Complete resection of symptomatic supratentorial cavernoma (SCA) and removal of the surrounding gliotic area is recommended to minimize the risk of persistent seizures or (re)bleeding. Surgery of SCA located in an eloquent area, can carry out severe postoperative neurological morbidity. We report a study aimed to assess feasibility, extent of resection and outcome after surgical removal of CA by cortico-subcortical intraoperative brain stimulation (ioBS) in the awake patient.
MethodsSix patients diagnosed of symptomatic SCA located on an eloquent area and operated on while awake under local anaesthesia ioBS, were included. Preoperative planning included neuropsychologic assessment of language-related functions, sociocognitive functions and executive functions. Intraoperatively, we recorded the results achieved in the planned neuropsychological tasks when stimulation was applied (cortical and subcortical). Postoperative control 3D MRI was scheduled at 1 month after surgery to calculate extent of resection. Neuropsychological assessment at 6 months after surgery was performed in all cases.
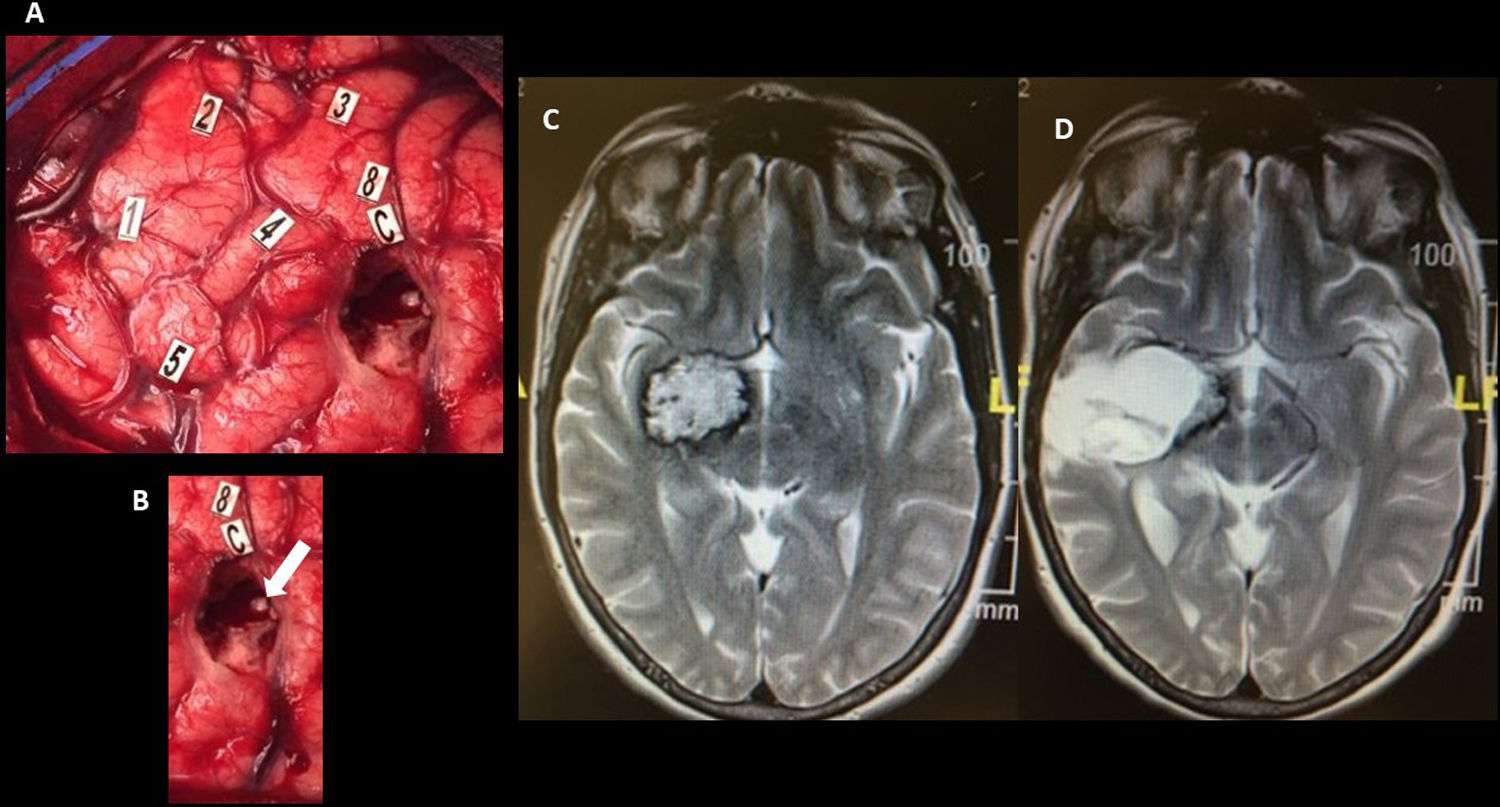
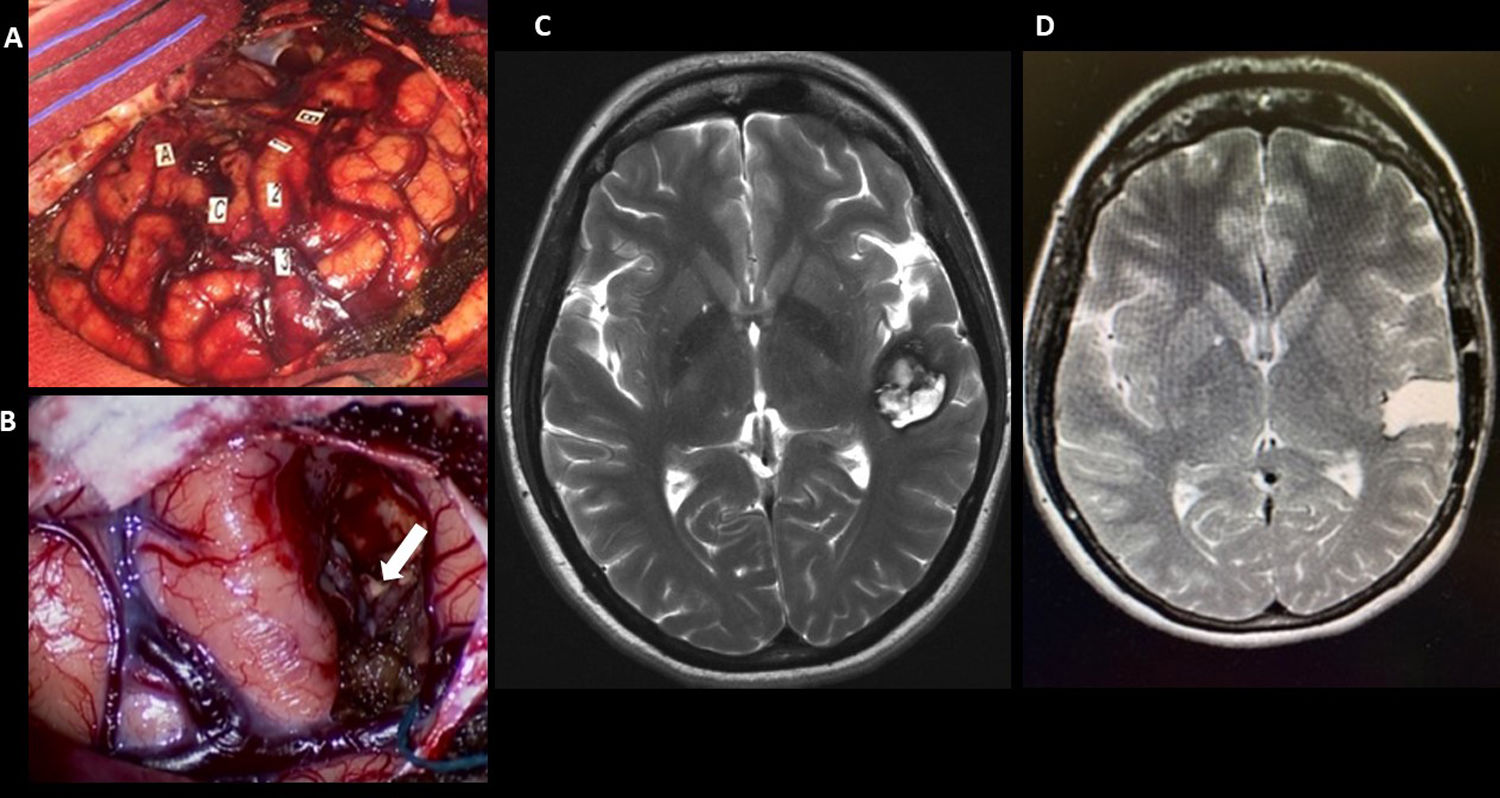
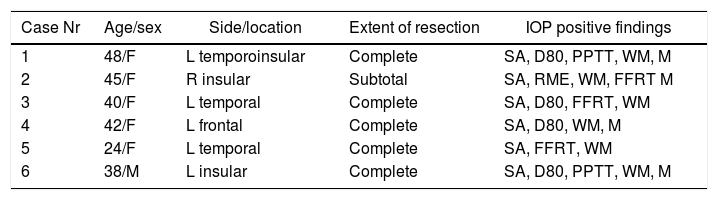
ResultsSix patients (5 females, 1 male) aged 24–48 years were included in our study. Locations of the lesions were right insular (n=1), left insular (n=1), left temporo-insular (n=1), left temporal (n=2) and left frontal (n=1). In all patients, positive findings were obtained during ioBS. In 5 patients, complete surgical resection was achieved. Two patients had postoperative transient neurological deficits, one case of hemiparesis, one case of dysnomia, both cleared over a 6-month period. Clinical follow-up revealed that all patients experienced complete recovery from preoperative symptoms within a year and five patients with seizures showed marked improvement and eventually quit antiepileptic drugs. Neuropsychological assessment at 6 months provided normal results compared to preoperative baseline in all domains.
ConclusionsOur study suggests that ioBS in the awake surgery of symptomatic SCA located in eloquent areas, allows to increase the rate of complete resection, minimizing postoperative neurological and neuropsychological deficit, and improving postoperative seizures control.
La resección completa de los cavernomas supratentoriales (SCA) sintomáticos, incluyendo el área gliótica perilesional, es el tratamiento de elección para evitar la persistencia de crisis y el resangrado. La cirugía de los SCA localizados en áreas elocuentes puede asociar graves complicaciones neurológicas. Presentamos un estudio cuyo objetivo es documentar la viabilidad de la estimulación corticosubcortical intraoperatoria (ioBS) en el paciente despierto y su impacto en el grado de exéresis y el resultado clínico final.
Materiales y métodosIncluimos 6 pacientes diagnosticados de SCA sintomático localizado en área elocuente, que fueron intervenidos mediante ioBS en el paciente despierto. El estudio preoperatorio incluyó una valoración neuropsicológica de funciones lingüísticas, sociocognitivas y ejecutivas. Durante la realización de la ioBS en el paciente despierto registramos los resultados obtenidos por los pacientes en las tareas neuropsicológicas planificadas. El grado de exéresis se estimó en una RM realizada un mes tras la cirugía. A los 6 meses de la cirugía se realizó una evaluación neuropsicológica de control.
ResultadosCinco mujeres y un hombre con edades comprendidas entre los 24 y 48 años fueron incluidos en el estudio. Las localizaciones de los cavernomas fueron insular derecha (n=1), insular izquierda (n=1), temporo-insular izquierda (n=1), temporal izquierda (n=2) y frontal izquierda (n=1). En todos los pacientes se encontraron hallazgos tras la ioBS. Se obtuvo una exéresis completa en 5 casos. Dos pacientes presentaron déficit neurológico transitorio, un caso de hemiparesia y un caso de disnomia, que mejoró a los 6 meses. El seguimiento clínico mostró que todos los pacientes presentaron al cabo de un año una recuperación completa de los síntomas por los que fueron diagnosticados. Los 5 pacientes con crisis de inicio pudieron dejar los fármacos antiepilépticos. La evaluación neuropsicológica a los 6 meses de la cirugía mostró una evolución normal en todos los dominios estudiados.
ConclusionesNuestro estudio sugiere que la ioBS con paciente despierto en la cirugía de SCA sintomático en área elocuente permite conseguir resecciones completas, reduciendo el riesgo de déficit neurológico y neuropsicológico posquirúrgico y mejorando el control de las crisis epilépticas.
Article

If it is the first time you have accessed you can obtain your credentials by contacting Elsevier Spain in suscripciones@elsevier.com or by calling our Customer Service at902 88 87 40 if you are calling from Spain or at +34 932 418 800 (from 9 to 18h., GMT + 1) if you are calling outside of Spain.
If you already have your login data, please click here .
If you have forgotten your password you can you can recover it by clicking here and selecting the option ¿I have forgotten my password¿.