Optic nerve sheath diameter (ONSD) ultrasound has proven to be a useful tool for the detection of intracranial hypertension (IH). The DVNO values, in patients with cessation of cerebral blood flow (CCBF), has not been clarified yet.
ObjectiveEstablish an association between DVNO and CFSC in neurocritical patients admitted to an ICU.
Patients and methodsCross-sectional study of patients admitted in a third level ICU, between April 2017 and April 2018, with neurological pathology. ONSD ultrasound was performed in the first 24 h and as the patient was diagnosed of CCBF. The ONSD values of patients with and without diagnosis of CCBF were compared.
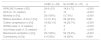
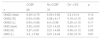
Results99 patients were included, 29 of whom showed CCBF in transcranial Doppler. The ONSD measurement did not demonstrate significant differences between both groups, 65.94 ± 7.55 in the group with CCBF and 63.88 ± 5.56 in the group without CCBF, p = 0.14.
ConclusionIn our study, ONSD values capable of recognizing CCBF were not identified.
La ecografía del diámetro de la vaina del nervio óptico (DVNO), ha demostrado ser una herramienta útil para la detección de hipertensión intracraneal (HIC). Los valors del DVNO en pacientes con cese del flujo sanguíneo cerebral (CFSC), todavía no han sido definidos.
ObjetivoEstablecer asociación entre el DVNO y el CFSC en pacientes neurocríticos ingresados en una UCI.
Pacientes y métodosEstudio transversal de pacientes ingresados en una UCI polivalente de tercer nivel, con patología neurológica, entre abril de 2017 y abril de 2018. Se incluyeron en el estudio pacientes neurocríticos con alteraciones clínico radiológicas. Se realizó una ecografía del DVNO en las primeras 24 h de ingreso, que se repitió en aquellos pacientes con evolución a CFSC, establecido mediante Doppler transcraneal. Se compararon los valorares de DVNO de los pacientes con y sin diagnóstico de CFSC.
ResultadosSe incluyeron 99 pacientes de los cuales 29 mostraron CFSC por Doppler transcraneal. La medición del DVNO no mostró diferencias significativas entre ambos grupos, 6,59 ± 0,75 en el grupo con CSFC y 6,39 ± 0,56 en el grupo sin CSFC, p = 0.141.
ConclusiónEn nuestro estudio, no se identificaron valores de DVNO capaces de diagnosticar el CFSC.
Article

If it is the first time you have accessed you can obtain your credentials by contacting Elsevier Spain in suscripciones@elsevier.com or by calling our Customer Service at902 88 87 40 if you are calling from Spain or at +34 932 418 800 (from 9 to 18h., GMT + 1) if you are calling outside of Spain.
If you already have your login data, please click here .
If you have forgotten your password you can you can recover it by clicking here and selecting the option ¿I have forgotten my password¿.