A series of 18 patients with symptomatic synovial cysts was analysed from May 2009 to November 2013. Different approaches were performed for their removal.
Material and methodsThe study included 18 patients, 8 men and 10 women, aged between 50 and 77 years. An analysis was made of the variables including age, gender, symptoms, imaging studies, histopathology, surgery, follow-up, complications, and clinical outcome.
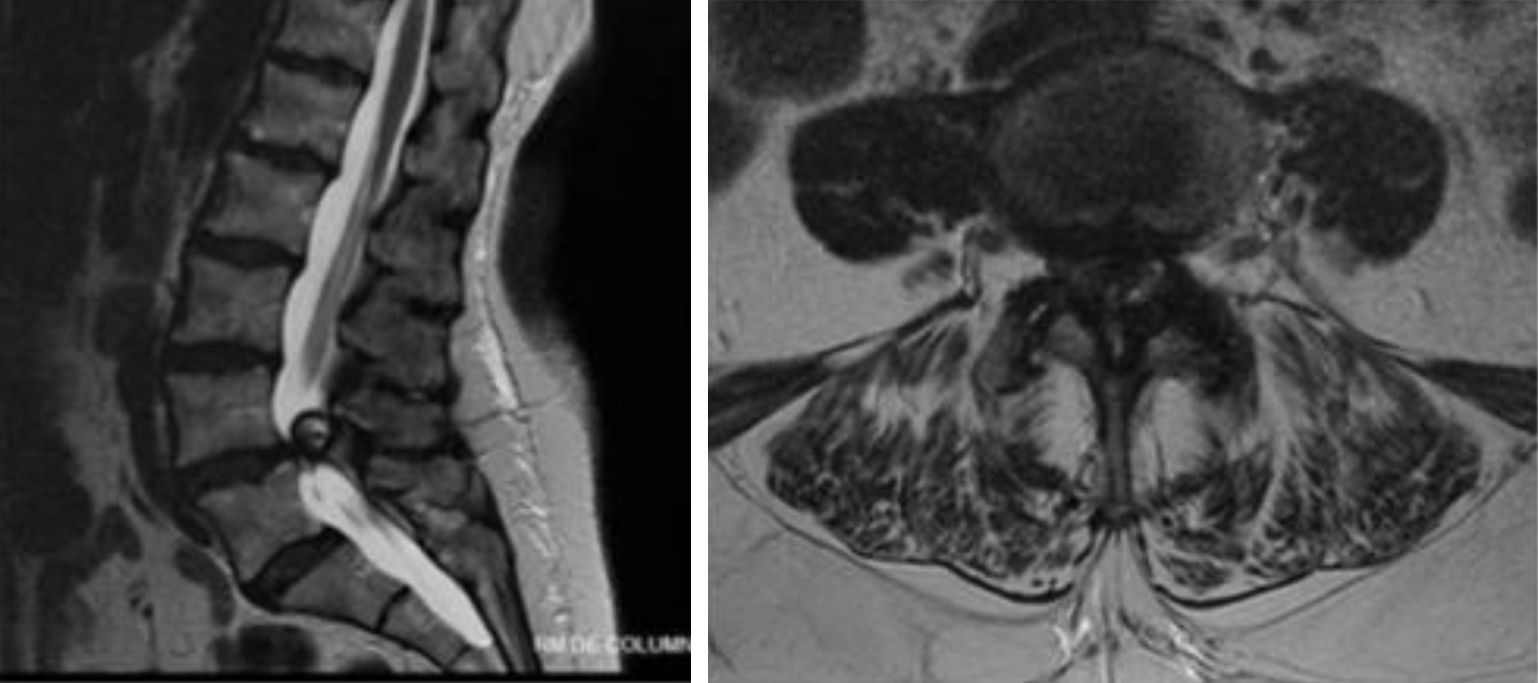
ResultsAn articular synovial cyst was diagnosed in 17 cases, and a ganglion in one cases. The most common symptom was back pain with radiculopathy (94%). Motor deficits occurred in 4 cases (22%), and 1 case (5%) presented with urinary incontinence. The most common level was L4-L5 (67%), with one atypical case observed in the D12-L1 location. Hemi-laminectomy was performed in 14 cases, with 9 of them having an interspinous spacer (ISP) device inserted. A laminectomy with a fusion procedure was performed in 3 patients and 1 patient had a bilateral decompression using a unilateral approach. The patients were followed-up for between 6 months to 2 years.
ConclusionsSynovial cysts are a cause of radiculopathy/neurogenic claudication. Spinal cysts are commonly found at the L4-L5 level. MRI is the tool of choice for diagnosis. The most common symptom was back pain with radiculopathy. Synovial cysts resistant to conservative therapy should be treated surgically. In our series, surgical resection of symptomatic juxtafacet cysts showed a good clinical outcome, but the optimal approach for patients with juxtafacet cysts remains unclear.
Se realiza un análisis retrospectivo a partir de una serie de 18 casos con quistes articulares sintomáticos, tratados quirúrgicamente mediante distintos abordajes para su extirpación desde mayo del 2009 hasta noviembre del 2013. Se muestran los resultados obtenidos con cada uno de los abordajes a medio y largo plazo.
Material y métodosSe incluye a 18 pacientes, 8 varones y 10 mujeres, de entre 50 y los 77 años. Se recogen de cada uno de ellos los síntomas, antecedentes, estudios por imagen, histopatología, intervención quirúrgica, seguimiento, complicaciones y resultados.
ResultadosDiecisiete casos fueron diagnosticados de quiste articular sinovial y un tuvo como resultado ganglión. El síntoma más común es la lumbalgia con radiculopatía (94%). La pérdida de fuerza se registró en 4 casos (22%) y un caso (1%) se acompañó de alteración de esfínteres. El nivel más frecuente fue L4-L5 (67%). Recogimos un caso en locación atípica D12-L1. Se practicó una descompresión unilateral del canal en 14 casos mediante hemilaminectomía, colocándose en 9 de ellos dispositivo interespinoso; en 3 casos se realizó laminectomía y artrodesis, y en uno solo se realizó un abordaje unilateral con descompresión bilateral del canal. Todos ellos tuvieron un seguimiento mínimo de 6 meses y máximo de 2 años.
ConclusionesLos quistes articulares son una causa de radiculopatía/claudicación neurógena. La localización más frecuente es el nivel L4-L5 y la forma más frecuente de presentación la lumbalgia con radiculopatía. La resonancia magnética lumbar es la prueba de elección para su diagnóstico. Los quistes articulares refractarios a tratamiento conservador serían subsidiarios de cirugía. En nuestra serie, la extirpación quirúrgica del quiste muestra un buen resultado clínico a medio-largo plazo, si bien la heterogeneidad del grupo y el número de casos no permiten escoger un abordaje óptimo para su resolución. El mejor abordaje quirúrgico para el tratamiento de los quistes articulares sigue siendo controvertido.
Article

If it is the first time you have accessed you can obtain your credentials by contacting Elsevier Spain in suscripciones@elsevier.com or by calling our Customer Service at902 88 87 40 if you are calling from Spain or at +34 932 418 800 (from 9 to 18h., GMT + 1) if you are calling outside of Spain.
If you already have your login data, please click here .
If you have forgotten your password you can you can recover it by clicking here and selecting the option ¿I have forgotten my password¿.