To assess the effectiveness and safety of vancomycin powder as surgical siteinfection (SSI) prophylaxis in posterior bilateral elective spinal surgery.
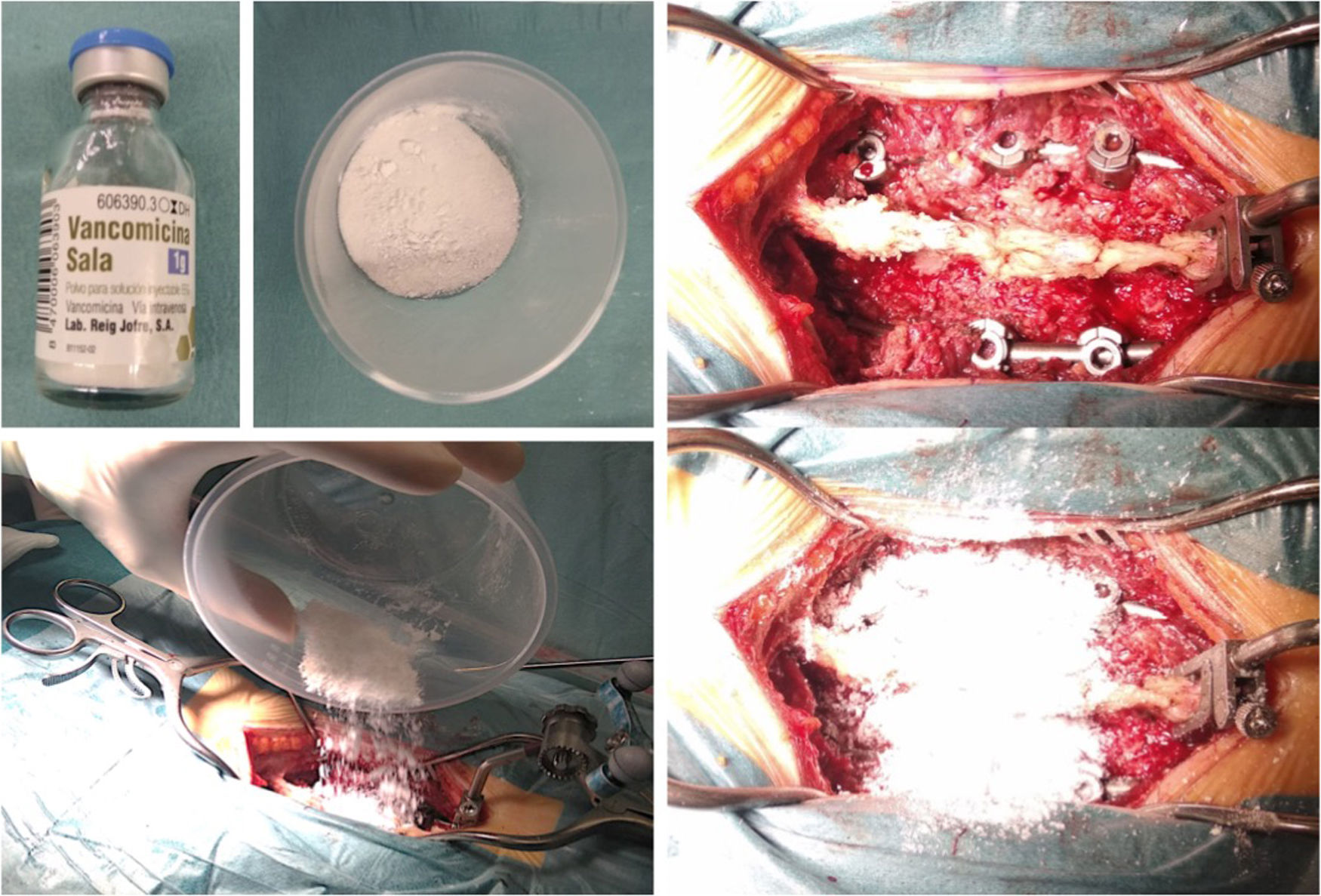
Materials and methodsSingle-center quasi-experimental pre and postintervention compa-rative cohort study. The post-intervention group received standard intravenous antibioticprophylaxis plus 1 g of vancomycin powder into the surgical field before wound closure, andthe pre-intervention group only the intravenous prophylaxis.
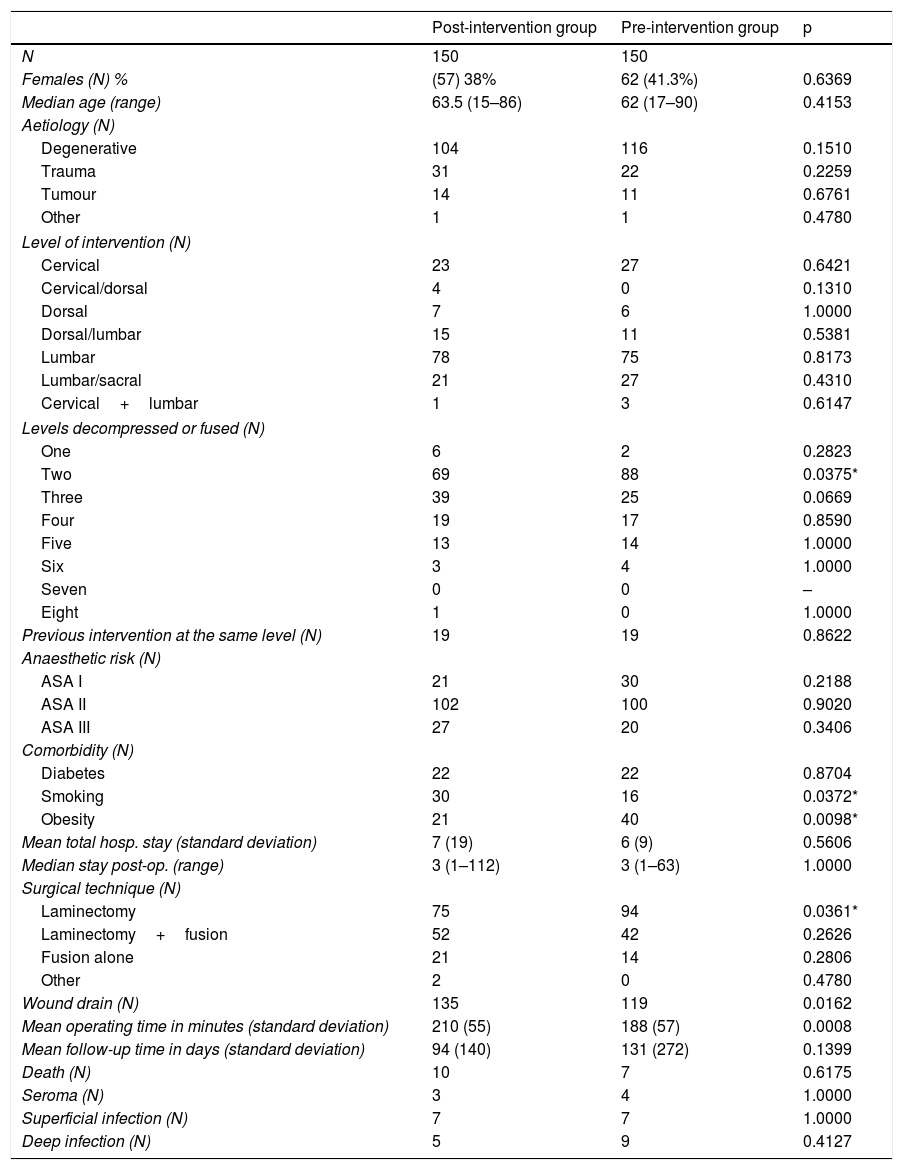
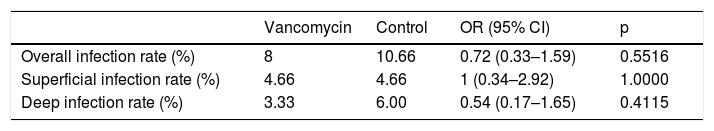
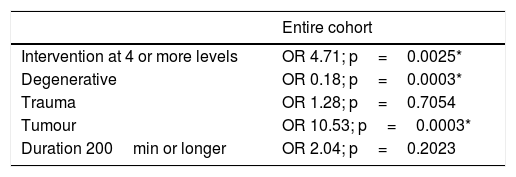
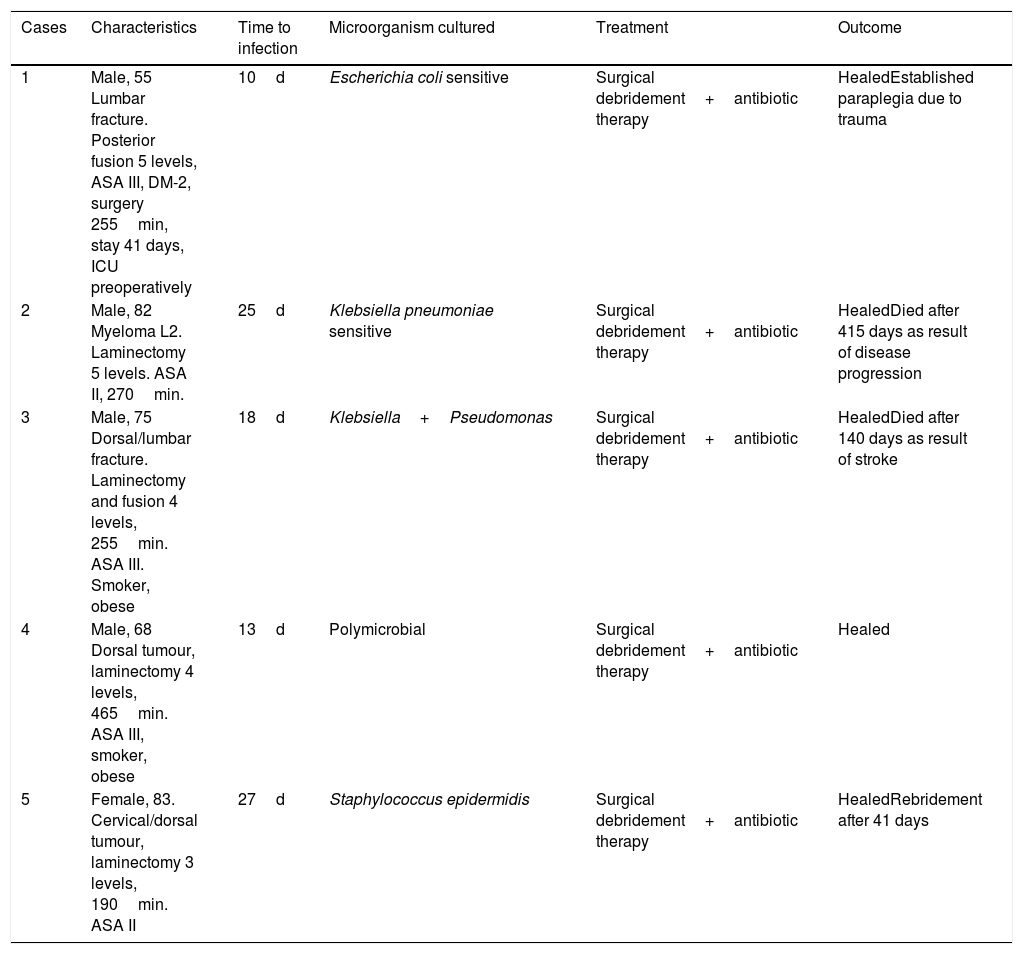
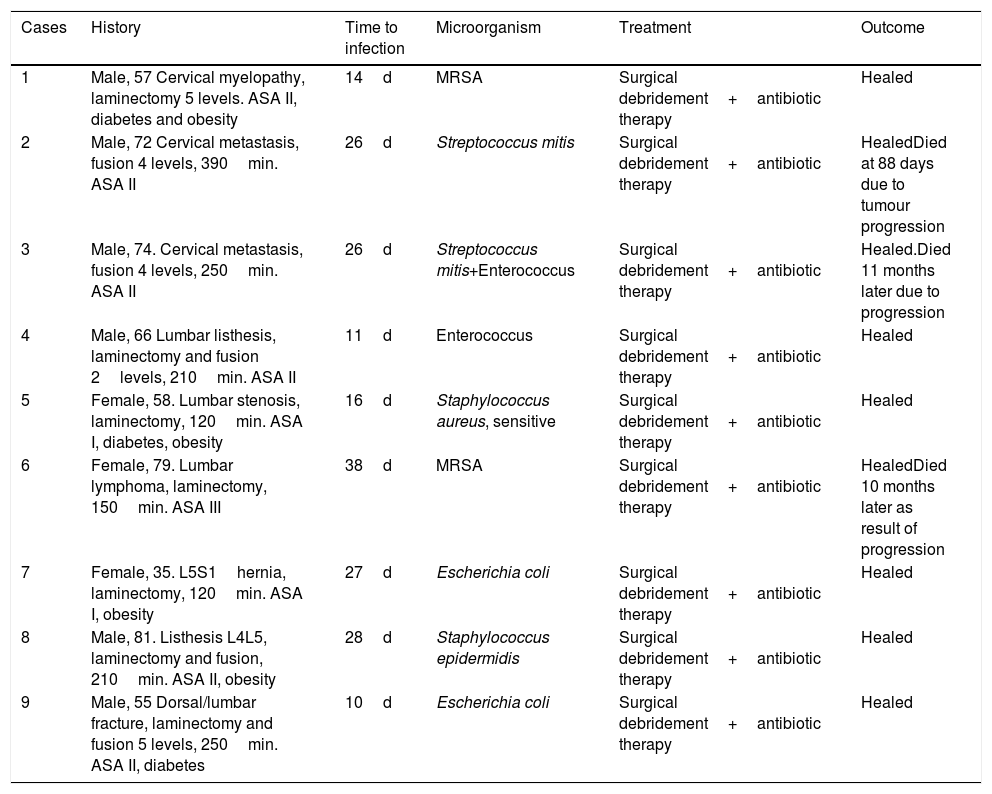
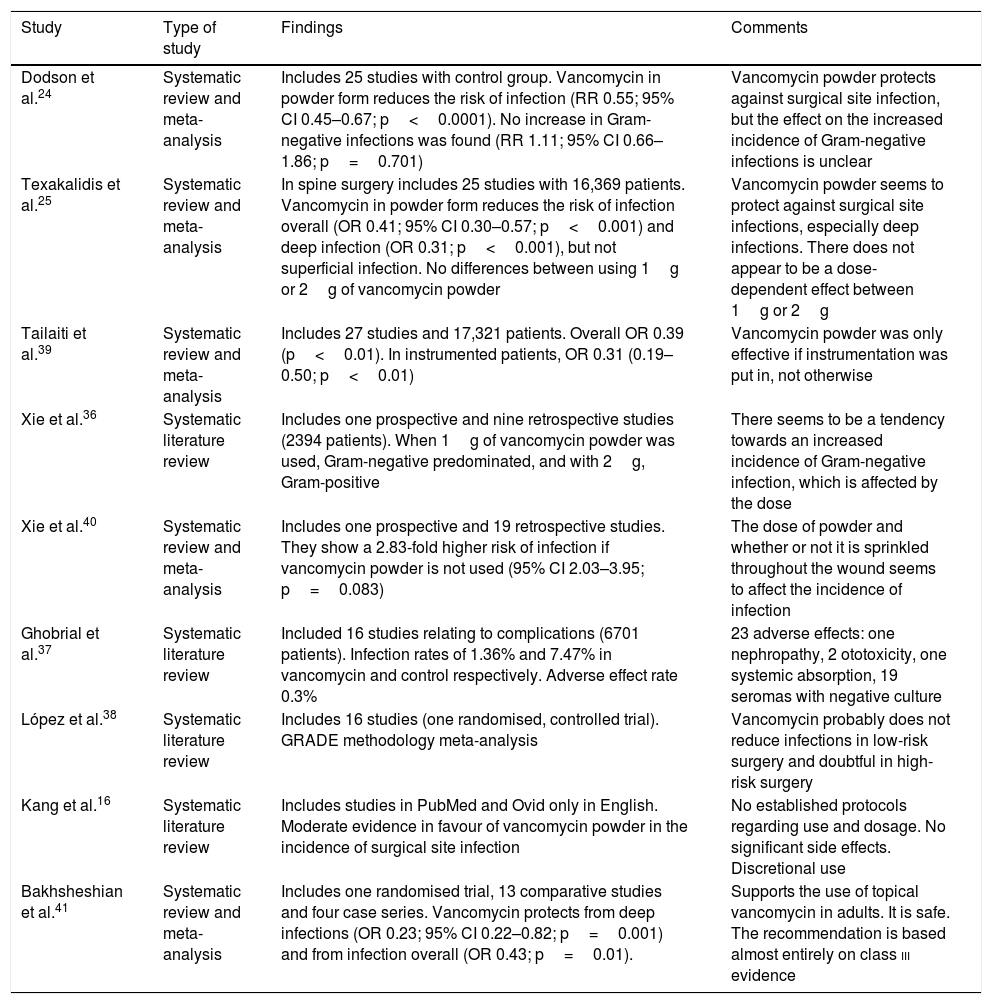
Results150 patients were included in each group. Twelve SSI (7 superficial and 5 deep)occurred in the post-intervention group and 16 SSI (7 superficial and 9 deep) in the pre-intervention group. The risk of deep SSI decreased from 6.0% to 3.3% (OR 0,54, 95%CI 0.17-1.65, p=0.411) with vancomycin powder. The percentage of deep SSI due to gramnegative-positive germs were 80%-20% and 33%–67% for the post- and pre-interventiongroups, respectively (p=0.265). No local or systemic adverse effects occurred attributableto vancomycin powder.
ConclusionIn posterior elective spinal surgery, prophylaxis with vancomycin powder didnot result in a significantly reduced incidence of superficial and deep SSI. There was a trendtowards a higher incidence of deep SSI caused by gram negative microorganisms amongthose treated with vancomycin.
Evaluar la efectividad y seguridad del polvo de vancomicina tópico como profilaxisde infección de herida quirúrgica (IHQ) en cirugía de columna electiva por abordaje posterior.
Material y métodosEstudio unicéntrico cuasiexperimental de comparación pre- y postin-tervención. El grupo postintervención recibió profilaxis antibiótica estándar preoperatoriajunto a 1 g de polvo de vancomicina en el lecho quirúrgico antes del cierre de la herida. Elgrupo preintervención solo recibió la profilaxis intravenosa.
ResultadosParticiparon 150 pacientes en cada grupo. Ocurrieron 12 infecciones (7 super-ficiales, 5 profundas) en el grupo postintervención y 16 infecciones (7 superficiales, 9profundas) en el grupo preintervención. El riesgo de IHQ profunda se redujo del 6% al 3,3% (OR 0,54; IC 95% 0,17–1,65; p=0,411) con el tratamiento. El porcentaje de IHQ profunda porgramnegativos-positivos fue del 80-20% en el grupo tratado con vancomicina y del 33–67% en los no tratados (p=0,265). No se produjeron efectos adversos locales ni sistémicos por eltratamiento.
ConclusiónLa profilaxis con polvo de vancomicina en cirugía electiva de columna por abor-daje posterior no redujo de forma significativa la incidencia de IHQ superficial o profunda. Seconstató una tendencia al aumento de IHQ profunda por microorganismos gramnegativosen los tratados con vancomicina.
Article

If it is the first time you have accessed you can obtain your credentials by contacting Elsevier Spain in suscripciones@elsevier.com or by calling our Customer Service at902 88 87 40 if you are calling from Spain or at +34 932 418 800 (from 9 to 18h., GMT + 1) if you are calling outside of Spain.
If you already have your login data, please click here .
If you have forgotten your password you can you can recover it by clicking here and selecting the option ¿I have forgotten my password¿.