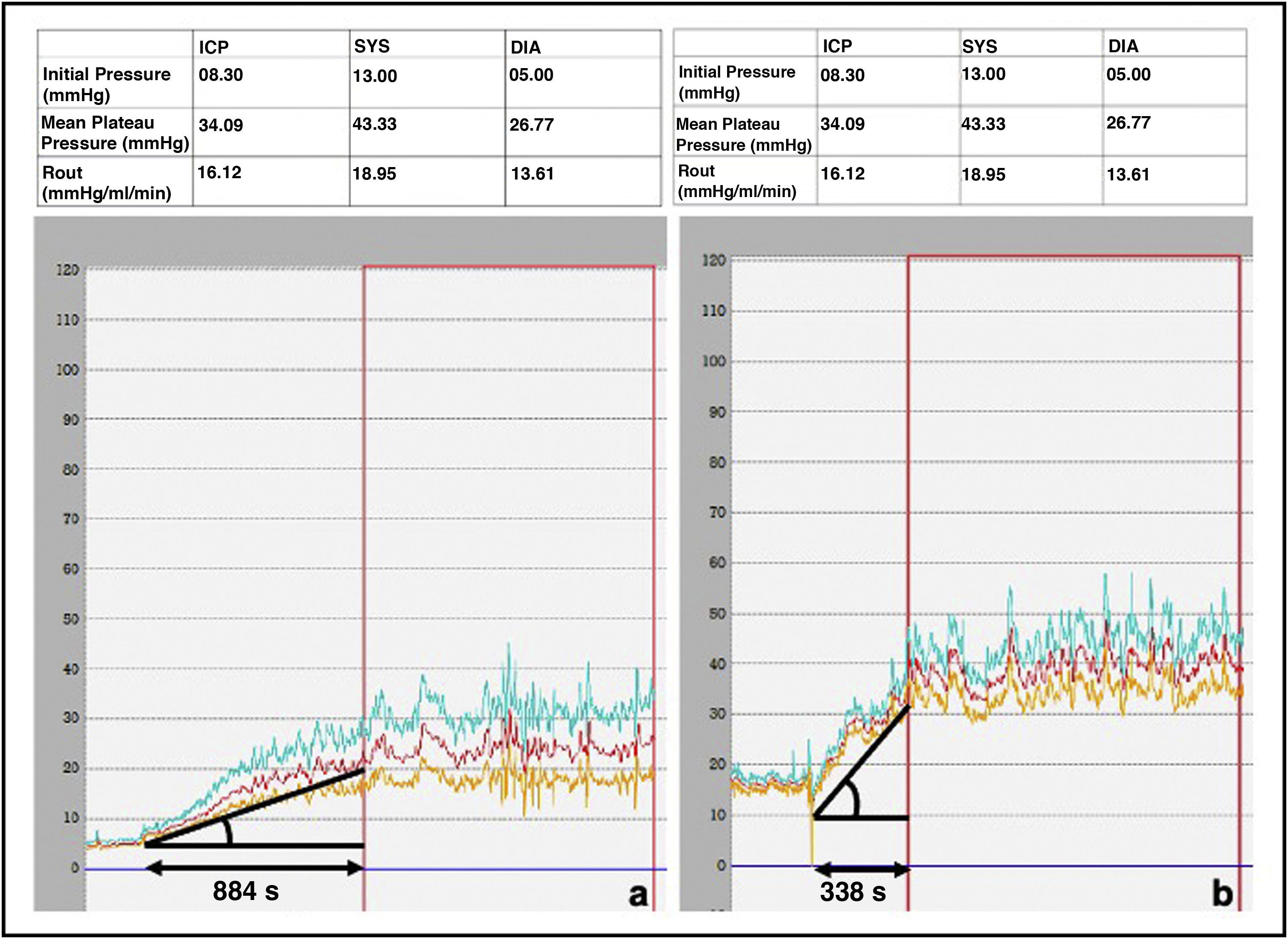
To study the prognostic value of the resistance to the cerebrospinal fluid outflow (Rout) obtained in the lumbar infusion test in idiopathic normal pressure hydrocephalus (iNPH), as well as the pulse pressure amplitudes in the different periods of the test and other new variables extracted by Neuropicture® software.
Material and methodsPatients with ‘probable iNPH’ who underwent a lumbar infusion test were retrospectively revised. The positive predictive values (PPV) of the cutoff point of the best prognostic accuracy of the Rout, the basal pulse pressure amplitude (AMPo), the pulse pressure amplitude during the first 10 min (AMP10min), the plateau pulse pressure amplitude (AMPmes), the Rout pulse pressure amplitude (AMPRout), the time to reach the plateau (T), and the slope until reaching the plateau were determined. Patients were categorized either as responders or non-responders.
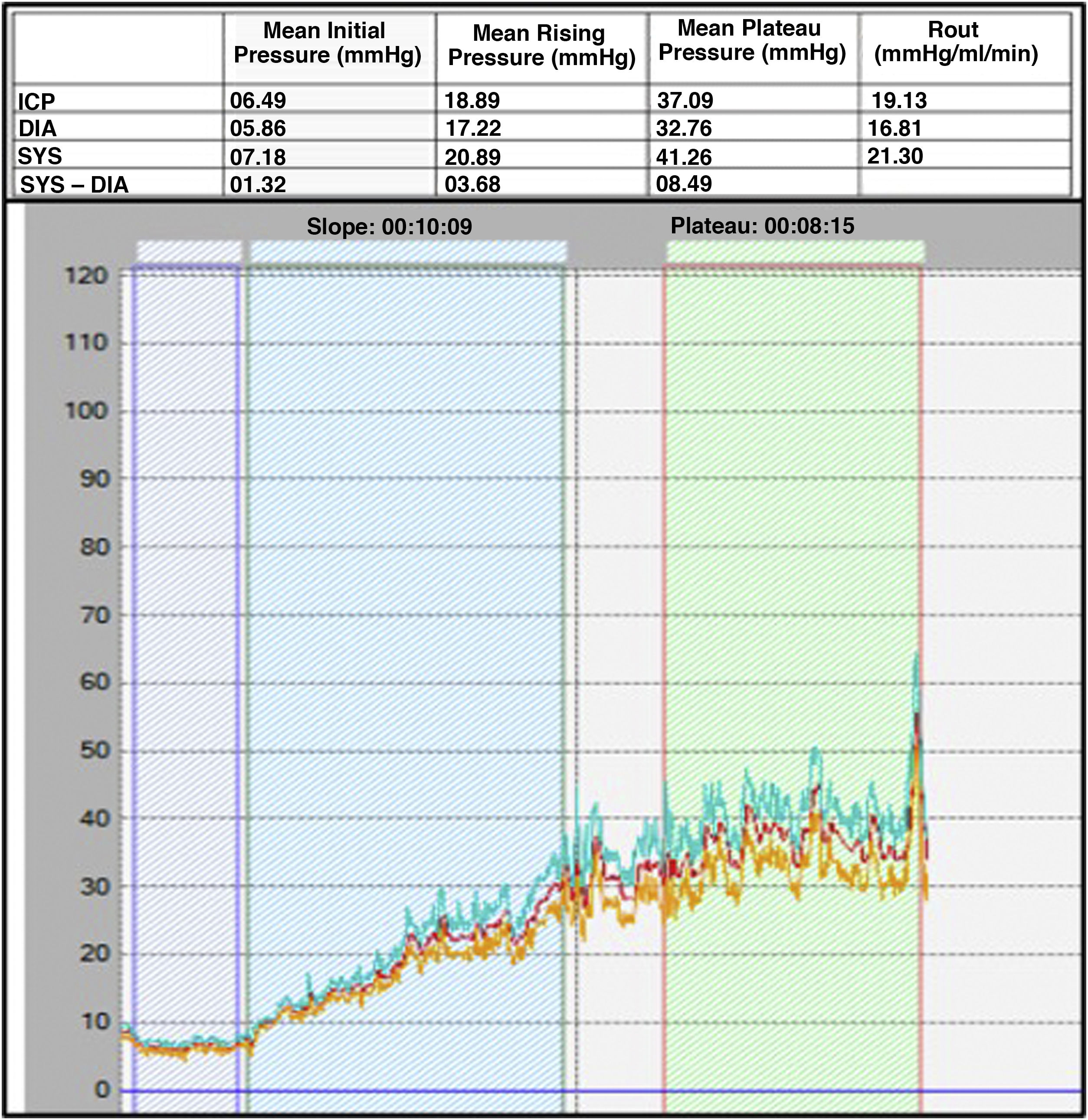
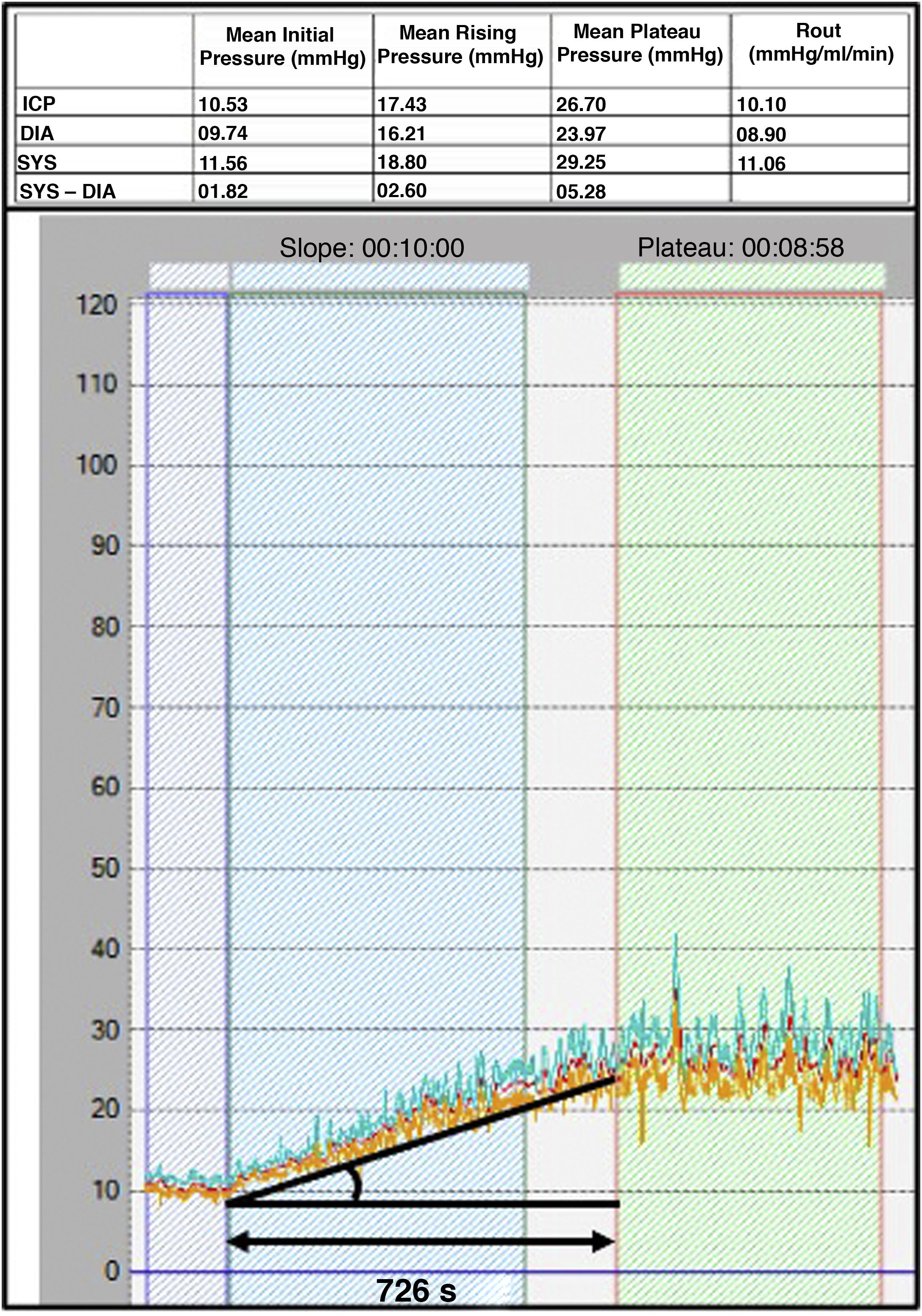
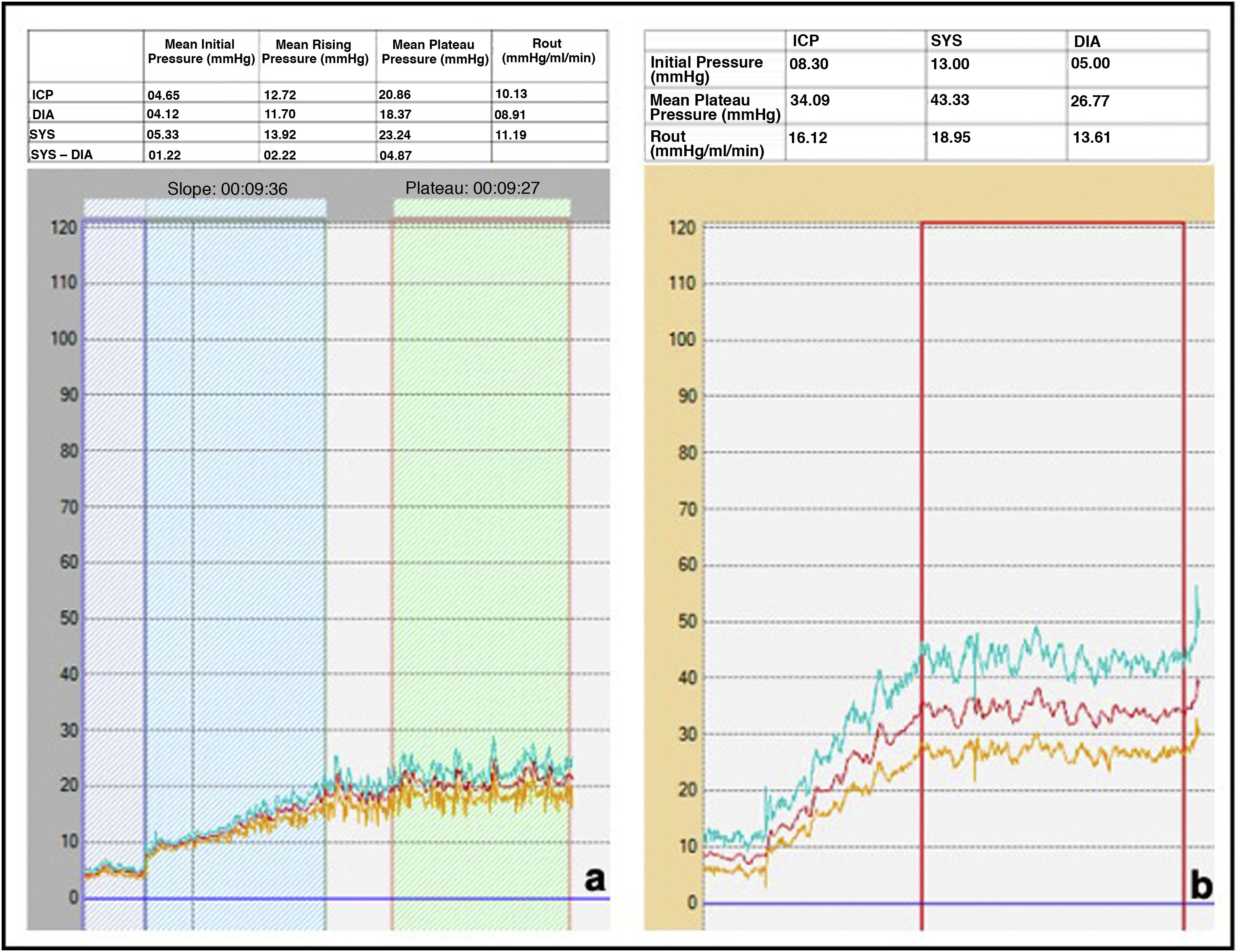
ResultsThe study included 64 responders patients and 16 non-responders patients. The PPV of Rout > 15 mmHg/mL/min was 91.7%; AMPo > 2.34 mmHg: 91.3%; AMP10 min > 4.34 mmHg: 83.3%; AMPmes > 12.44 mmHg: 84.6%; AMPRout > 6.34 mmHg: 85%; T < 634 s: 86.7%; p > 0.040 mmHg/s: 96.3%.
ConclusionsRout is a valid criterion to indicate a ventricular shunt. Pulse pressure amplitudes in the different periods of the lumbar infusion test, in addition to T and P, are other variables whose positivity is indicative of shunt response and should be considered in the diagnostic protocol of the iNPH.
Estudiar la validez pronóstica de la resistencia a la salida de líquido cefalorraquídeo (Rout) obtenida en el test de infusión lumbar en el estudio de la hidrocefalia idiopática de presión normal (iNPH), al igual que de las amplitudes en los diferentes tramos del test y otras nuevas variables obtenidas con el software Neuropicture®.
Materiales y métodosRevisamos retrospectivamente pacientes con “probable iNPH” a los que se les sometió a un test de infusión lumbar. Se determinó el valor predictivo positivo (VPP) del punto de corte con mayor precisión pronóstica de la Rout, la amplitud de pulso en reposo (AMPo), la amplitud en los primeros 10 minutos (AMP10min), la amplitud de meseta (AMPmes), la amplitud de Rout (AMPRout), el tiempo en alcanzar la meseta (T) y la pendiente de la curva hasta alcanzar la meseta (P). Se dividió a los pacientes en respondedores y no respondedores.
ResultadosEl estudio incluyó 64 pacientes respondedores y 16, no respondedores. El VPP de Rout > 15 mmHg/mL/min fue 91,7%; de la AMPo > 2,34 mmHg, 91,3%; de la AMP10min > 4,34 mmHG, 83,3%; de AMPmes > 12,44 mmHg, 84,6%; de AMPRout > 6,34 mmHG, 85%; de T < 634 segundos, 86,7%; y de p > 0,040 mmHg/seg, 96,3%.
ConclusionesLa Rout sigue siendo un criterio válido para indicar un shunt ventricular. Las amplitudes en diferentes tramos del test, junto a la T y la P son otras variables cuya positividad es indicativa de respuesta valvular y deberían formar parte del protocolo diagnóstico.
Article

If it is the first time you have accessed you can obtain your credentials by contacting Elsevier Spain in suscripciones@elsevier.com or by calling our Customer Service at902 88 87 40 if you are calling from Spain or at +34 932 418 800 (from 9 to 18h., GMT + 1) if you are calling outside of Spain.
If you already have your login data, please click here .
If you have forgotten your password you can you can recover it by clicking here and selecting the option ¿I have forgotten my password¿.