Despite the existence of published guidelines for more than a decade, there is still a substantial variation in the management of idiopathic normal pressure hydrocephalus due to its diagnostic and therapeutic complexity.
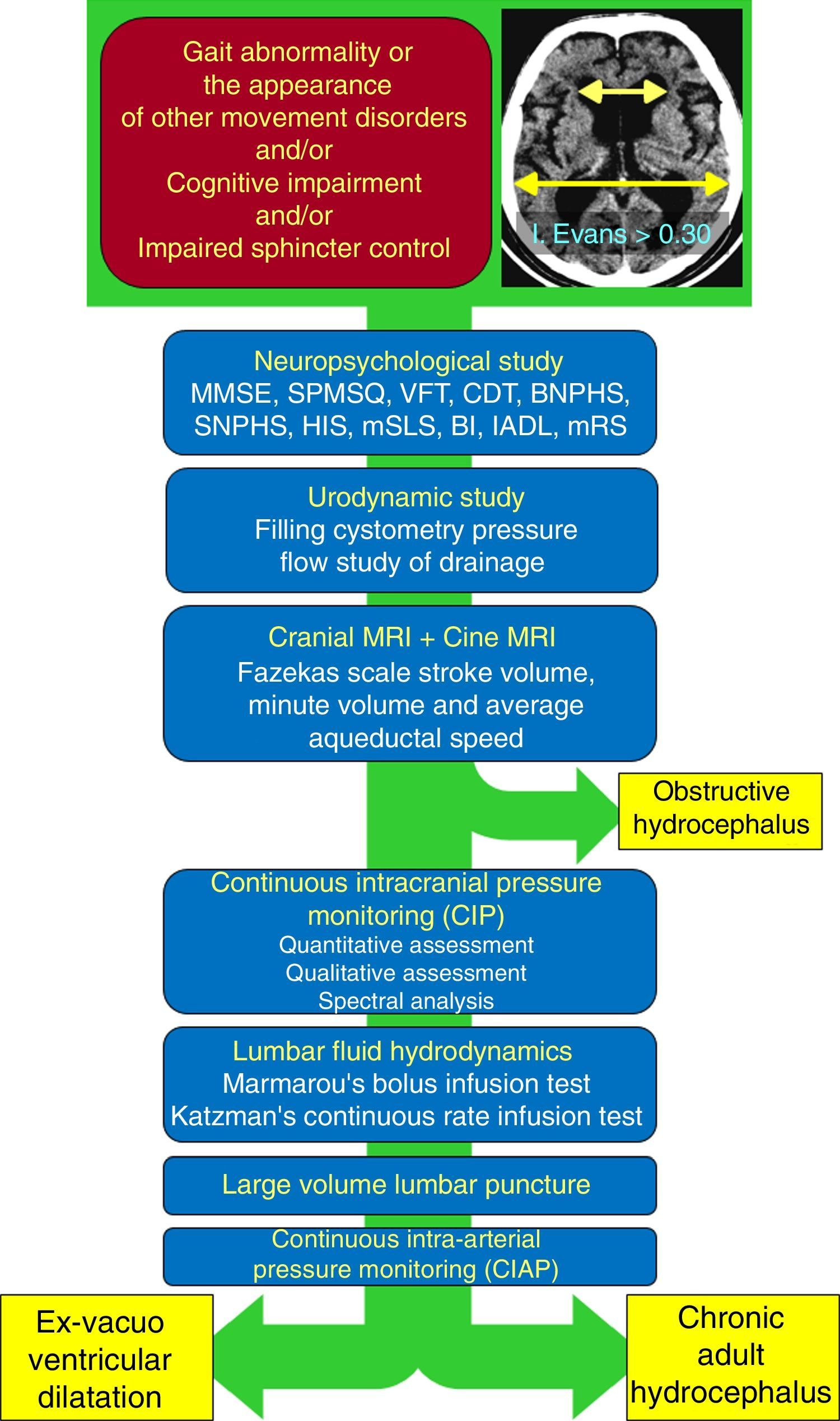
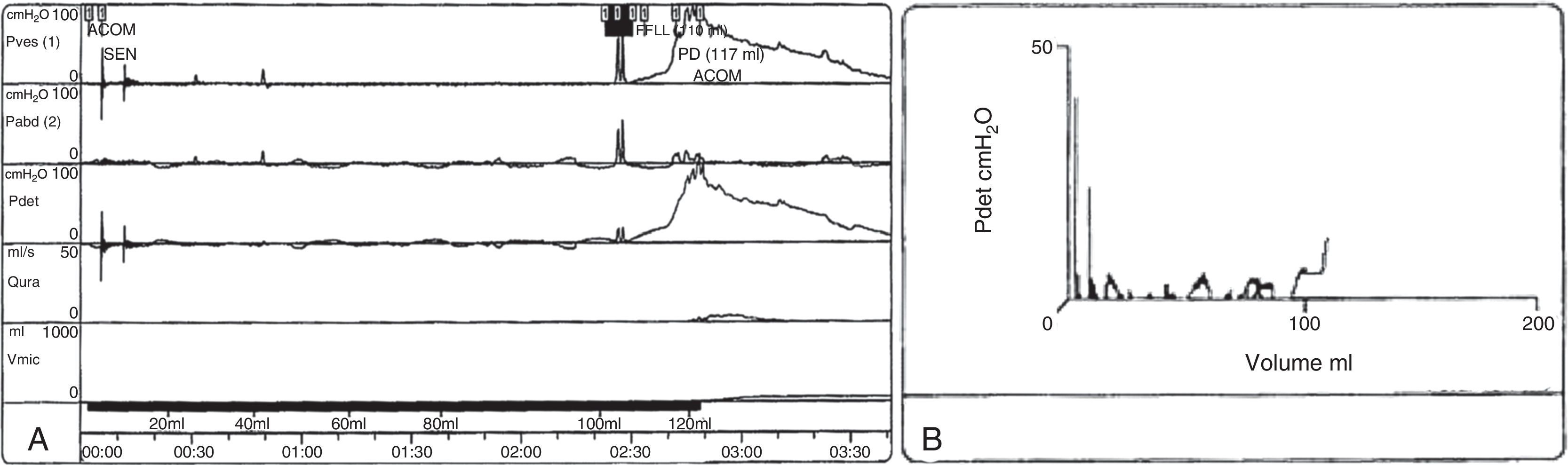
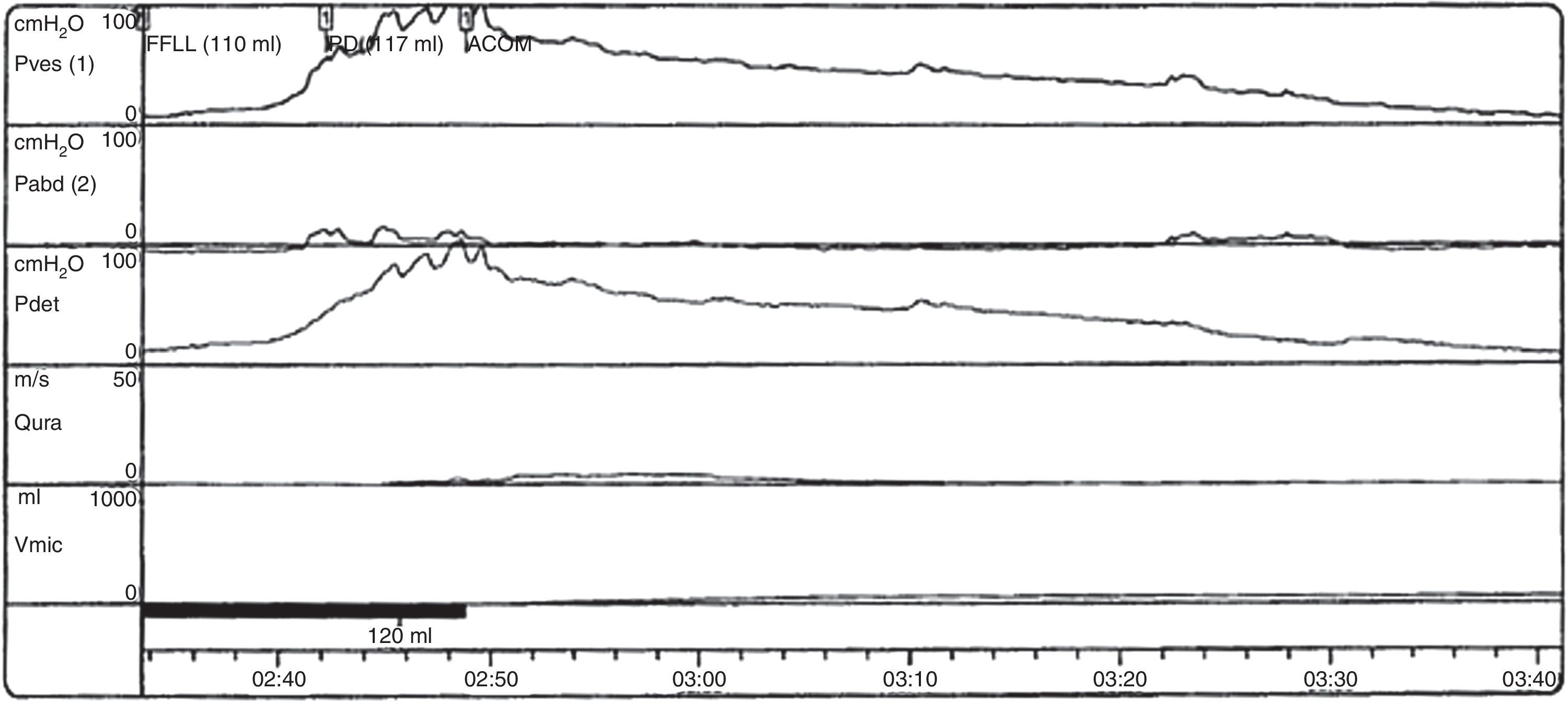
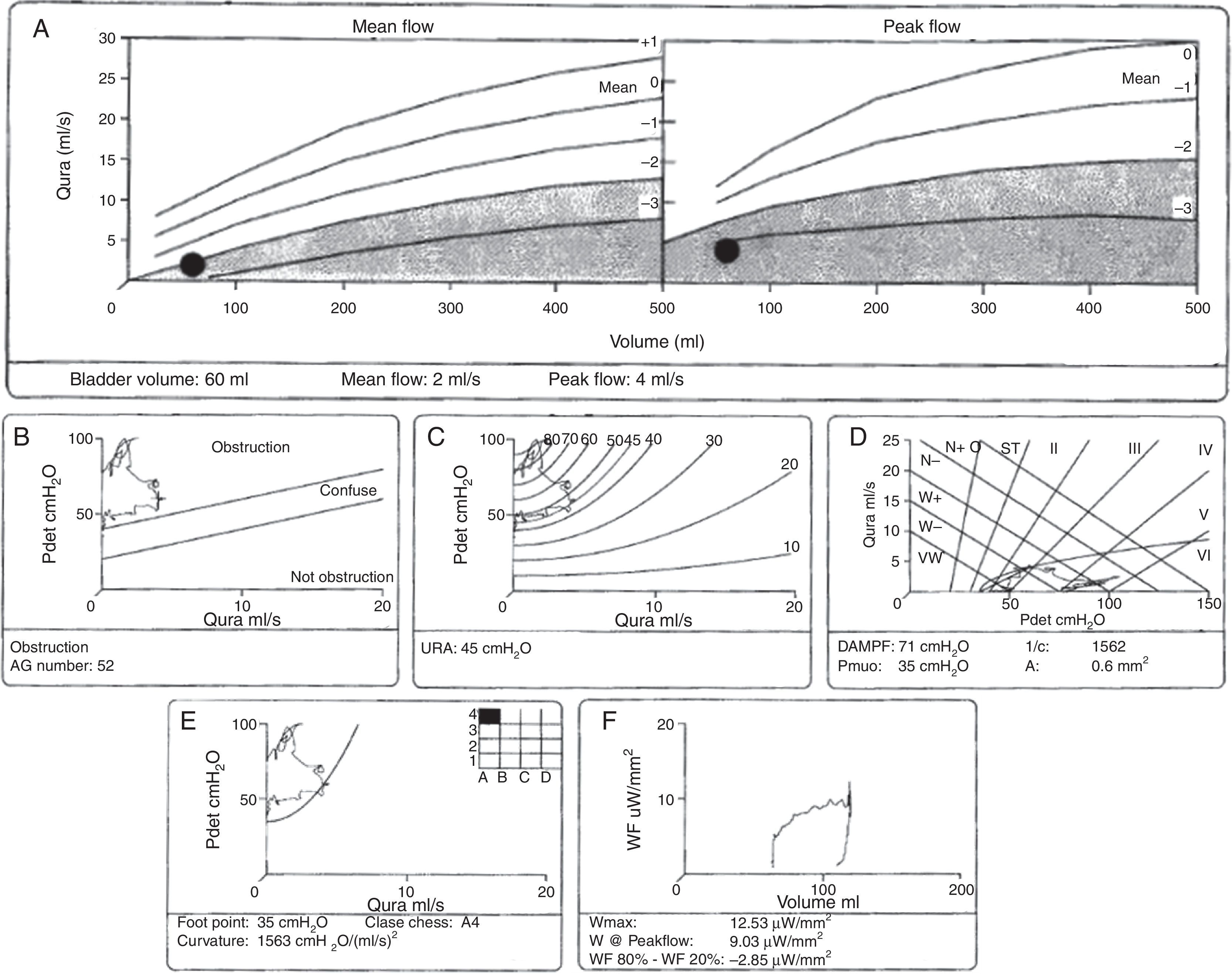
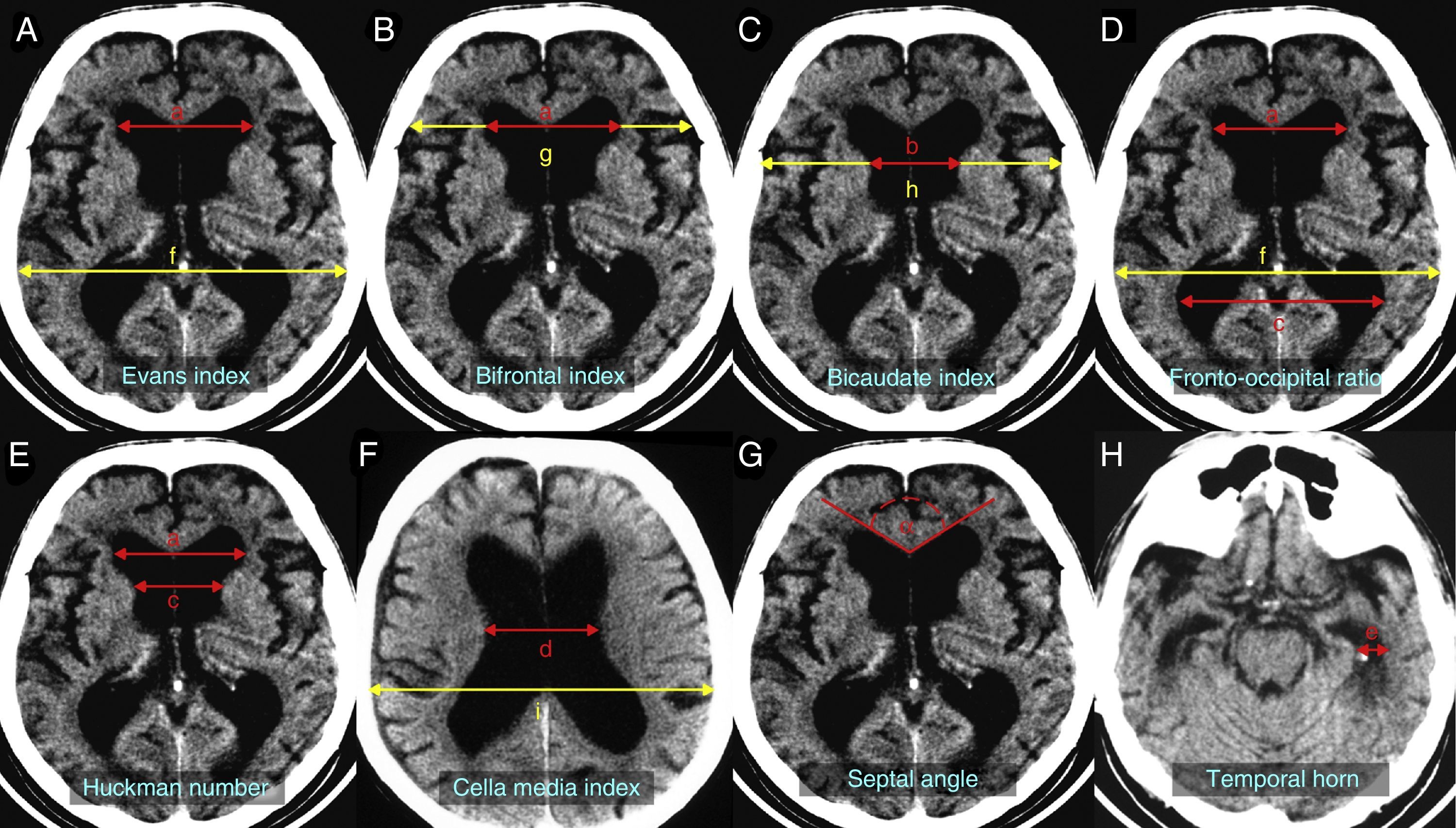
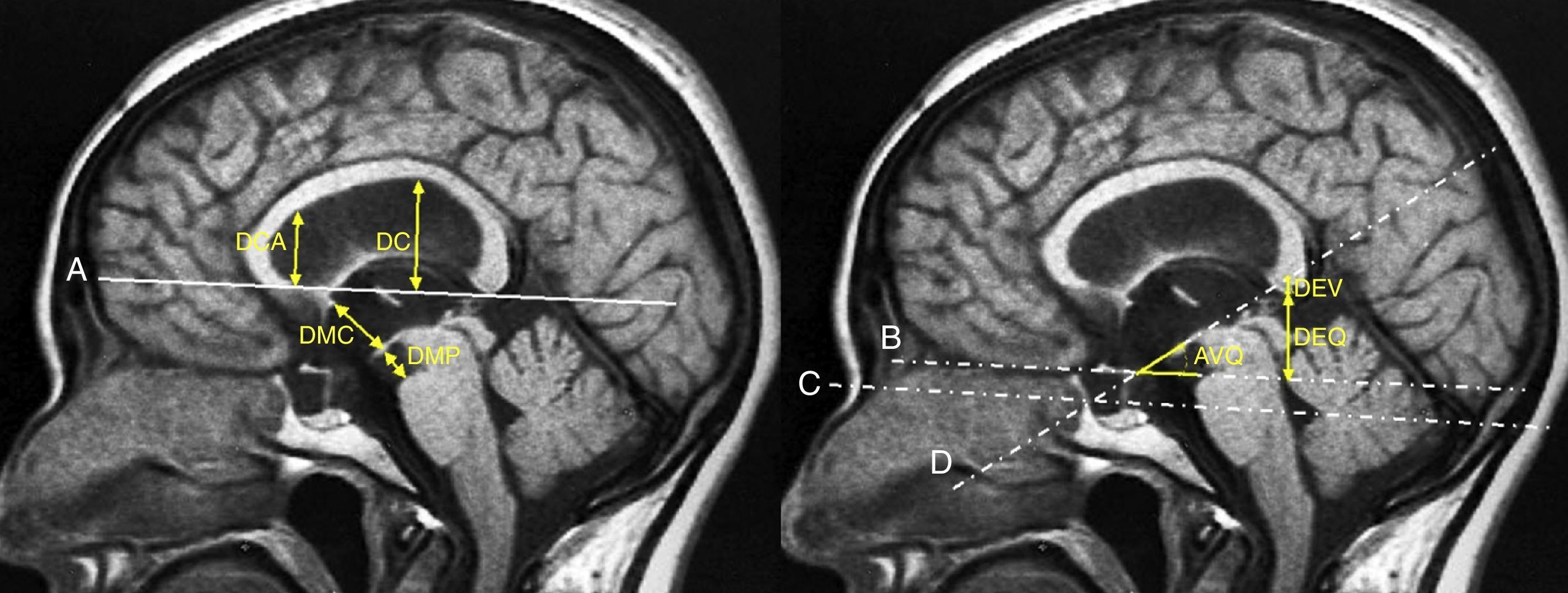
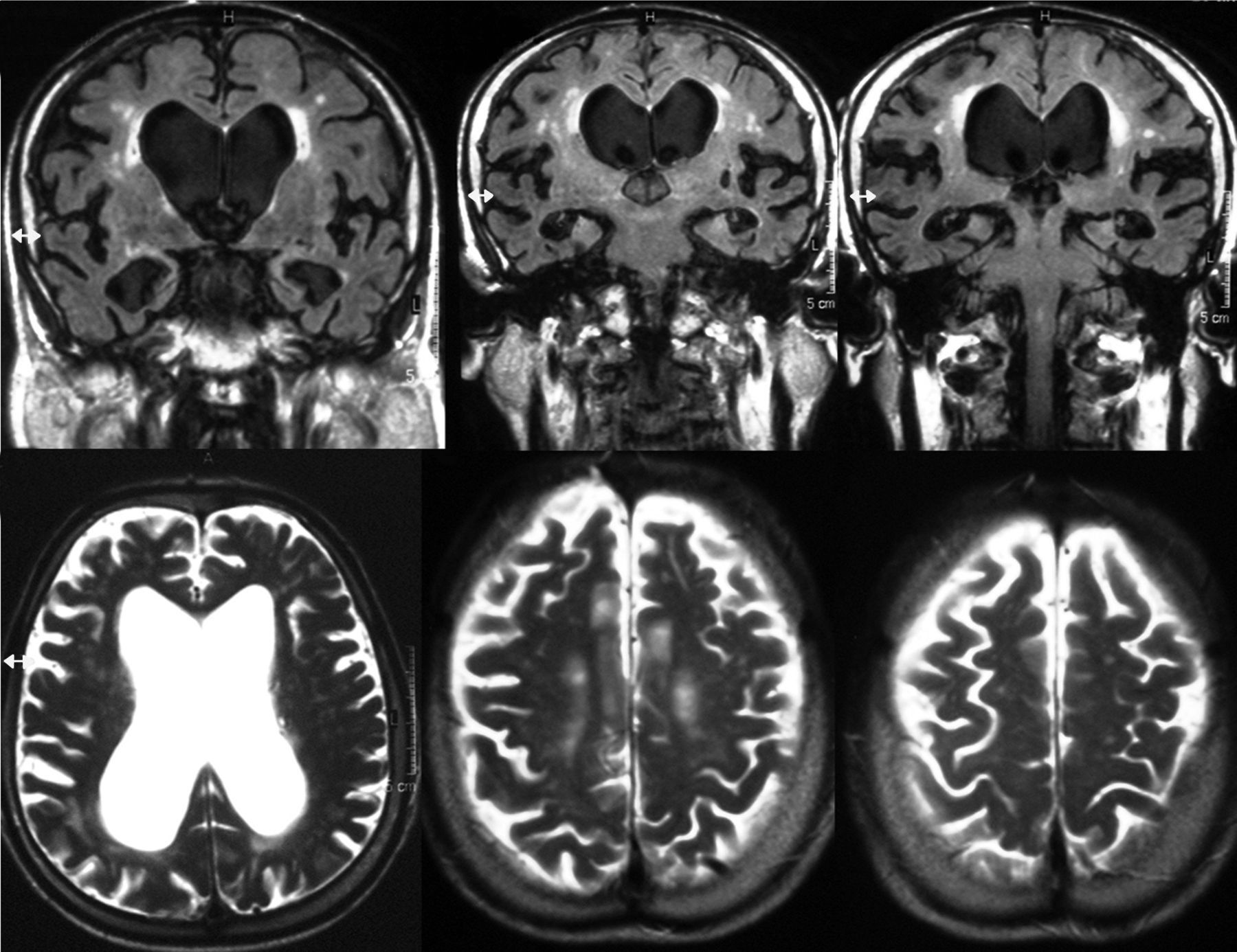
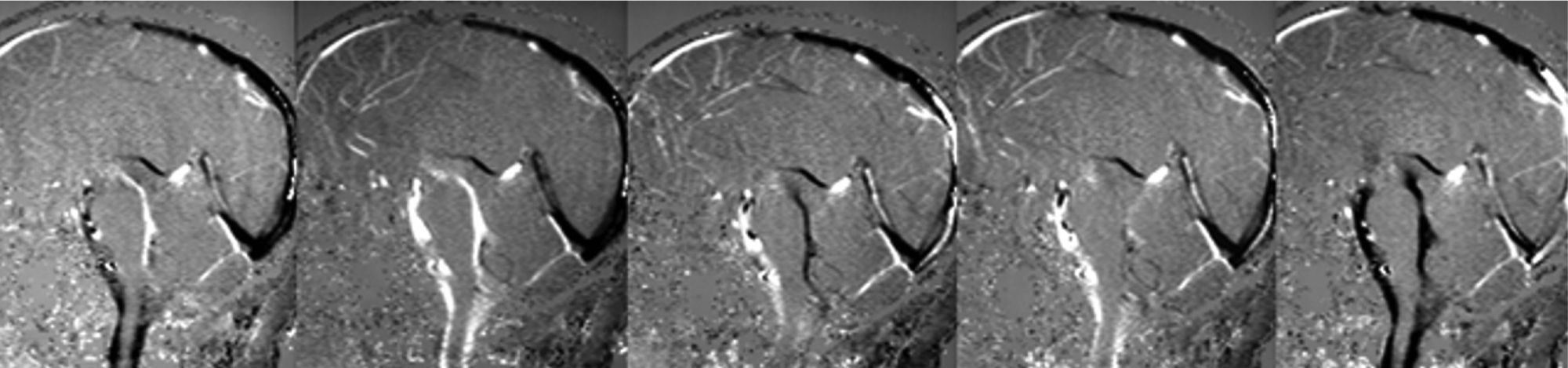
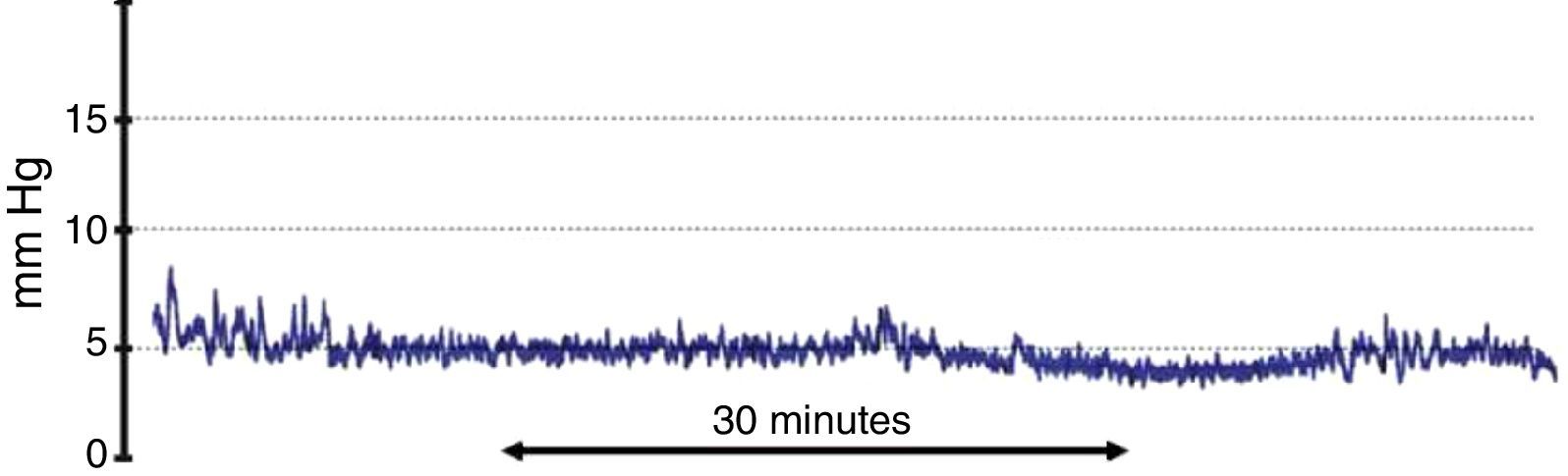
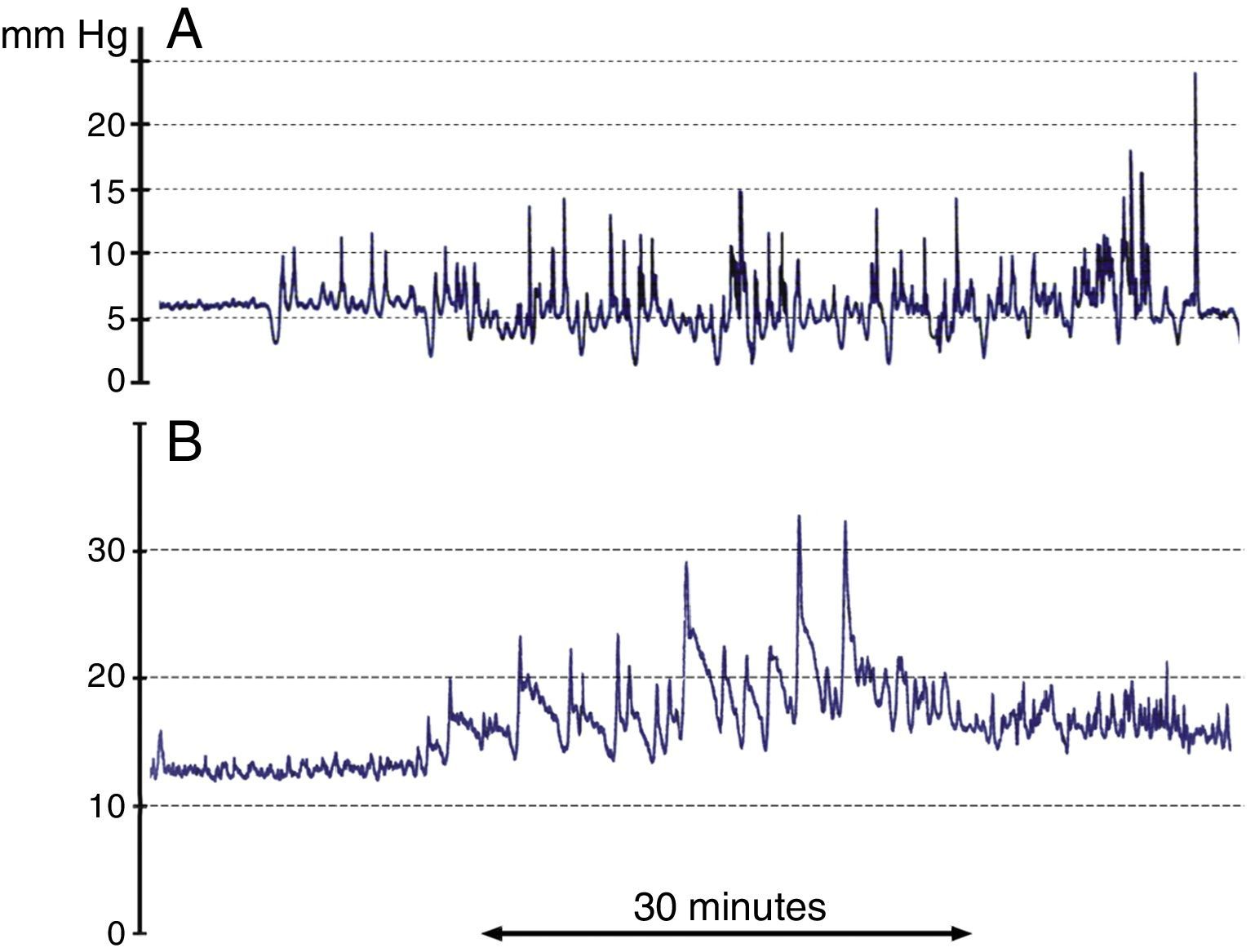
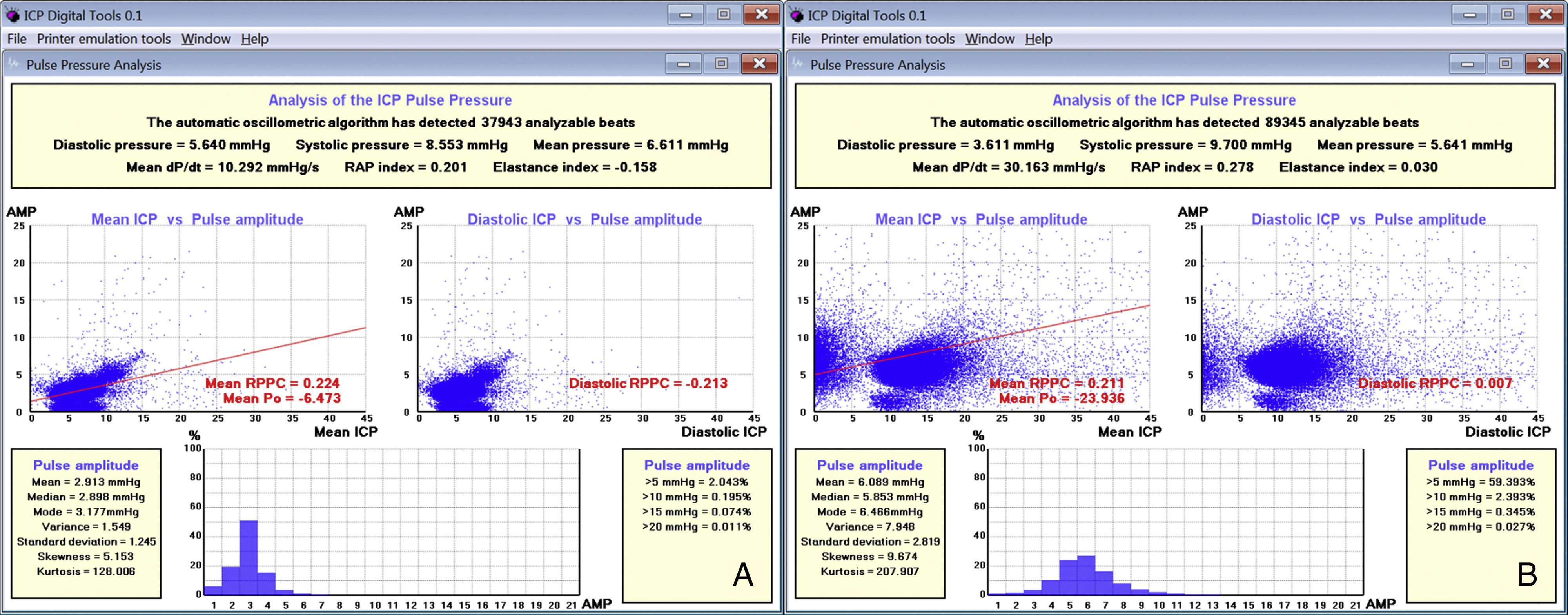
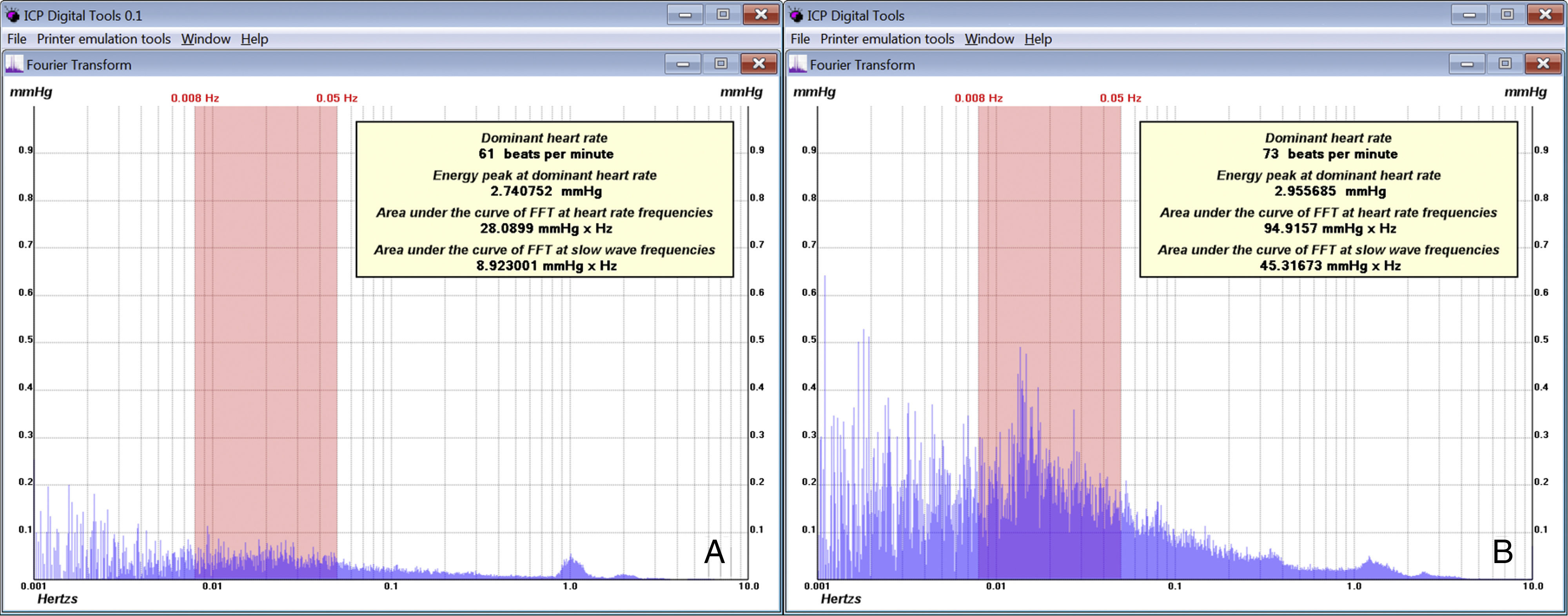
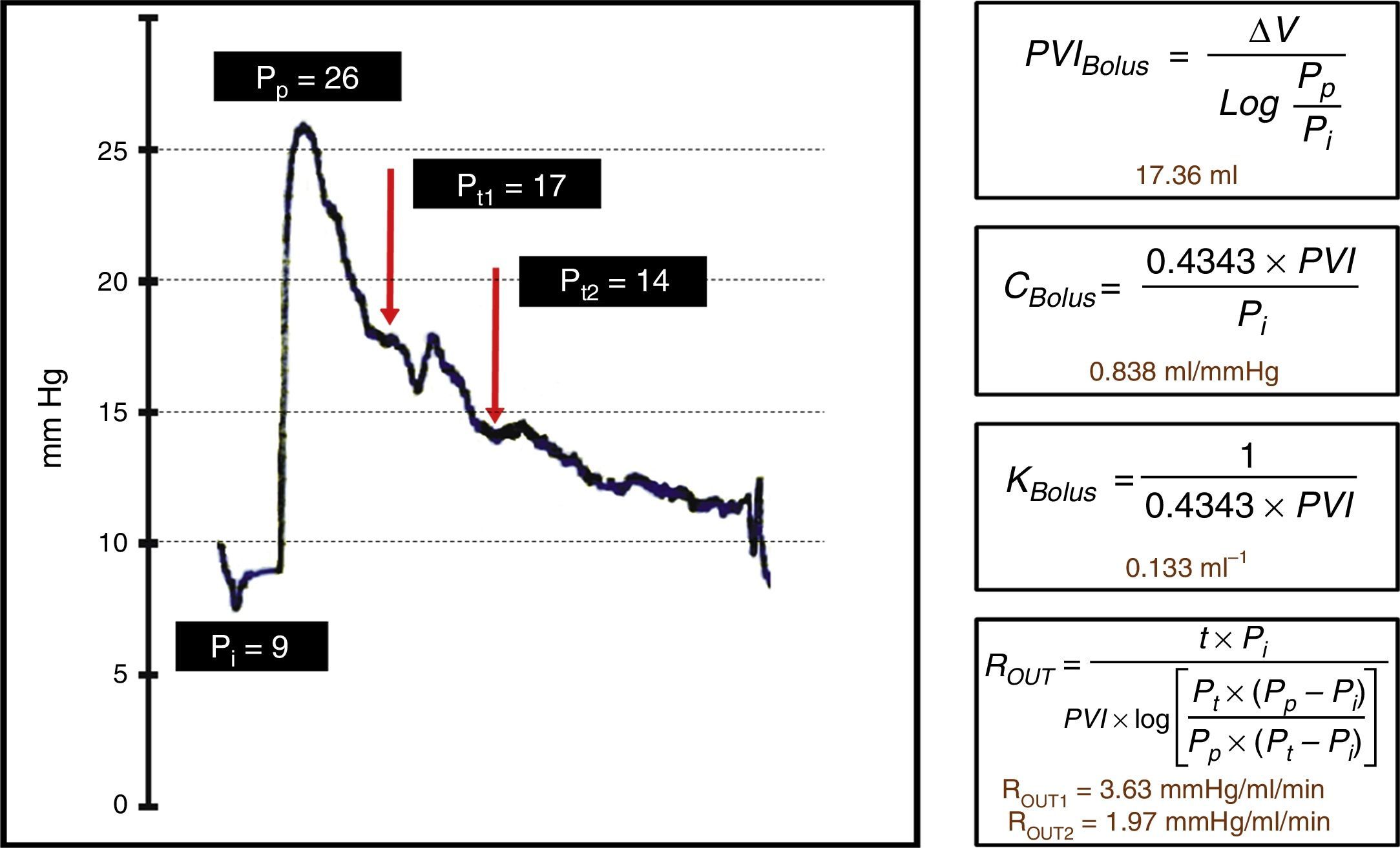
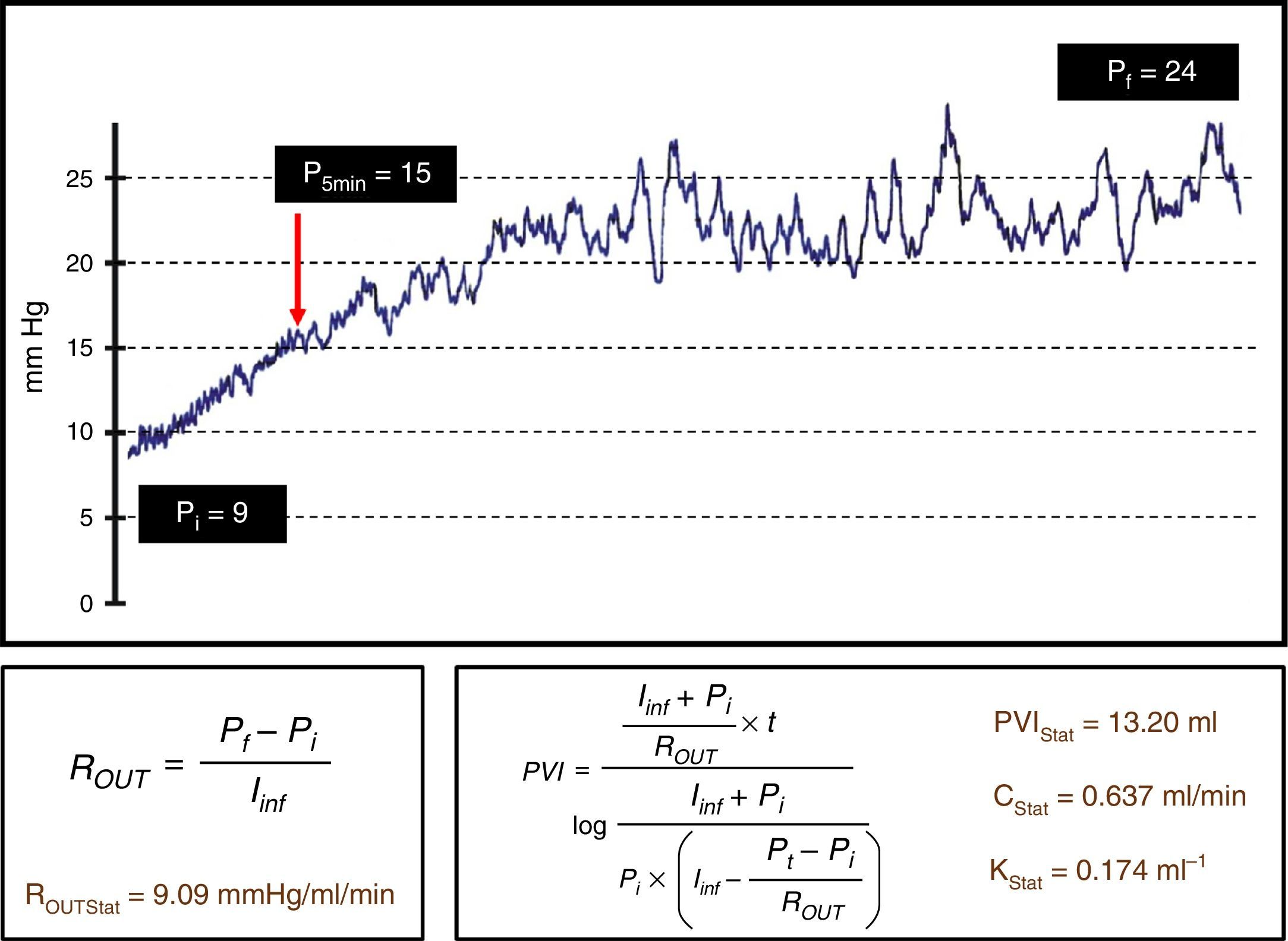
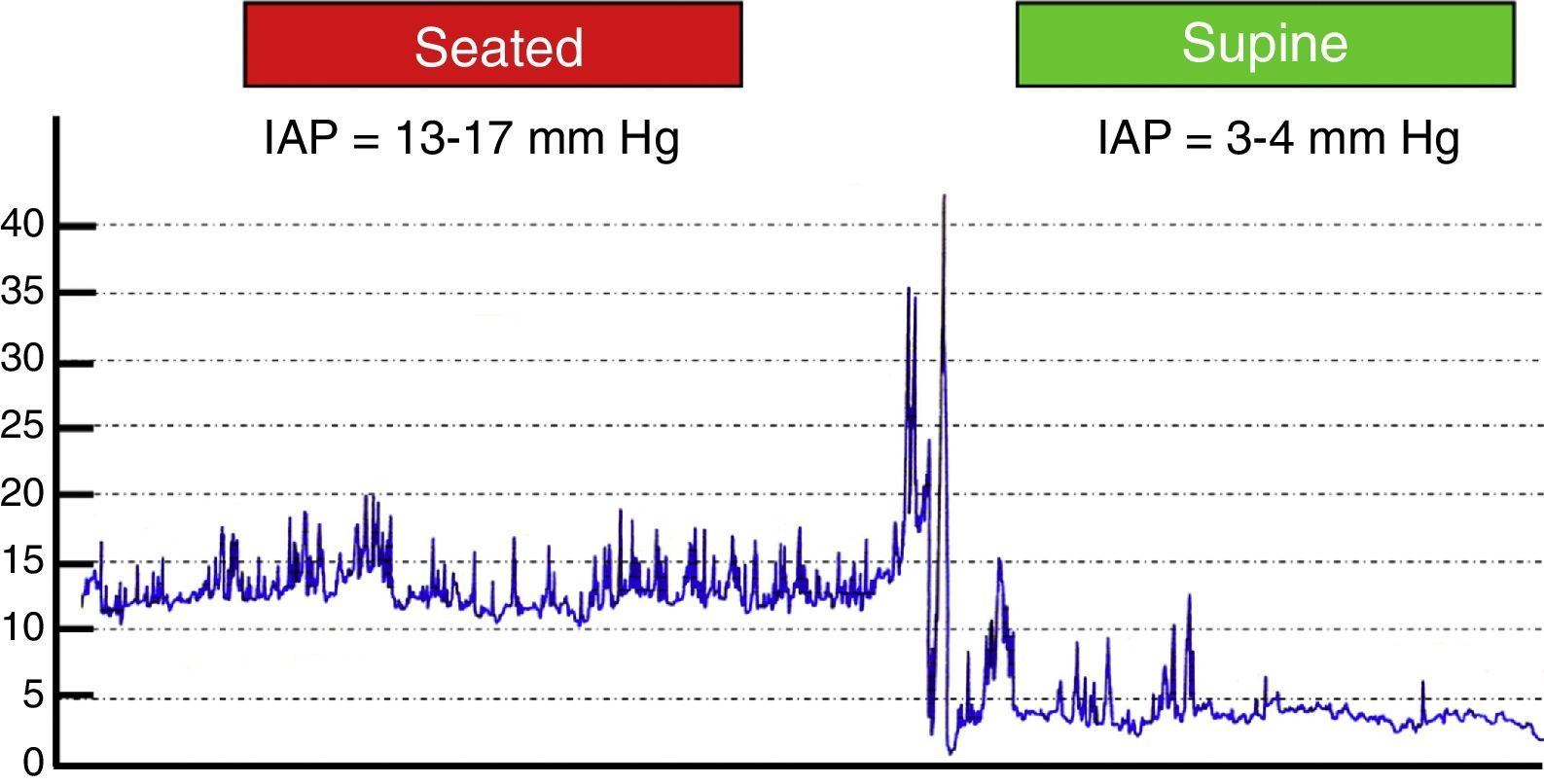
DevelopmentThe diagnostic and therapeutic protocol for the management of idiopathic normal pressure hydrocephalus in use at the Department of Neurosurgery of the University Hospital Marqués de Valdecilla is presented. The diagnostic process includes neuropsychological testing, phase contrast cine MRI, urodynamic evaluation, continuous intracranial pressure monitoring, cerebrospinal fluid hydrodynamics by means of lumbar infusion testing, and intra-abdominal pressure measurement. A patient is considered a surgical candidate if any of the following criteria is met: mean intracranial pressure >15mmHg, or B-waves present in >10% of overnight recording; pressure–volume index <15ml, or resistance to cerebrospinal fluid outflow (ROUT) >4.5mmHg/ml/min in bolus infusion test; ROUT >12mmHg/ml/min, intracranial pressure >22mmHg, or high amplitude B-waves in the steady-state of the continuous rate infusion test; or a clinical response to high-volume cerebrospinal fluid withdrawal.
ConclusionsThe implementation of a diagnostic and therapeutic protocol for idiopathic normal pressure hydrocephalus management could improve various aspects of patient care. It could reduce variability in clinical practice, optimise the use of health resources, and help in identifying scientific uncertainty areas, in order to direct research efforts in a more appropriate way.
A pesar de la existencia de guías clínicas desde hace más de una década, la complejidad diagnóstica y terapéutica de la hidrocefalia crónica del adulto idiopática hace que la variabilidad en su manejo sea elevada.
DesarrolloSe presenta el protocolo diagnóstico-terapéutico empleado en el Servicio de Neurocirugía del Hospital Universitario Marqués de Valdecilla para evaluar a los pacientes remitidos por sospecha diagnóstica de hidrocefalia crónica del adulto idiopática. El proceso diagnóstico incluye valoración neuropsicológica, RM craneal con secuencias de Cine-RM por contraste de fase, estudio urodinámico, registro continuo de presión intracraneal, hidrodinámica licuoral mediante test de infusión lumbar y medición de la presión intraabdominal. Se consideran candidatos quirúrgicos a los pacientes que cumplen cualquiera de los siguientes criterios: presión intracraneal media >15mmHg u ondas B en >10% del registro nocturno; índice presión-volumen <15ml o resistencia al drenaje del líquido cefalorraquídeo (ROUT) >4,5mmHg/ml/min en el test de bolos; ROUT >12mmHg/ml/min, presión intracraneal >22mmHg o presencia de ondas B de alta amplitud en la meseta del test de Katzman; o respuesta a la evacuación licuoral de alto volumen.
ConclusionesLa implementación de protocolos diagnóstico-terapéuticos podría mejorar varios aspectos del proceso asistencial de la hidrocefalia crónica del adulto idiopática, no solo al disminuir la variabilidad en la práctica clínica sino también al optimizar el uso de recursos sanitarios y ayudar a la identificación de áreas de incertidumbre científica, permitiendo dirigir los esfuerzos en investigación de una forma más adecuada.
Article

If it is the first time you have accessed you can obtain your credentials by contacting Elsevier Spain in suscripciones@elsevier.com or by calling our Customer Service at902 88 87 40 if you are calling from Spain or at +34 932 418 800 (from 9 to 18h., GMT + 1) if you are calling outside of Spain.
If you already have your login data, please click here .
If you have forgotten your password you can you can recover it by clicking here and selecting the option ¿I have forgotten my password¿.