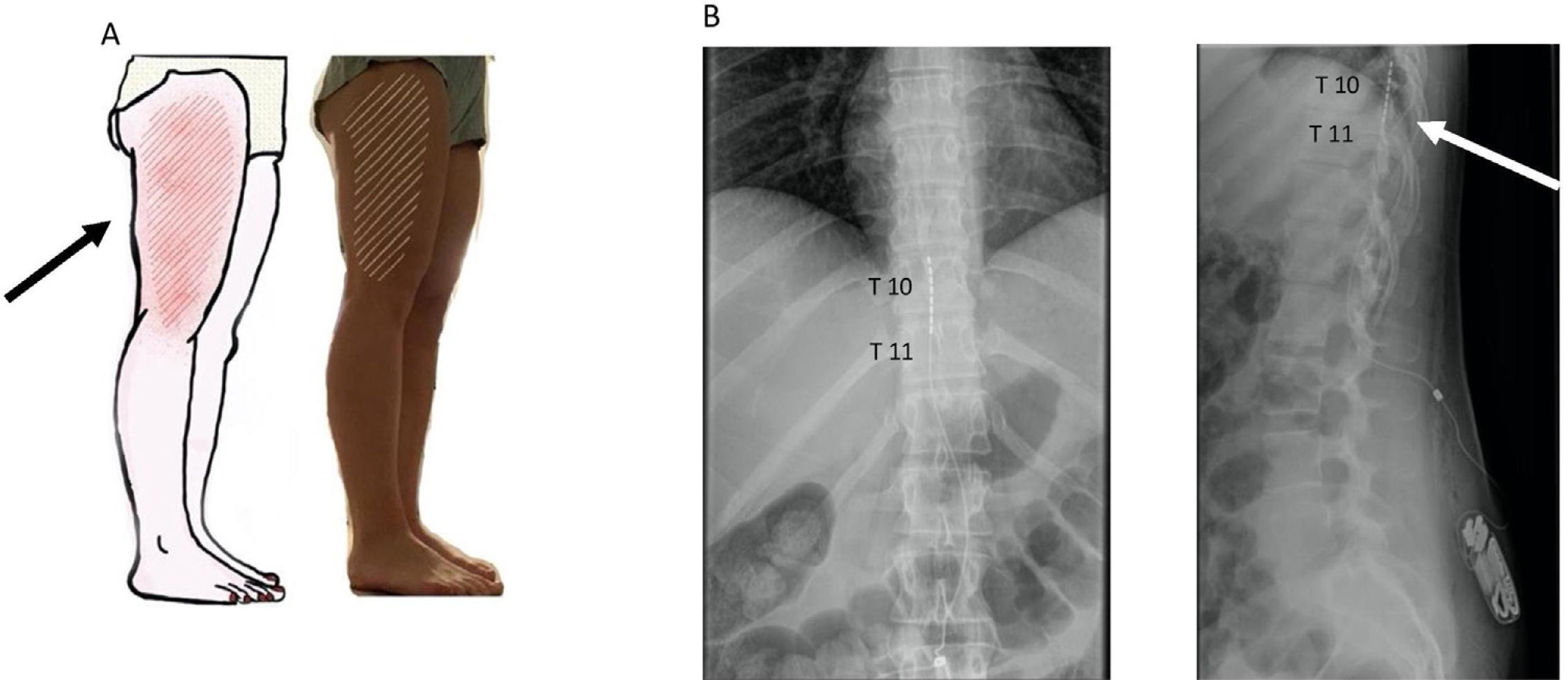
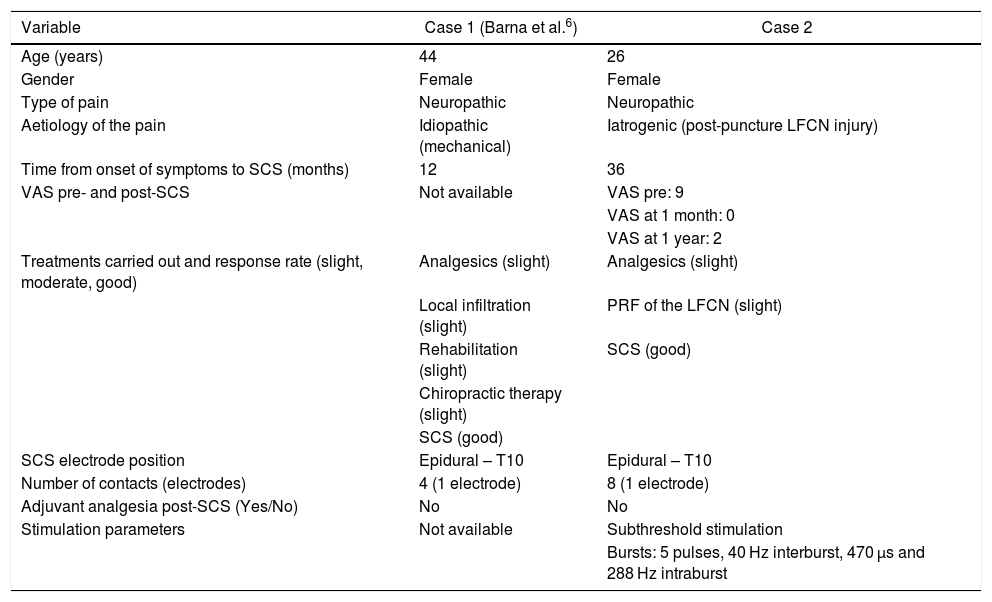
Meralgia paresthetica is a neurological disorder caused by a neuropathy of the lateral femoral cutaneous nerve. Its aetiology can be spontaneous or iatrogenic. It is characterized by pain, paresthesia, and numbness in the anterolateral aspect of the thigh. Diagnosis is based on clinical examination, although image and neurophysiological tests can be useful as well. Despite conservative measures use to be effective in most of patients, refractory cases can benefit from alternative treatments. Available surgical procedures are: nerve decompression (neurolysis) or section (neurectomy) and radiofrequency ablation. We present a case of refractory meralgia paresthetica where spinal cord stimulation was used as a possible effective technique in pain relief and to avoid the neurectomy of the lateral femoral cutaneous nerve.
La meralgia parestésica es un desorden neurológico causado por una neuropatía del nervio fémoro-cutáneo lateral. Su etiología puede ser idiopática o iatrogénica. Se caracteriza por dolor, parestesias y entumecimiento en la cara antero-lateral del muslo. Su diagnóstico es básicamente clínico, aunque pueden ser útiles pruebas de imagen o neurofisiológicas. A pesar de que el tratamiento conservador suele ser eficaz en la mayoría de pacientes, existen casos refractarios que pueden precisar de otras formas de tratamiento. Los procedimientos quirúrgicos disponibles son la descompresión nerviosa (neurolisis) o la sección (neurectomía) y las ablaciones por radiofrecuencia. Presentamos un caso de meralgia parestésica invalidante refractaria en el cual empleamos la estimulación medular como posible técnica eficaz en el alivio del dolor y poder evitar la realización de una neurectomía del nervio fémoro-cutáneo lateral.
Article

If it is the first time you have accessed you can obtain your credentials by contacting Elsevier Spain in suscripciones@elsevier.com or by calling our Customer Service at902 88 87 40 if you are calling from Spain or at +34 932 418 800 (from 9 to 18h., GMT + 1) if you are calling outside of Spain.
If you already have your login data, please click here .
If you have forgotten your password you can you can recover it by clicking here and selecting the option ¿I have forgotten my password¿.