To use third ventricle morphometric variables as a tool for the selection of patients with idiopathic normal pressure hydrocephalus (iNPH) who are candidates for ventriculoperitoneal shunts (VPS).
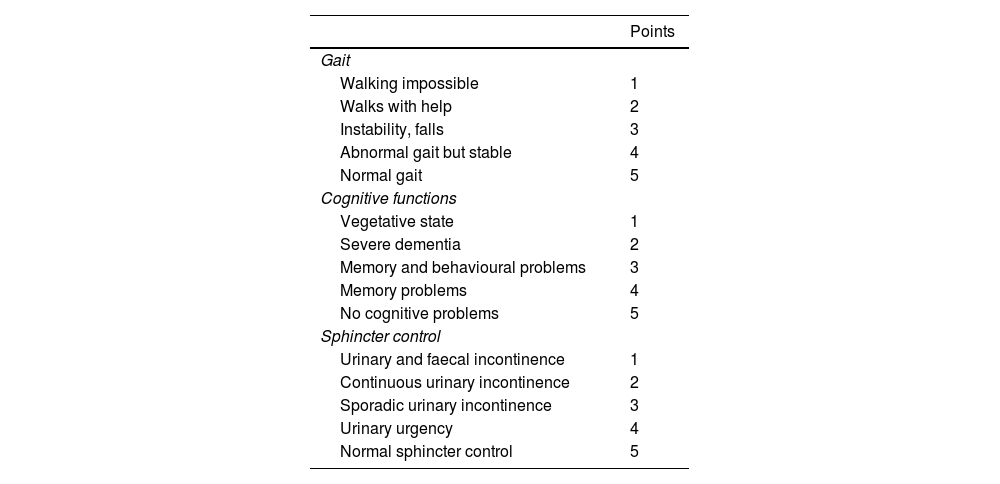
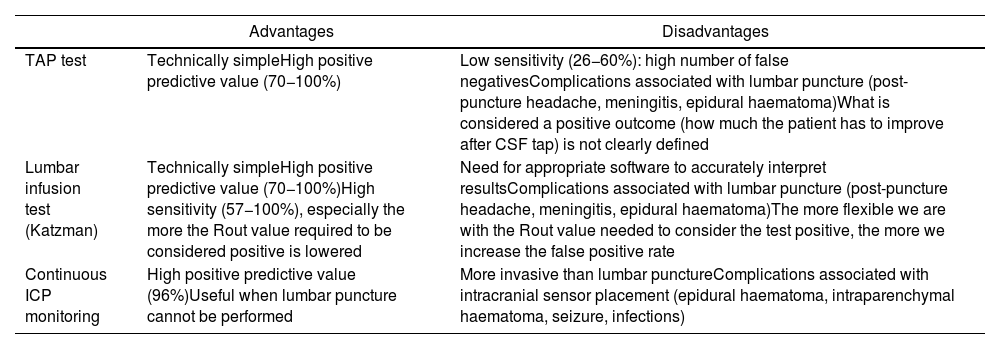
Material and methodsRetrospective study enrolling patients with iNPH. Katzman infusion test was performed and a Rout > 12 mmHg/mL/min was considered a positive result. The transverse diameter and the volume of the third ventricle were measured in the preoperative MRI. Postoperative improvement was assessed with the NPH score. The results were analysed with SPSS software.
Results52 patients with a mean age of 76 years were analysed. There was no difference in the diameter of the third ventricle among patients with a positive result and those with a negative result in the infusion test (12.28 vs 11.68 mm; p = 0.14). Neither were difference detected in the ventricle volume of both groups (3.6 vs 3.5cc; p = 0.66). Those patients who improved after VPS had a smaller third ventricle compared to those who did not respond after surgery (11.85 mm vs. 12.96 mm; p = 0.009). Diameter and volume of third ventricle present a significant strong correlation (Pearson correlation coefficient = 0.72; p < 0.0001).
ConclusionMorphometric variables of third ventricle may be useful in predicting a good response to VPS in patients with idiopathic normal pressure hydrocephalus.
Utilizar parámetros relacionados con el tamaño del tercer ventrículo como herramienta para la selección de pacientes con hidrocefalia a presión normal idiopática (HPNi) candidatos a derivación ventrículoperitoneal (DVP).
Material y métodosEstudio retrospectivo basado en una serie de pacientes con sospecha de HPNi. Se les realizó un test de infusión de Katzman y se consideró resultado positivo una Rout >12 mmHg/mL/min. En todos ellos se midió el diámetro transverso y el volumen del tercer ventrículo en la resonancia prequirúrgica. Se valoró el grado de mejoría postoperatoria utilizando la escala NPH. Los datos fueron analizados con el programa SPSS.
ResultadosSe analizaron un total de 52 pacientes con una edad media de 76 años. No hubo diferencias en el diámetro del tercer ventrículo entre los pacientes con resultado positivo y aquellos con resultado negativo en el test de infusión (12,28 vs 11,68 mm; p = 0,14). Tampoco se detectaron diferencias en el volumen ventricular de ambos grupos (3,6 vs 3,5cc; p = 0,66). Aquellos pacientes que mejoraron tras la DVP presentaban un tercer ventrículo de menor tamaño en comparación con los que no obtuvieron respuesta tras la cirugía (11,85 mm vs. 12,96 mm; p = 0,009). El diámetro y el volumen del tercer ventrículo presentan una correlación fuerte significativa (coeficiente de Pearson = 0,72; p < 0,0001).
ConclusiónLos parámetros morfométricos del tercer ventrículo pueden resultar útiles para predecir una buena respuesta al shunt en los pacientes con HPNi.
Article

If it is the first time you have accessed you can obtain your credentials by contacting Elsevier Spain in suscripciones@elsevier.com or by calling our Customer Service at902 88 87 40 if you are calling from Spain or at +34 932 418 800 (from 9 to 18h., GMT + 1) if you are calling outside of Spain.
If you already have your login data, please click here .
If you have forgotten your password you can you can recover it by clicking here and selecting the option ¿I have forgotten my password¿.