The coincidence in a patient of Hemifacial Spasm and Trigeminal Neuralgia is not frequent. A case is presented with the objective of showing this association due to the abnormal activation of the Trigemino-Facial Reflex.
A 55-year-old woman with an 8-year history of left-sided hemifacial spasm and typical trigeminal pain in the ipsilateral V1 and V2 territory.
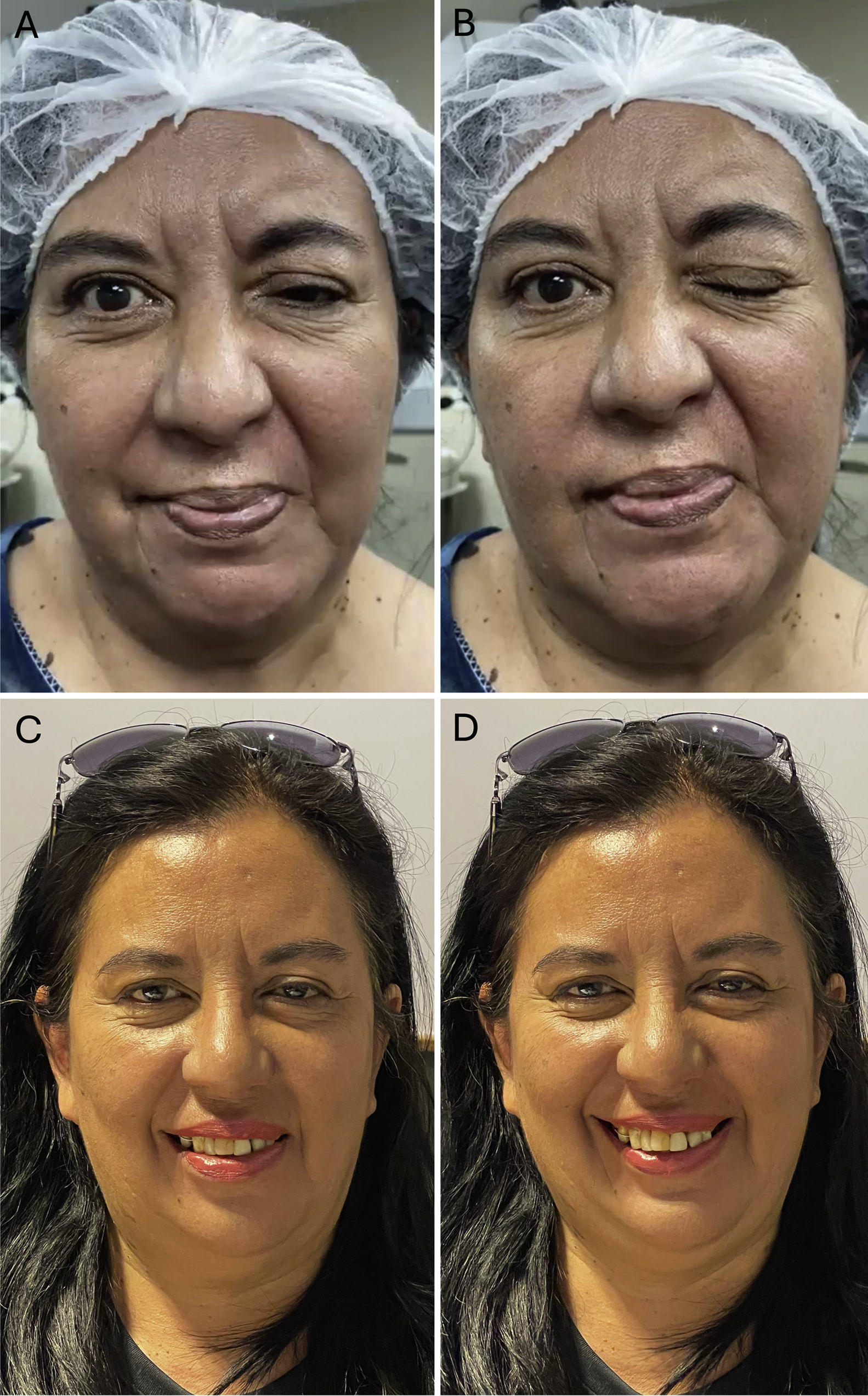
The physical examination shows spasms in the left hemiface, with reproduction of intense pain upon sensory stimulation of the skin on the forehead and upper dental arch.
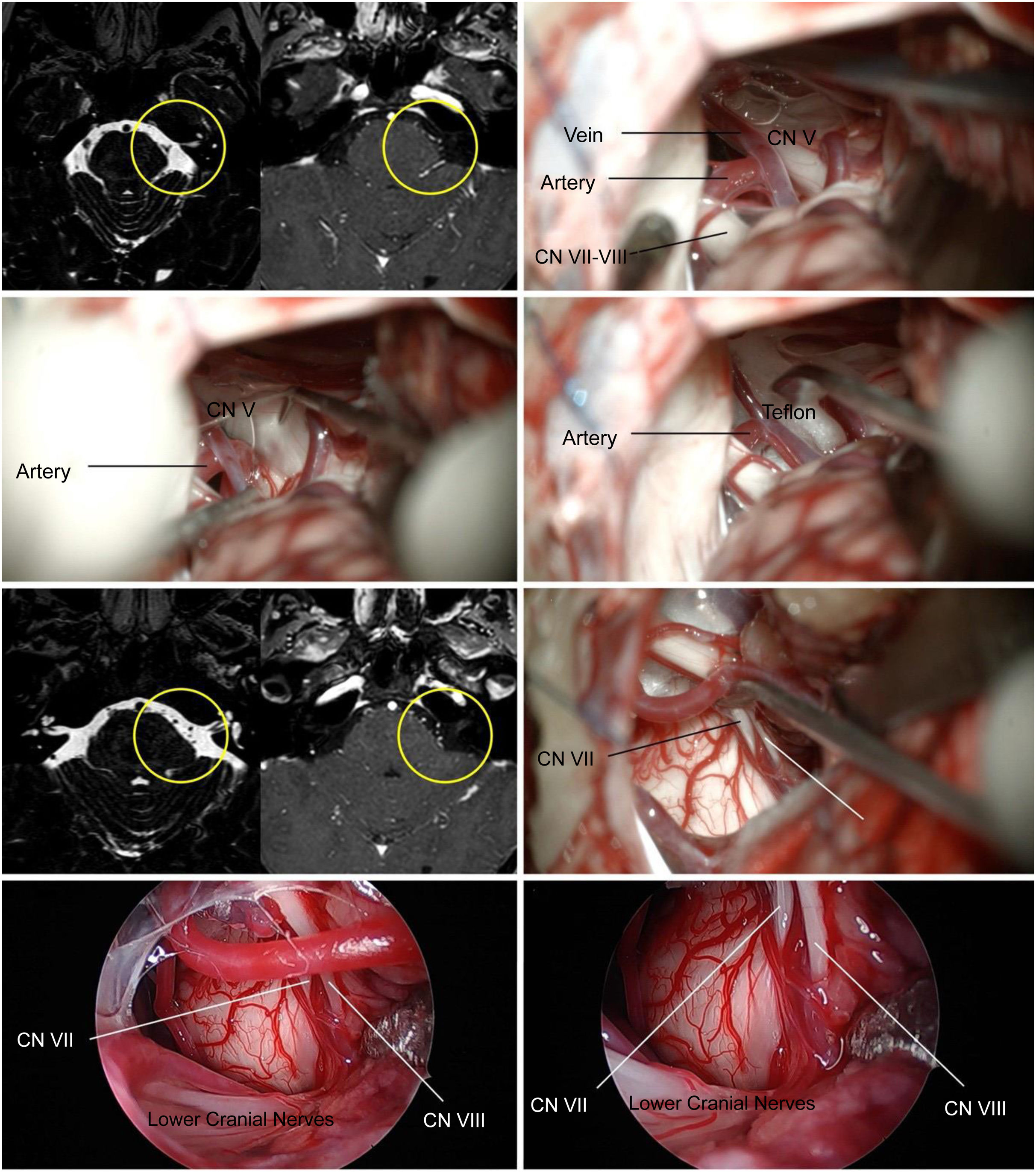
The MRI showed a vessel in intimate contact with the entrance area of the left trigeminal nerve.
A left retrosigmoid approach was performed. First, the entrance area of the trigeminal nerve was accessed, finding a clear vascular conflict, which was isolated with Teflon. Then, the trajectory was changed and the exit zone of the facial nerve was accessed, and no type of vascular conflict was identified.
The patient presented complete resolution of the Hemifacial Spasm and the associated trigeminal pain.
The analysis of this case allows us to conclude that during microvascular decompression of the Facial Nerve, if frank proximal compression is not evident, the Trigeminofacial structural relationship must be taken into account, making it necessary to explore the Trigeminal Nerve.
La coincidencia en un paciente de espasmo hemifacial y de neuralgia trigeminal no es frecuente. Se presenta un caso con el objetivo de mostar esta asociación por la activación anormal del reflejo trigémino-facial.
Mujer de 55 años, con antecedentes de 8 años de espasmo hemifacial de lado izquierdo y dolor trigeminal típico en el territorio de V1 y V2 ipsilateral.
El examen físico muestra espasmos en hemicara izquierda, con reproducción de dolor intenso al estímulo sensitivo de la piel en la frente y arcada dentaria superior.
La RM mostró un vaso en íntimo contacto con la zona de entrada del nervio trigémino izquierdo.
Se realizó un abordaje retrosigmoideo izquierdo. Primero se accedió a la zona de entrada del nervio trigémino encontrándose un claro conflicto vascular, el cual se aisla con teflón. Luego, se cambió de trayectoria y se accedió a la zona de salida del nervio facial, no identificandose ningun tipo de conflicto vascular.
La paciente presentó resolución total del espasmo hemifacial y del dolor trigeminal asociado.
El análisis de este caso nos permite concluir que durante la descompresion microvascular del nervio facial si no se evidencia una franca compresión proximal, se debe tener en cuenta la relación estructural trigeminofacial, siendo necesario la exploración del nervio trigeminal.
Article

If it is the first time you have accessed you can obtain your credentials by contacting Elsevier Spain in suscripciones@elsevier.com or by calling our Customer Service at902 88 87 40 if you are calling from Spain or at +34 932 418 800 (from 9 to 18h., GMT + 1) if you are calling outside of Spain.
If you already have your login data, please click here .
If you have forgotten your password you can you can recover it by clicking here and selecting the option ¿I have forgotten my password¿.