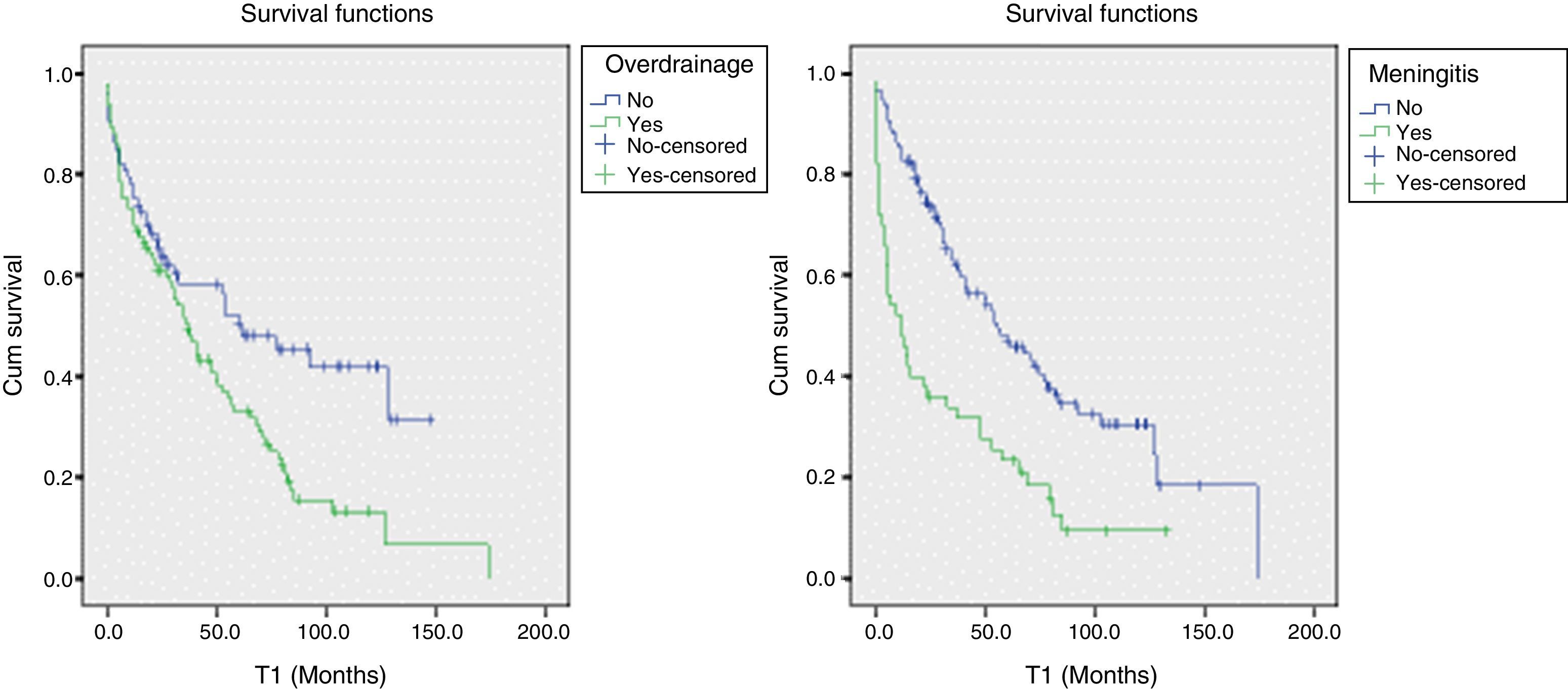
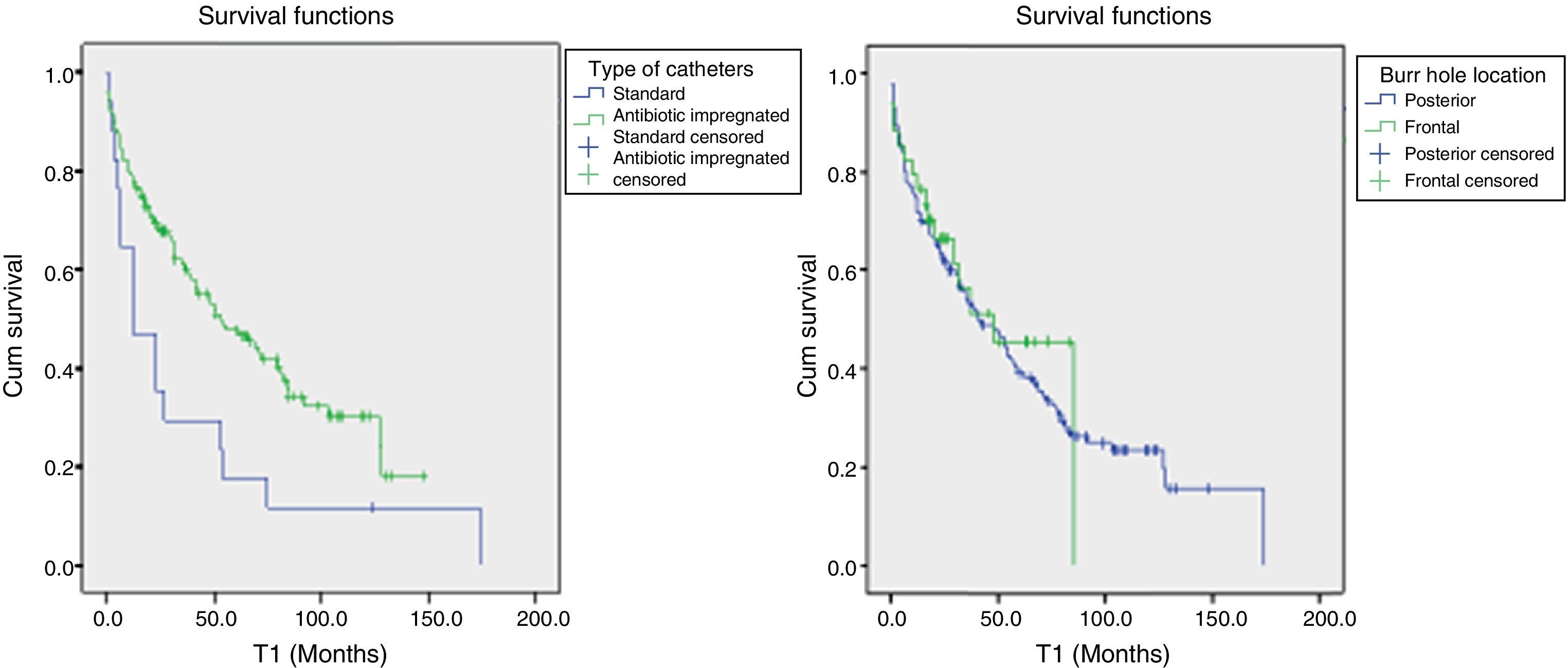
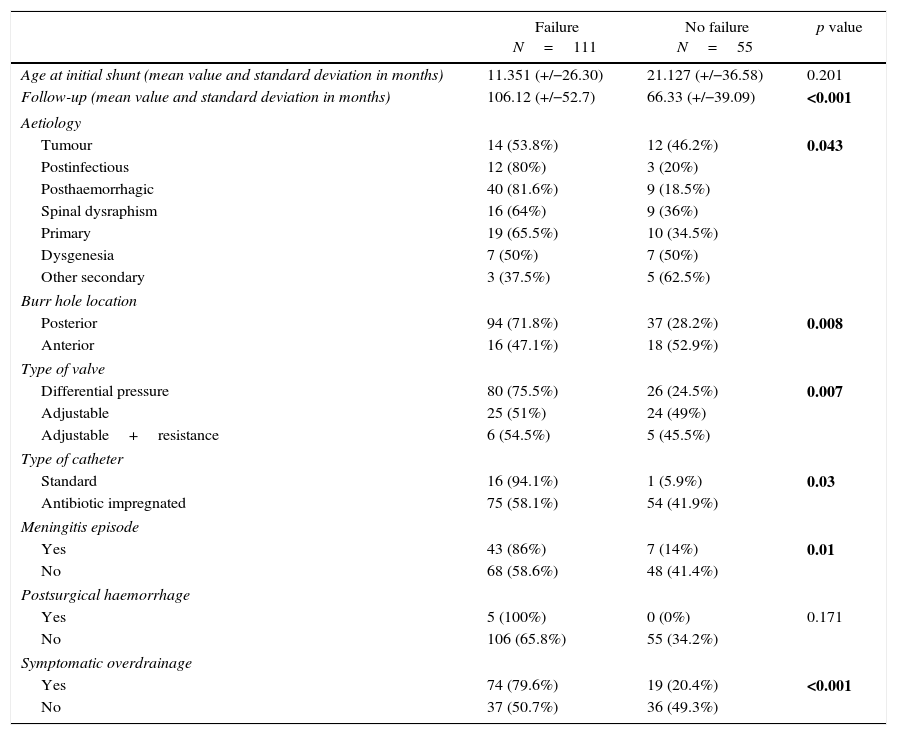
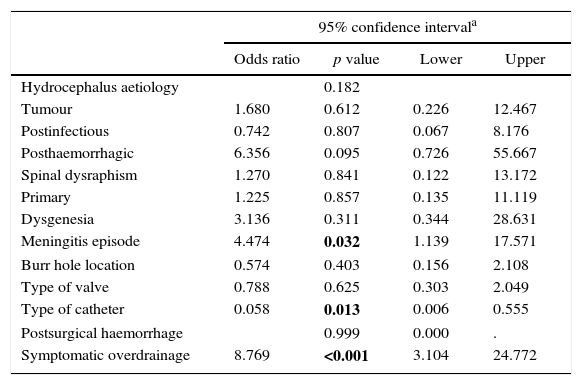
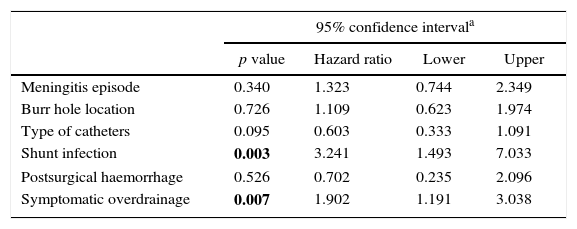
ResultsOf the 166 shunts implanted in our centre during the study period, 111 required revision over a mean follow-up period of 93 months. Factors significantly related to failure were post-haemorrhagic and post-infectious hydrocephalus, meningitis episode, posterior burr hole, differential pressure valve, standard catheter in first surgery, and symptomatic over-drainage. Multivariable analysis showed that previous meningitis and symptomatic over-drainage were risk factors for shunt failure, whereas frontal burr hole location and antibiotic-impregnated catheters were protective factors. Cox regression determined that independent factors significantly related to a worse shunt survival, were shunt infection and symptomatic over-drainage.
ConclusionsMeningitis, symptomatic over-drainage, frontal burr hole, and antibiotic impregnated catheters are significant prognostic factors for shunt survival. Shunt infection and symptomatic over-drainage are independent factors significantly related to a shorter shunt survival. Prospective, randomised, controlled trials are required to validate these results.
Mejorar la supervivencia del shunt y conocer los factores relacionados con el fallo valvular continúa siendo un reto en neurocirugía pediátrica, con el propósito de evitar la morbimortalidad y el impacto económico de las revisiones valvulares repetidas. Por este motivo, se estudiaron los factores relacionados con el primer fallo valvular en una serie propia con un seguimiento prolongado.
MétodosEstudio retrospectivo de 166 pacientes pediátricos con hidrocefalia derivada por primera vez entre los años 2000-2014. Se analizó la asociación estadística entre el primer fallo valvular y las variables demográficas, etiológicas, quirúrgicas y clínicas.
ResultadosDe 166 válvulas implantadas durante el periodo de estudio, 111 requirieron revisión en un seguimiento medio de 93 meses. Los factores relacionados de forma significativa con el fallo valvular fueron las etiologías posthemorrágica y postinfecciosa; una meningitis previa; trépano posterior, válvula de presión diferencial o catéter estándar en la primera intervención, y sobredrenaje sintomático. El análisis multivariante mostró que la meningitis previa y el sobredrenaje sintomático fueron factores de riesgo para la disfunción valvular, mientras que el trépano frontal y los catéteres con impregnación antibiótica fueron factores protectores. La regresión de Cox determinó que la infección del shunt y el sobredrenaje sintomático fueron los factores relacionados de forma independiente con una menor supervivencia valvular.
ConclusionesMeningitis, sobredrenaje sintomático, trépano frontal y catéteres de impregnación antibiótica son factores pronósticos significativos en la supervivencia valvular. La infección del shunt y el sobredrenaje sintomático son factores independientes relacionados de forma significativa con una menor supervivencia valvular. Estudios controlados, prospectivos y aleatorizados son necesarios para validar estos resultados.
Article

If it is the first time you have accessed you can obtain your credentials by contacting Elsevier Spain in suscripciones@elsevier.com or by calling our Customer Service at902 88 87 40 if you are calling from Spain or at +34 932 418 800 (from 9 to 18h., GMT + 1) if you are calling outside of Spain.
If you already have your login data, please click here .
If you have forgotten your password you can you can recover it by clicking here and selecting the option ¿I have forgotten my password¿.