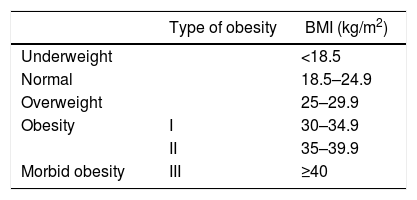
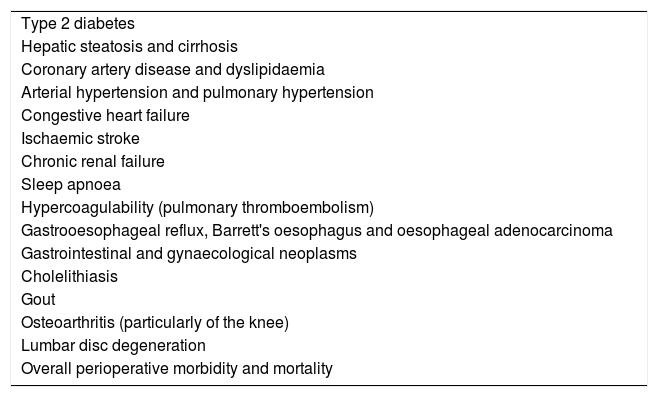
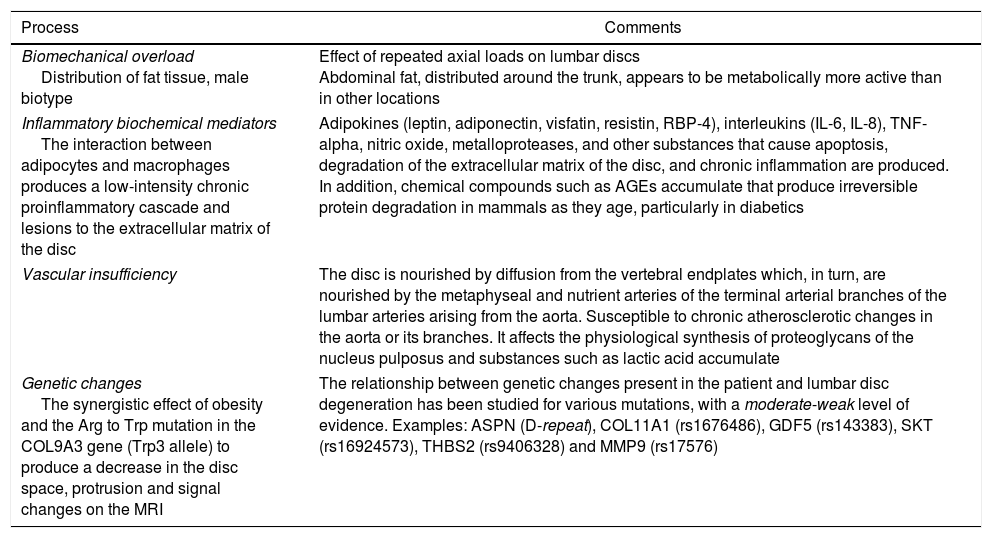
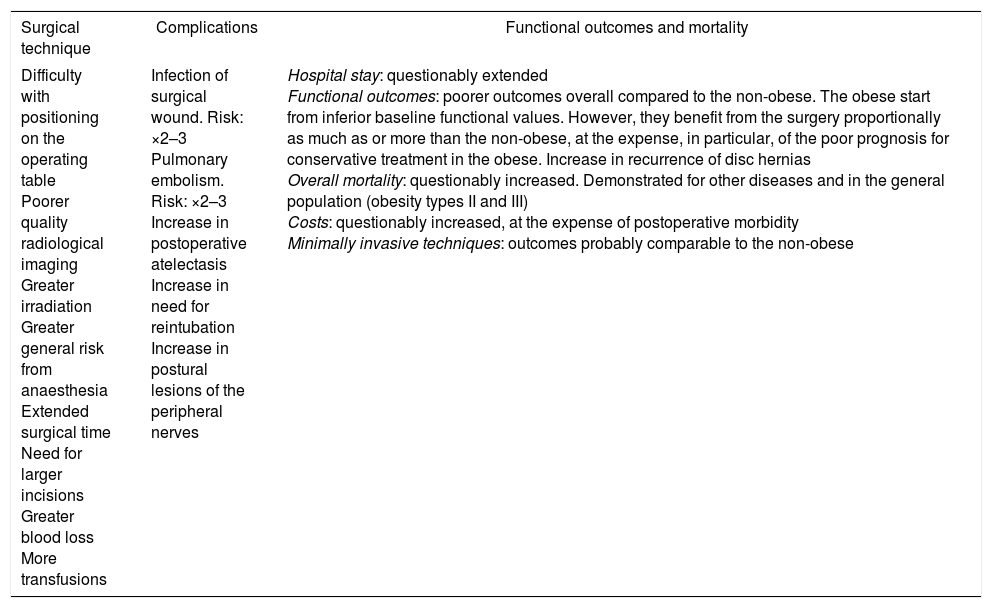
Obesity (BMI >30kg/m2) is a pandemic with severe medical and financial implications. There is growing evidence that relates certain metabolic processes within the adipose tissue, preferentially abdominal fat, with a low-intensity chronic inflammatory state mediated by adipokines and other substances that favour disk disease and chronic low back pain. Obesity greatly conditions both the preoperative evaluation and the spinal surgical technique itself. Some meta-analyses have confirmed an increase of complications following lumbar spine surgery (mainly infections and venous thrombosis) in obese subjects. However, functional outcomes after lumbar spine surgery are favourable although inferior to the non-obese population, acknowledging that obese patients present with worse baseline function levels and the prognosis of conservatively treated obese cohorts is much worse. The impact of preoperative weight loss in spine surgery has not been prospectively studied in these patients.
La obesidad (IMC>30kg/m2) es una pandemia con graves implicaciones médicas y económicas. Existe una creciente evidencia que relaciona procesos relacionados con el metabolismo del tejido adiposo, preferentemente abdominal, con un estado inflamatorio crónico de baja intensidad mediado por adipocinas y otras sustancias que favorecen la lesión discal y el dolor lumbar crónico. La obesidad condiciona en gran medida la evaluación preoperatoria y la técnica quirúrgica en cirugía de columna. Diversos metaanálisis confirman un aumento de complicaciones tras cirugía lumbar en el paciente obeso (especialmente infecciones y trombosis venosas). Sin embargo, los resultados funcionales de estas intervenciones son favorables aunque inferiores a los de la población no obesa, teniendo en cuenta que parten de valores basales inferiores y el pronóstico de los obesos tratados conservadoramente es mucho peor. El impacto de una reducción de peso preoperatoria no se ha estudiado de forma prospectiva en este tipo de pacientes.
Article

If it is the first time you have accessed you can obtain your credentials by contacting Elsevier Spain in suscripciones@elsevier.com or by calling our Customer Service at902 88 87 40 if you are calling from Spain or at +34 932 418 800 (from 9 to 18h., GMT + 1) if you are calling outside of Spain.
If you already have your login data, please click here .
If you have forgotten your password you can you can recover it by clicking here and selecting the option ¿I have forgotten my password¿.