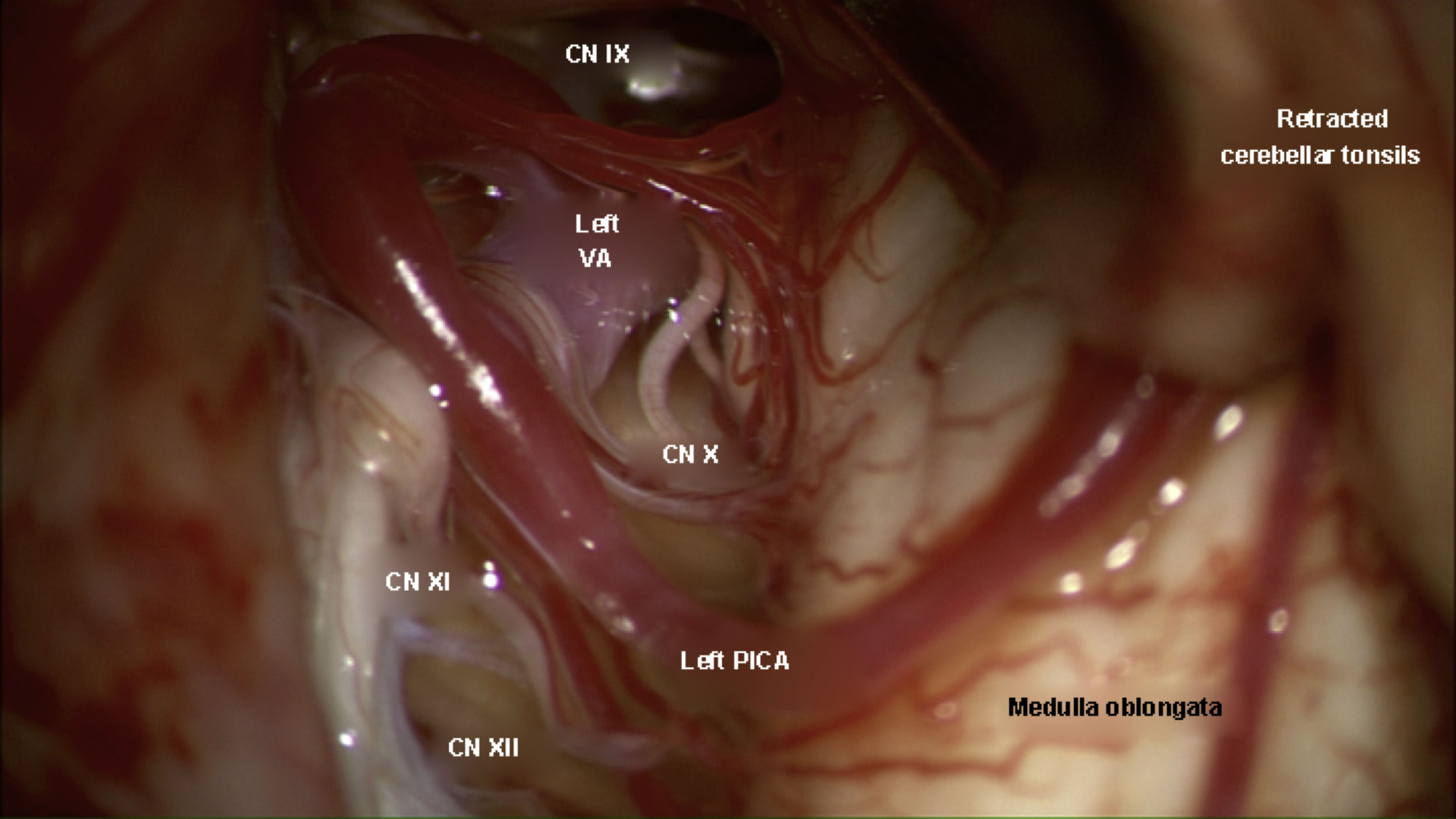
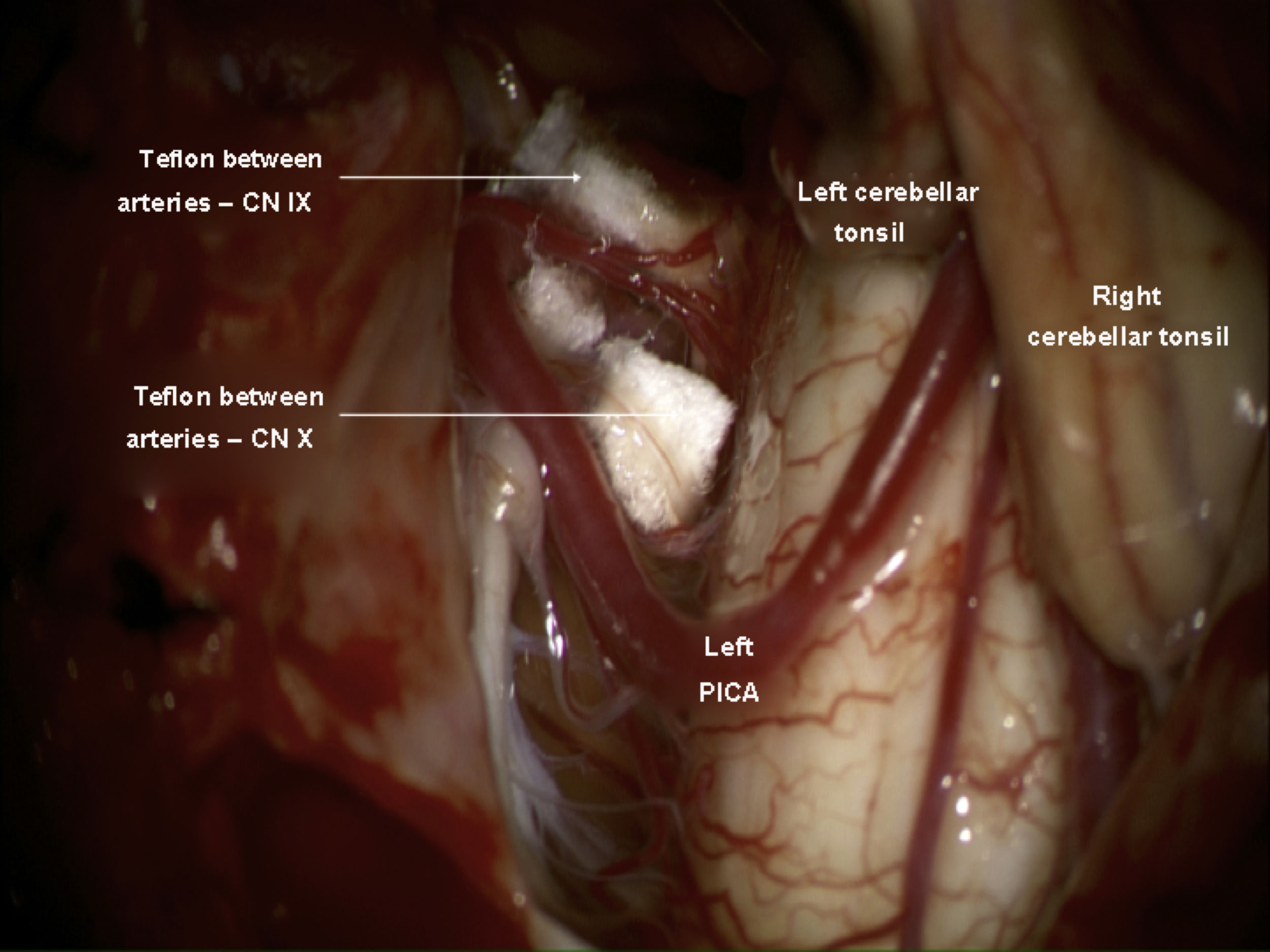
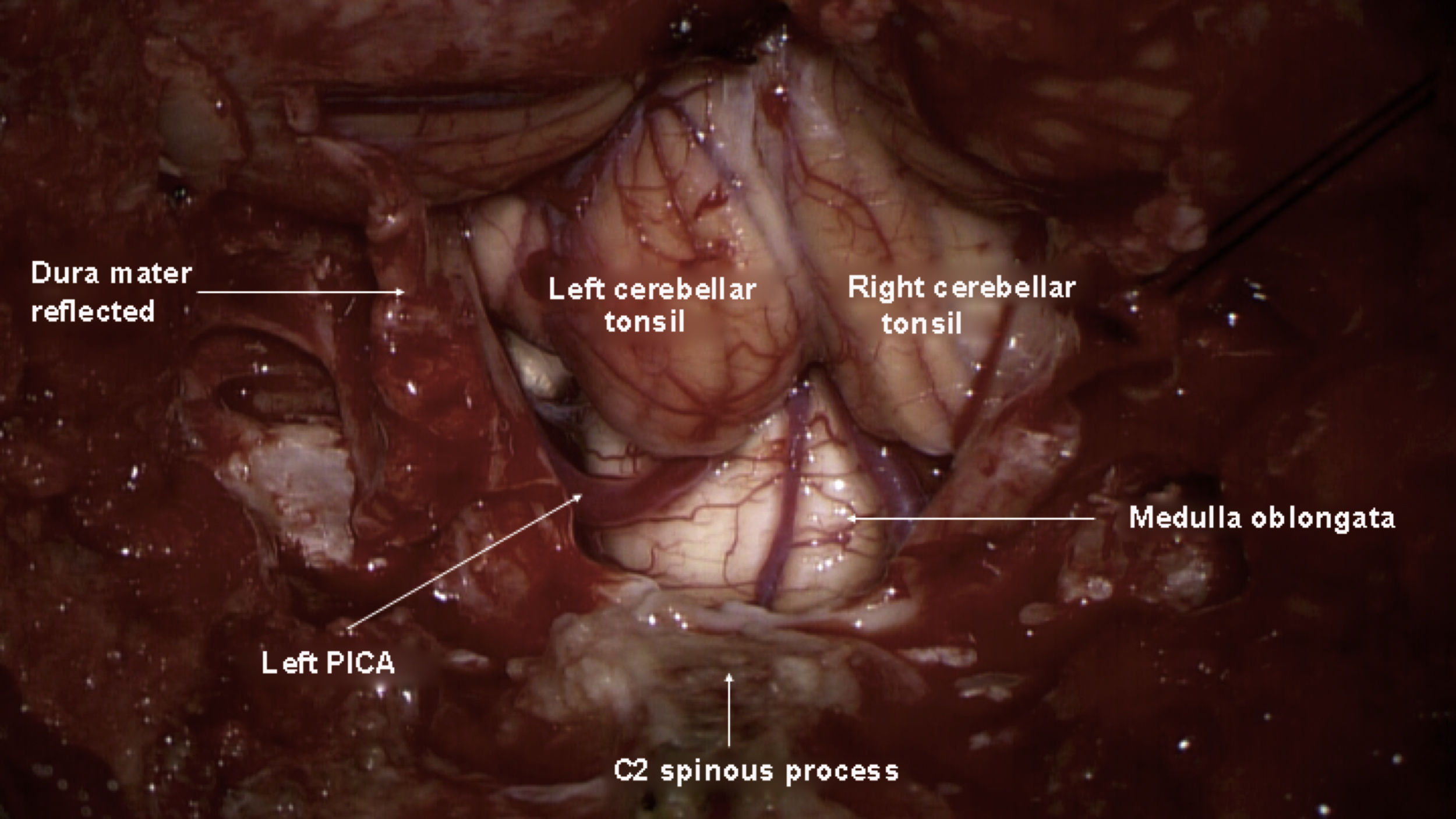
Glossopharyngeal neuralgia is a rare disease whose initial treatment is pharmacological. When medical therapy is not effective, different surgical options are available including stereotactic radiosurgery, microvascular decompression or nerve section.
It is reported a case of a 26-year-old female with glossopharyngeal neuralgia and Chiari malformation. This rare type of neuralgia sometimes is associated with an abnormality of the cranio-cervical junction. It was performed a posterior fossa expansion with duraplasty and microvascular decompression. The patient showed a complete disappearance of the pain, with no need of tonsil resection.
La neuralgia glosofaríngea es una enfermedad rara cuyo tratamiento inicial es farmacológico. Cuando la terapia médica no es eficaz, se encuentran disponibles diferentes opciones quirúrgicas, incluida la radiocirugía estereotáctica, la descompresión microvascular o la sección de nervios.
Se presenta el caso de una mujer de 26 años con neuralgia glosofaríngea y malformación de Chiari. Este tipo raro de neuralgia a veces se asocia con una anomalía de la unión cráneo-cervical. Se realizó una expansión de fosa posterior con duraplastia y descompresión microvascular. La paciente mostró una completa desaparición del dolor, sin necesidad de llevar a cabo la resección de las amígdalas cerebelosas.
Article

If it is the first time you have accessed you can obtain your credentials by contacting Elsevier Spain in suscripciones@elsevier.com or by calling our Customer Service at902 88 87 40 if you are calling from Spain or at +34 932 418 800 (from 9 to 18h., GMT + 1) if you are calling outside of Spain.
If you already have your login data, please click here .
If you have forgotten your password you can you can recover it by clicking here and selecting the option ¿I have forgotten my password¿.