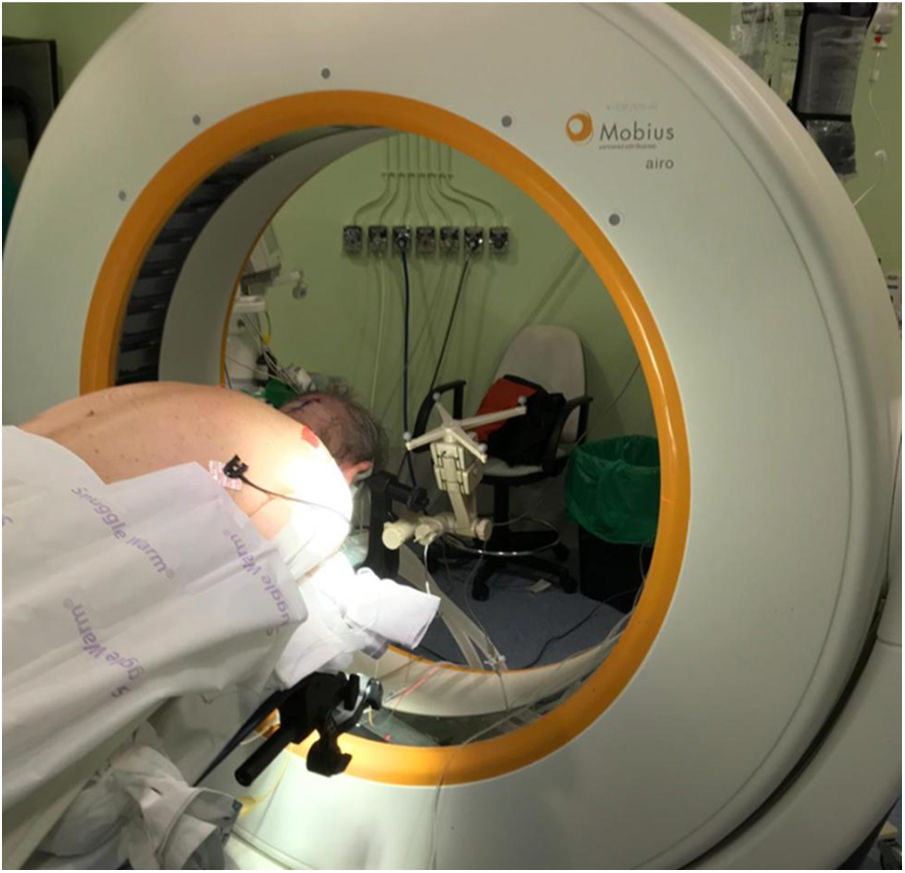
New intraoperative imaging techniques, which aim to improve tumour resection, have been implemented in recent years in brain tumour surgery, although they lead to an increase in resources. In order to carry out an update on this topic, this manuscript has been drafted by a group from the Sociedad Española de Neurocirugía [Spanish Society of Neurosurgery].
Material and MethodsExperts in the use of each one of the most-used intraoperative techniques in brain tumour surgery were presented with a description of the technique and a brief review of the literature. Indications for use, their advantages and disadvantages based on clinical experience and on what is published in the literature will be described.
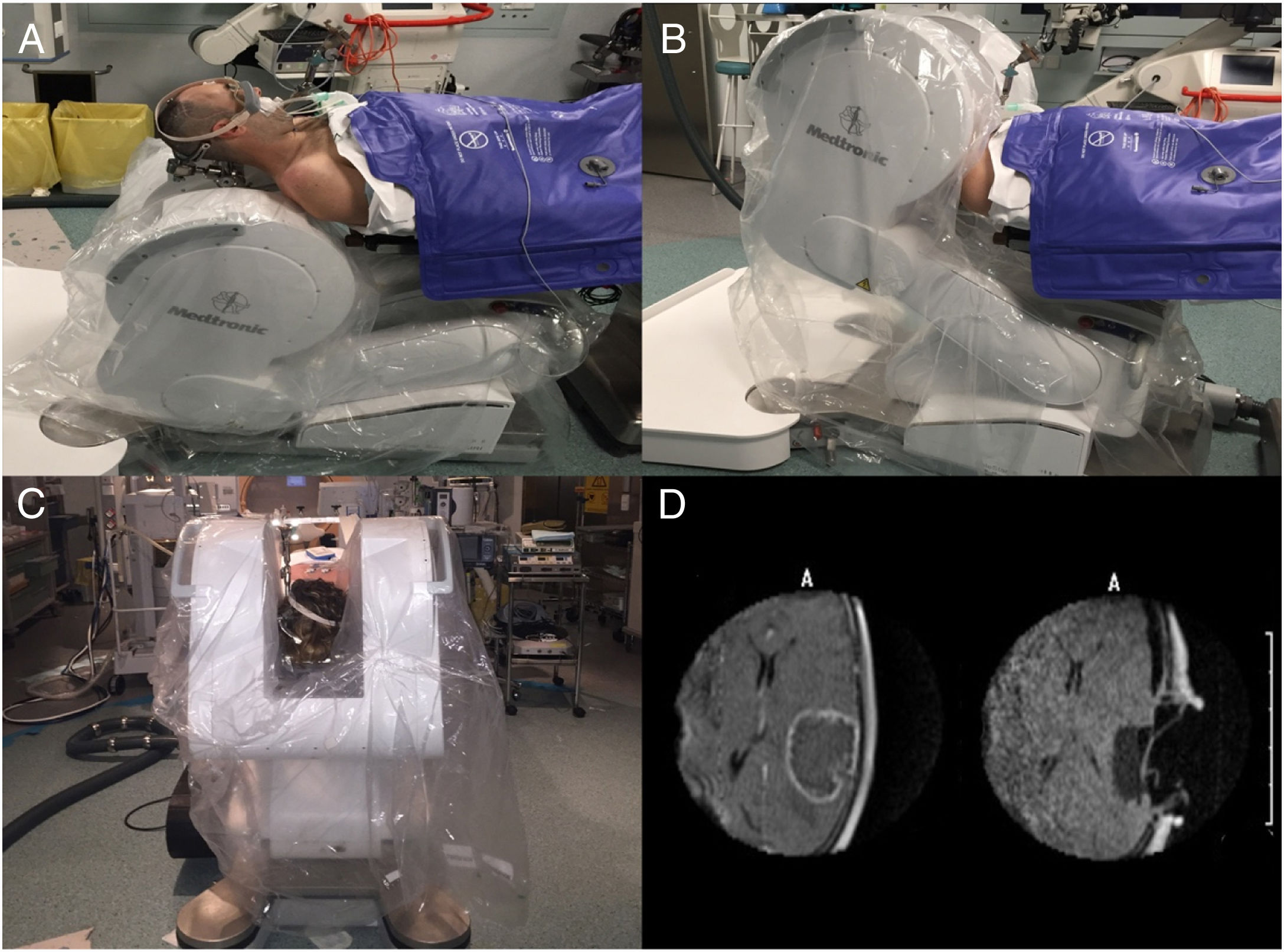
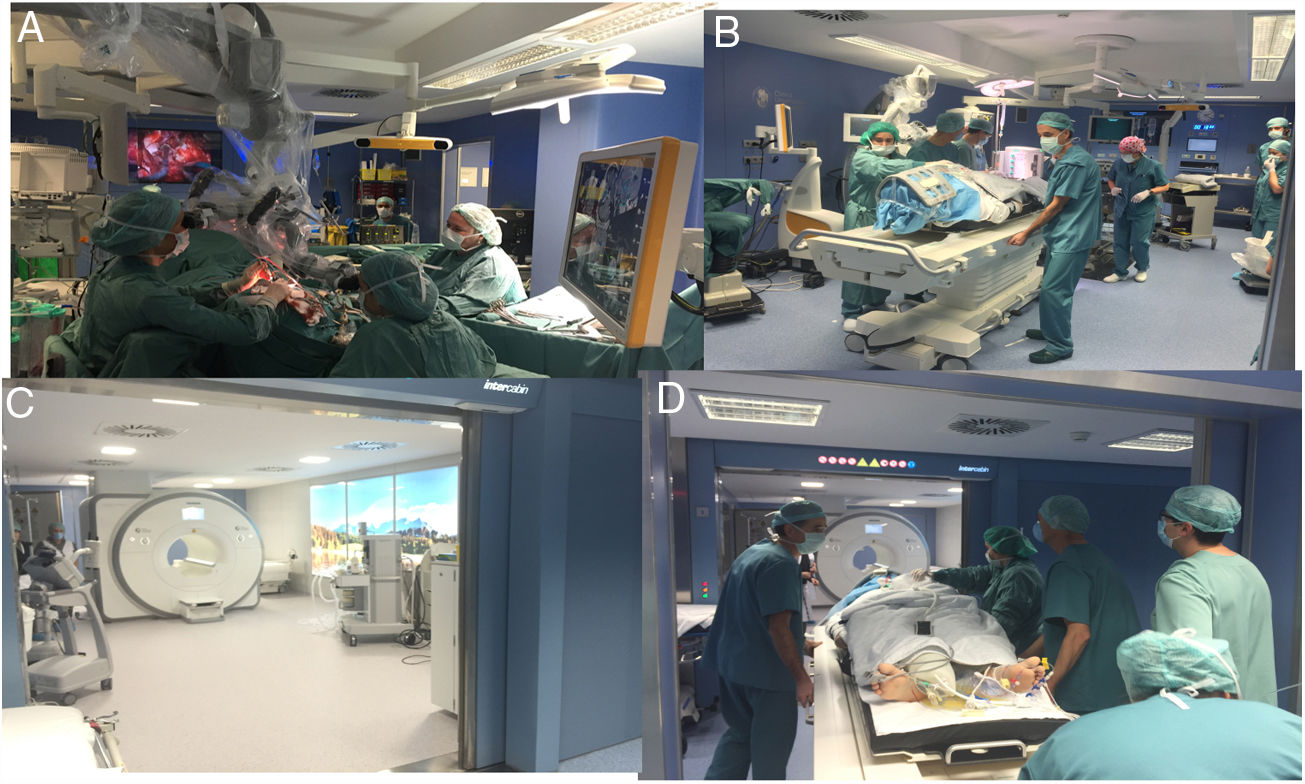
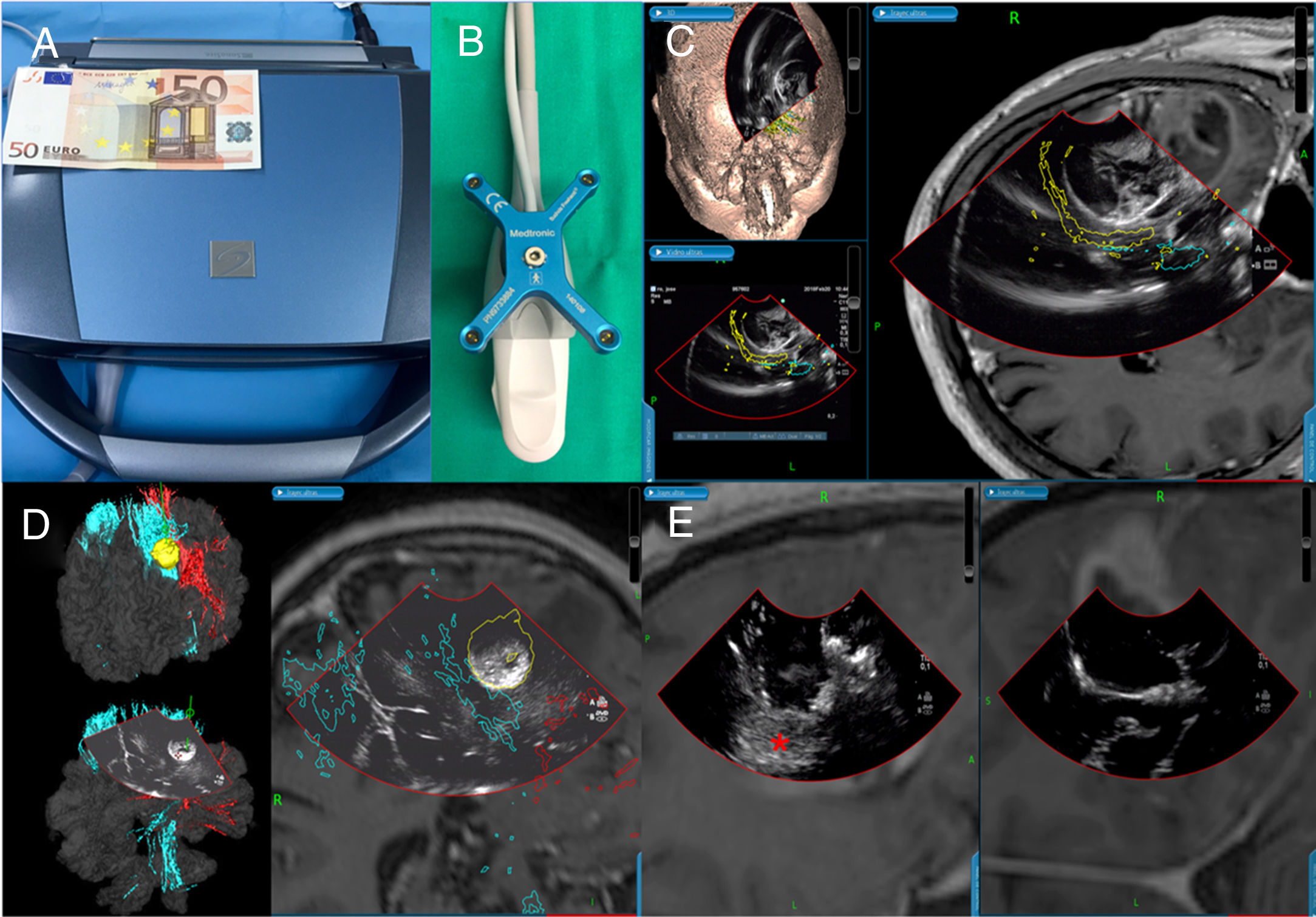
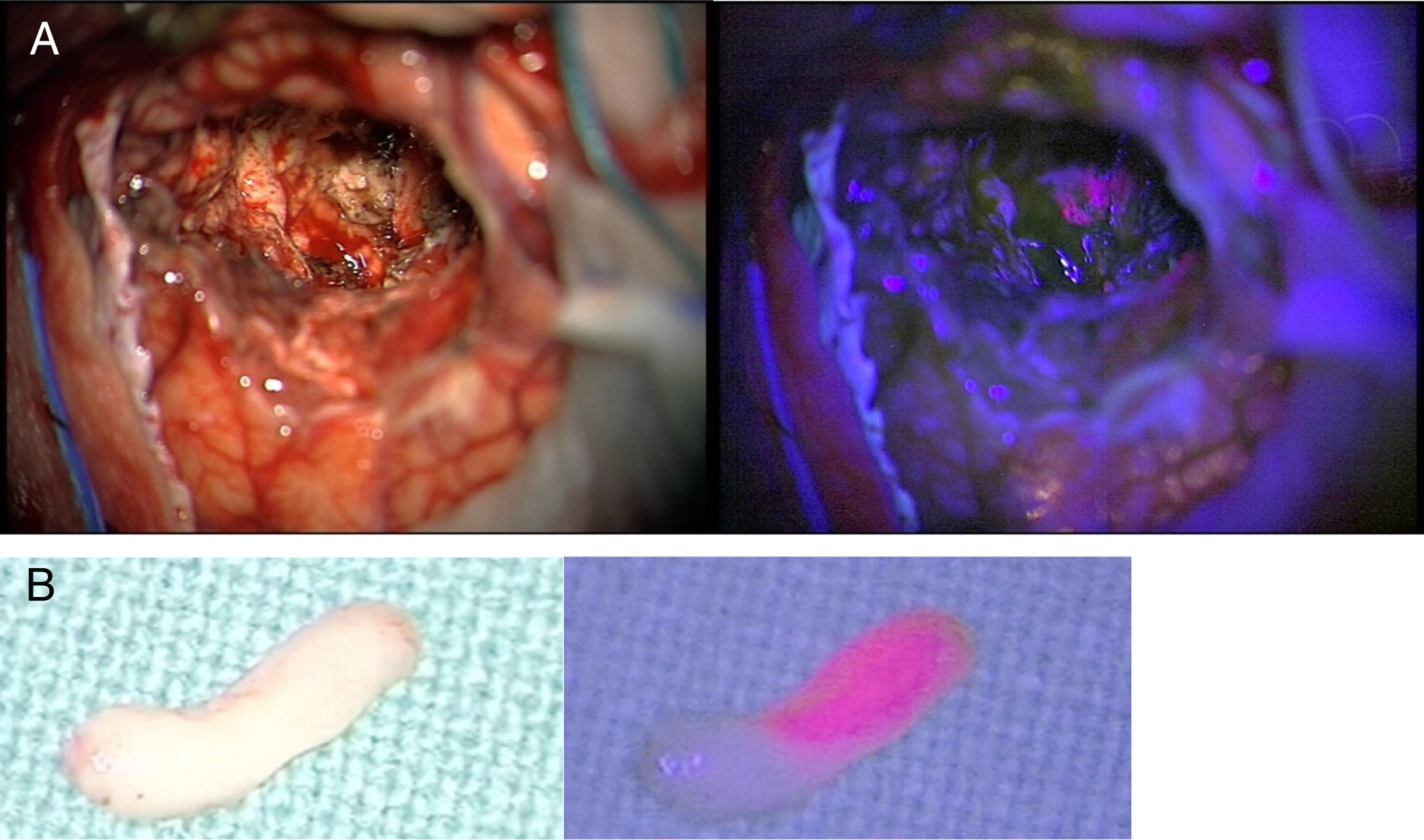
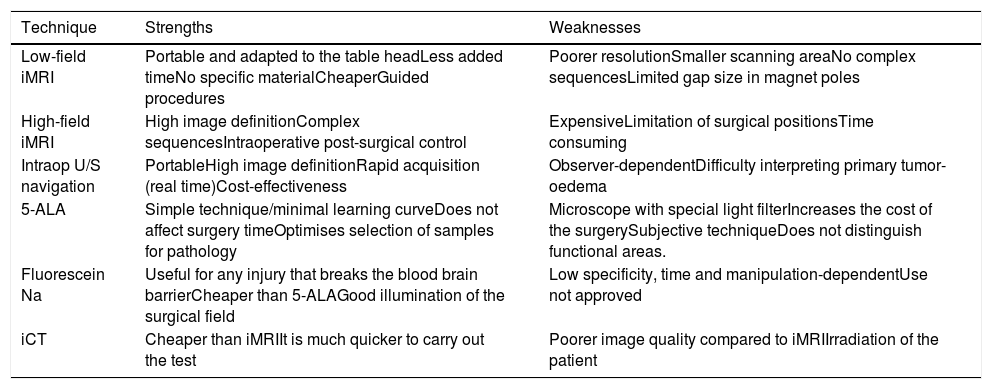
ResultsThe most robust intraoperative imaging technique appears to be low- and high-field magnetic resonance imaging, but this is the technique which results in the greatest expenditure. Intraoperative ultrasound navigation is portable and less expensive, but it provides poorer differentiation of high-grade tumours and is observer-dependent. The most-used fluorescence techniques are 5-aminolevulinic acid for high-grade gliomas and fluorescein, useful in lesions which rupture the blood-brain barrier. Last of all, intraoperative CT is more versatile in the neurosurgery operating theatre, but it has fewer indications in neuro-oncology surgery.
ConclusionsIntraoperative imaging techniques are used with increasingly greater frequency in brain tumour surgery, and the neurosurgeon should assess their possible use depending on their resources and the needs of each patient.
La cirugía de los tumores cerebrales se ha implementado en los últimos años con nuevas técnicas de imagen intraoperatoria, que tratan de mejorar la resección tumoral, aunque conllevan un aumento de recursos. Con el fin de hacer una actualización de este tema, se ha elaborado este manuscrito desde el grupo de tumores de la sociedad española de neurocirugía.
Material y MetodosSe ha propuesto a expertos en el uso de cada una de las técnicas intraoperatorias más empleadas en la cirugía de los tumores cerebrales, la descripción de la técnica y una breve revisión de la literatura. Se describirán indicaciones de uso, sus ventajas e inconvenientes basados en la experiencia clínica y en lo publicado en la literatura.
ResultadosLa técnica de imagen intraoperatoria más robusta sería la resonancia de bajo y alto campo, pero a su vez es la que supone un mayor gasto de recursos. La ecografía intraoperatoria navegada es portátil y tiene un menor coste, aunque discrimina peor los tumores de alto grado y es observador dependiente. Las técnicas de fluorescencia más empleadas son el 5-aminolevulínico para gliomas de alto grado y la fluoresceína, de utilidad en lesiones que rompen la barrera hematoencefálica. Por último, el TAC intraoperatorio es el más versátil en el quirófano de neurocirugía, pero tiene menos indicaciones en la cirugía neurooncológica.
ConclusionesLas técnicas de imagen intraoperatoria se emplean cada vez con más frecuencia en la cirugía de los tumores cerebrales, y el neurocirujano debe valorar su posible uso en función de sus recursos y las necesidades de cada paciente.
Article

If it is the first time you have accessed you can obtain your credentials by contacting Elsevier Spain in suscripciones@elsevier.com or by calling our Customer Service at902 88 87 40 if you are calling from Spain or at +34 932 418 800 (from 9 to 18h., GMT + 1) if you are calling outside of Spain.
If you already have your login data, please click here .
If you have forgotten your password you can you can recover it by clicking here and selecting the option ¿I have forgotten my password¿.