To evaluate the incidence of significant intraoperative electrophysiological signal changes during surgical positioning, and to assess the effectiveness of head and neck repositioning on the restoration of signals, among patients undergoing surgery for cervical myelopathy.
Material and methodsWe used multimodal intraoperative monitoring (somatosensory [SEP] and motor evoked potentials [MEP] and spontaneous electromyography) before and after patients’ positioning in a consecutive cohort of 103 patients operated for symptomatic cervical myelopathy. Significant changes were defined as>50% attenuation in amplitude or>10% increase in latency of SEP, or abolishment or 50–80% attenuation of MEP.
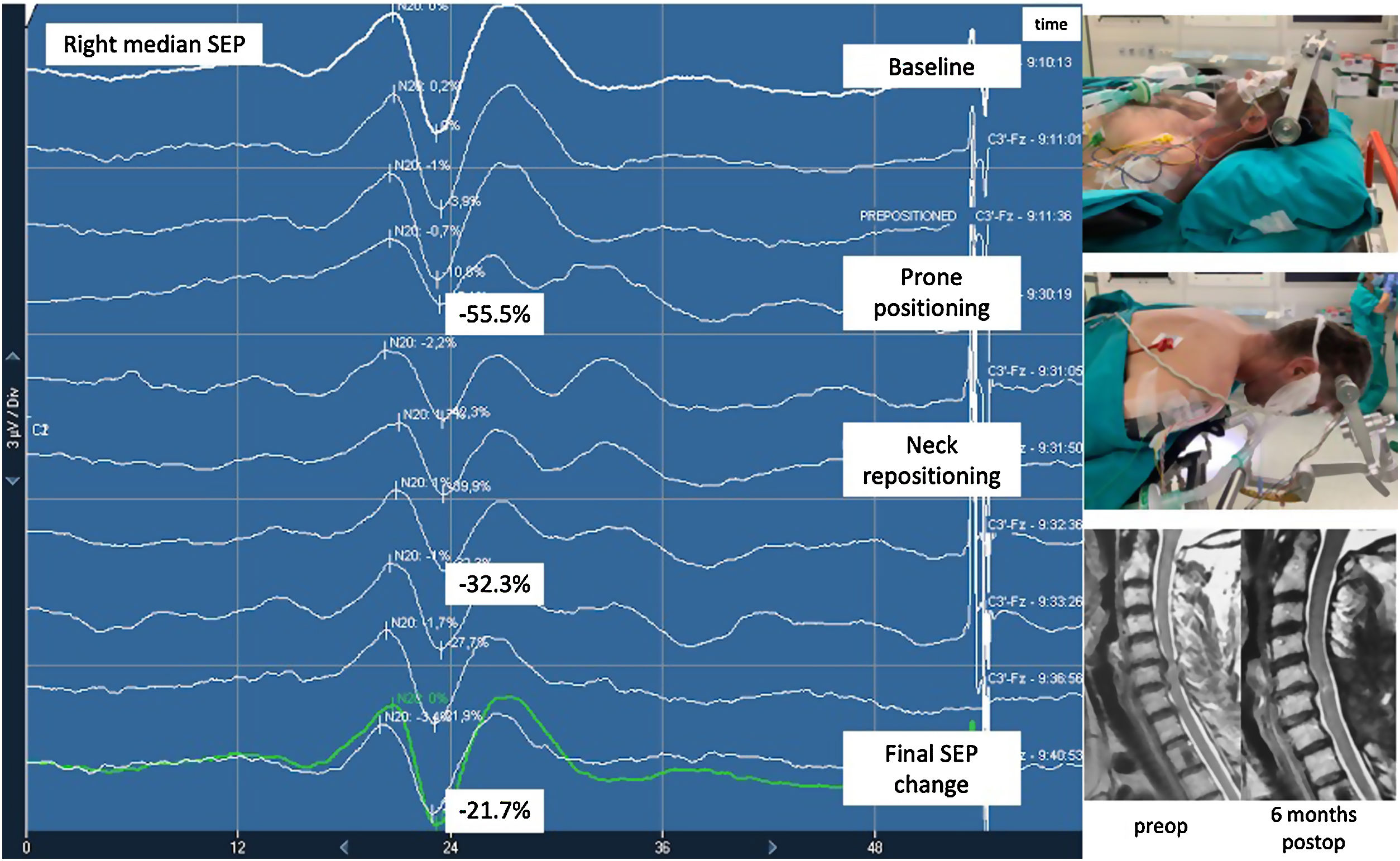
ResultsOut of 103 patients (34.9% female, median age 54.5 years) 88 underwent laminectomy (85.4%) and 15 (14.6%) anterior approach. At the time of positioning, signal alterations occurred in 44 patients (42.7%), yet only 11 patients (10.7%) showed alarming changes. Immediate neck repositioning of these resulted in complete (n=6) or partial (n=4) restoration of potentials, yielding no postoperative deficits. The patient in which signals could not be restored after repositioning resulted in added postoperative deficit. The accuracy (true positives plus true negatives) of monitoring to detect new neurological deficits was 99.0% (102/103) for the entire cohort, and 100% (11/11) for those showing significant changes at the moment of positioning. Overall, only 1 patient, with non-significant SEP attenuation, experienced a new postoperative deficit, yielding a 0.97% rate of false negatives.
ConclusionAmong patients undergoing surgery for cervical myelopathy, 10.7% showed alarming electrophysiological signal changes at the time of positioning. Immediate repositioning of the neck resulted in near always restoration of potentials and avoidance of added neurological damage. Complete or partial restoration of potentials after repositioning yielded no postoperative deficits.
Evaluar la incidencia de alteraciones neurofisiológicas intraoperatorias graves en el momento del posicionamiento del paciente, y la efectividad de la recolocación del cuello para revertir dichos cambios en los pacientes que se intervienen de mielopatía cervical.
Material y métodosSe empleó una monitorización intraoperatoria multimodal (potenciales evocados sensoriales [PES], motores [PEM] y electromiografía) antes y después de colocar al paciente en posición, en una cohorte de 103 pacientes consecutivos operados de mielopatía cervical. Se consideraron cambios significativos (de alarma): una disminución >50% de la amplitud o un aumento >10% de la latencia de los PES, o la abolición o disminución >50-80% en amplitud de los PEM.
ResultadosDe los 103 pacientes (el 34,9% mujeres, mediana de edad: 54,5 años), a 88 se les realizó laminectomía (85,4%) y a 15 (14,6%) un abordaje anterior. En el momento del posicionamiento, ocurrieron alteraciones de señal en 44 pacientes (42,7%), aunque solo en 11 (10,7%) estas fueron significativas. La recolocación inmediata del cuello consiguió revertir la alteración de señal completa (n=6) o parcialmente (n=4), sin producirse déficits postoperatorios. El paciente en el cual la recolocación no consiguió restaurar los potenciales despertó con déficit neurológico añadido. La precisión (verdaderos positivos+verdaderos negativos) de la monitorización intraoperatoria para detectar déficits postoperatorios fue del 99% (102/103) para la cohorte completa y del 100% (11/11) para el subgrupo con alteraciones significativas. Globalmente, solo un paciente, que mostró cambios no significativos, despertó con nuevo déficit neurológico (0,97% de falsos negativos).
ConclusiónEl 10,7% de los pacientes intervenidos de mielopatía cervical mostraron cambios neurofisiológicos de alarma en el momento del posicionamiento quirúrgico. La inmediata recolocación del cuello revirtió dichos cambios (completa o parcialmente) en prácticamente todos los casos, sin producirse déficits neurológicos posquirúrgicos.
Article

If it is the first time you have accessed you can obtain your credentials by contacting Elsevier Spain in suscripciones@elsevier.com or by calling our Customer Service at902 88 87 40 if you are calling from Spain or at +34 932 418 800 (from 9 to 18h., GMT + 1) if you are calling outside of Spain.
If you already have your login data, please click here .
If you have forgotten your password you can you can recover it by clicking here and selecting the option ¿I have forgotten my password¿.