To describe the anatomical measurements of the trigeminal nerve in patients with trigeminal neuralgia (TN) during Linac (linear accelerator)-based stereotactic radiosurgery (SRS) simulation, targeting the root entry zone (REZ), with a 30% isodose line tangential to the pons, using 4-mm and 6-mm collimators.
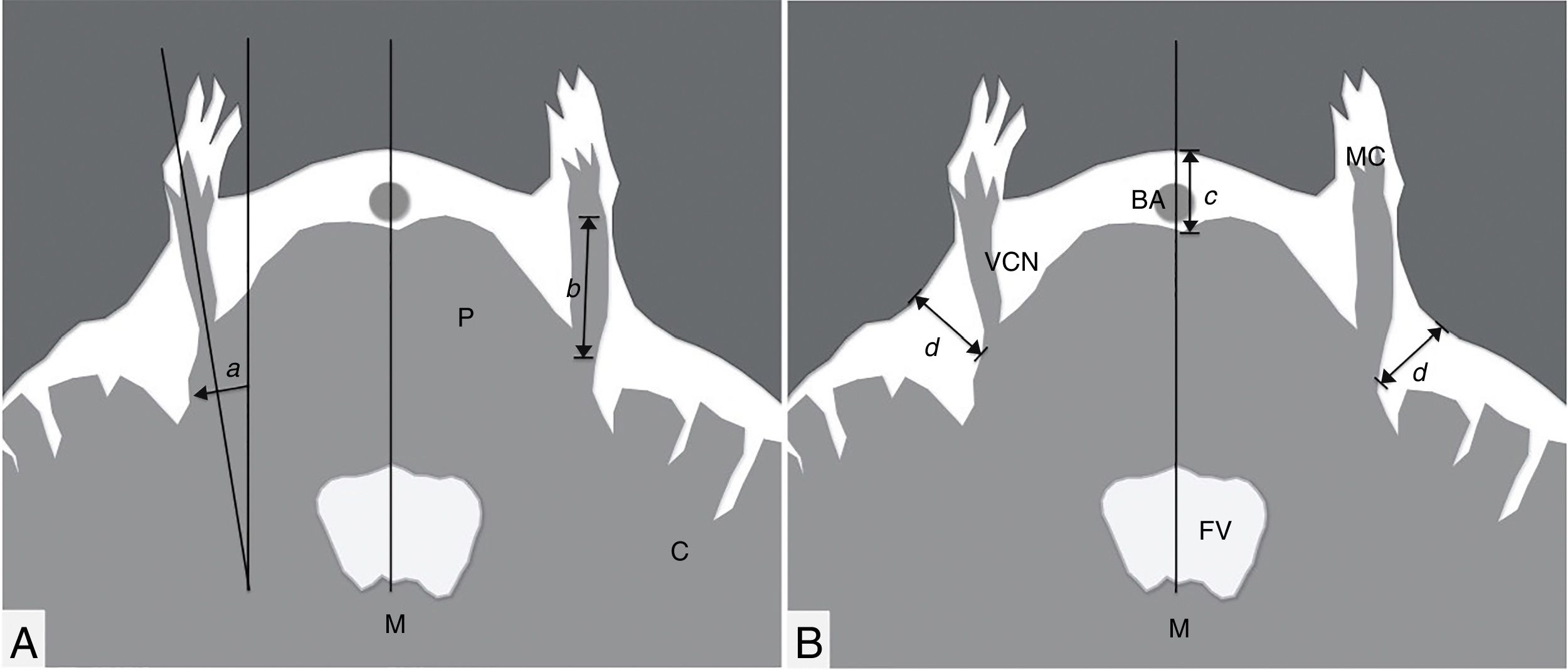
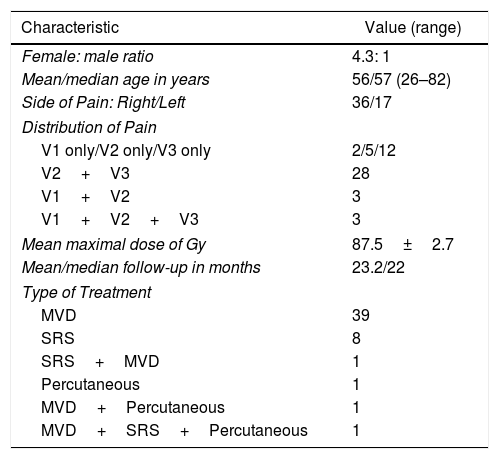
MethodsIn this retrospective study, 53 TN patients, who underwent Fiesta sequence scanning prior to any treatment modality, were assessed. Bilateral measurements were obtained from the cisternal segment of the trigeminal nerve, the trigeminal-pontine angle, and the lateral width of the pontine cistern on the Fiesta MRI sequence. Linac-based SRS simulations were estimated with a radiation dosage of 90Gy to 30% isodose line tangential to the pons, with both 4- and 6-mm collimators. Distances from the calculated targets to the pons and the Gasserian ganglion were measured for later analysis. The statistical analysis was performed comparing the affected side against the unaffected side.
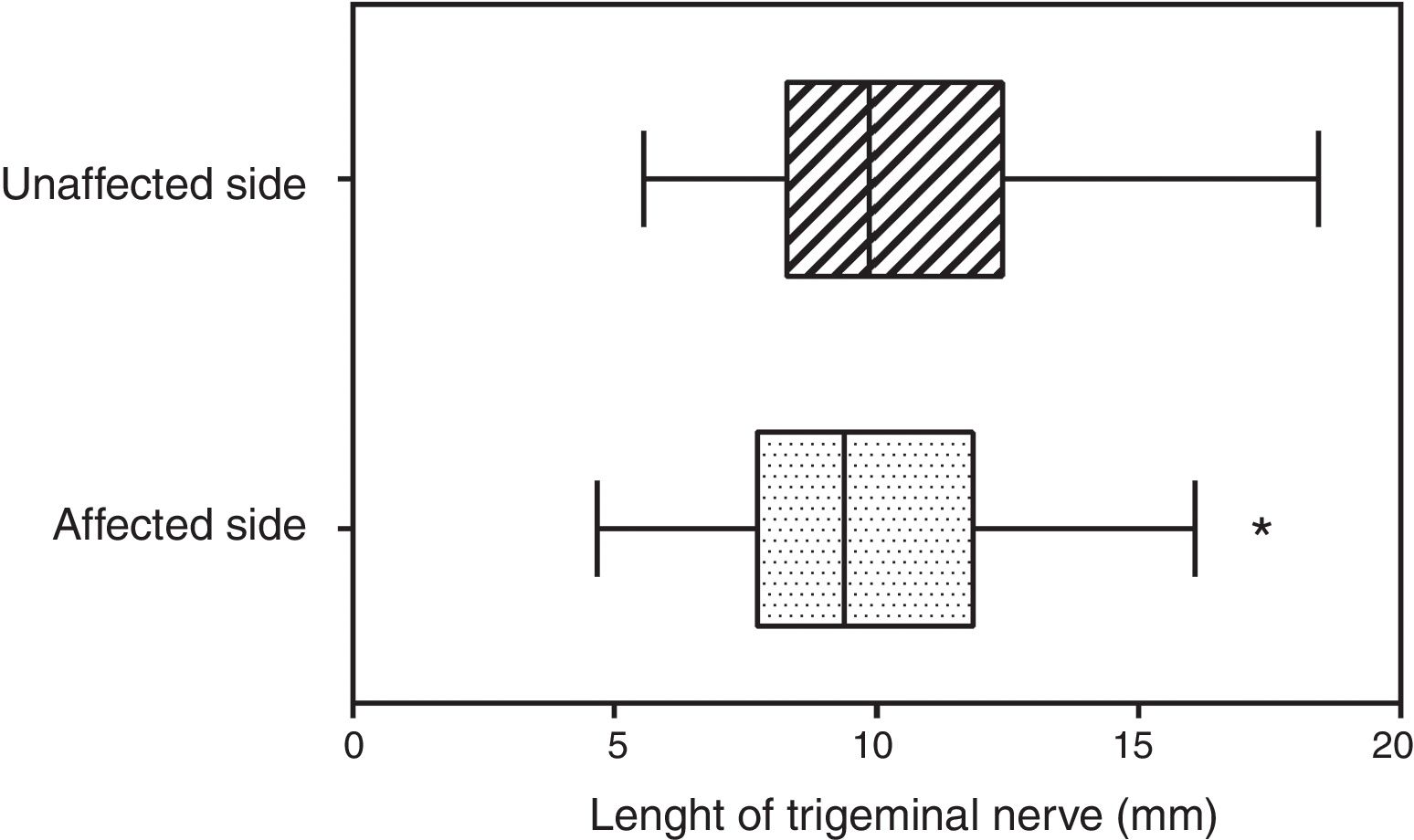
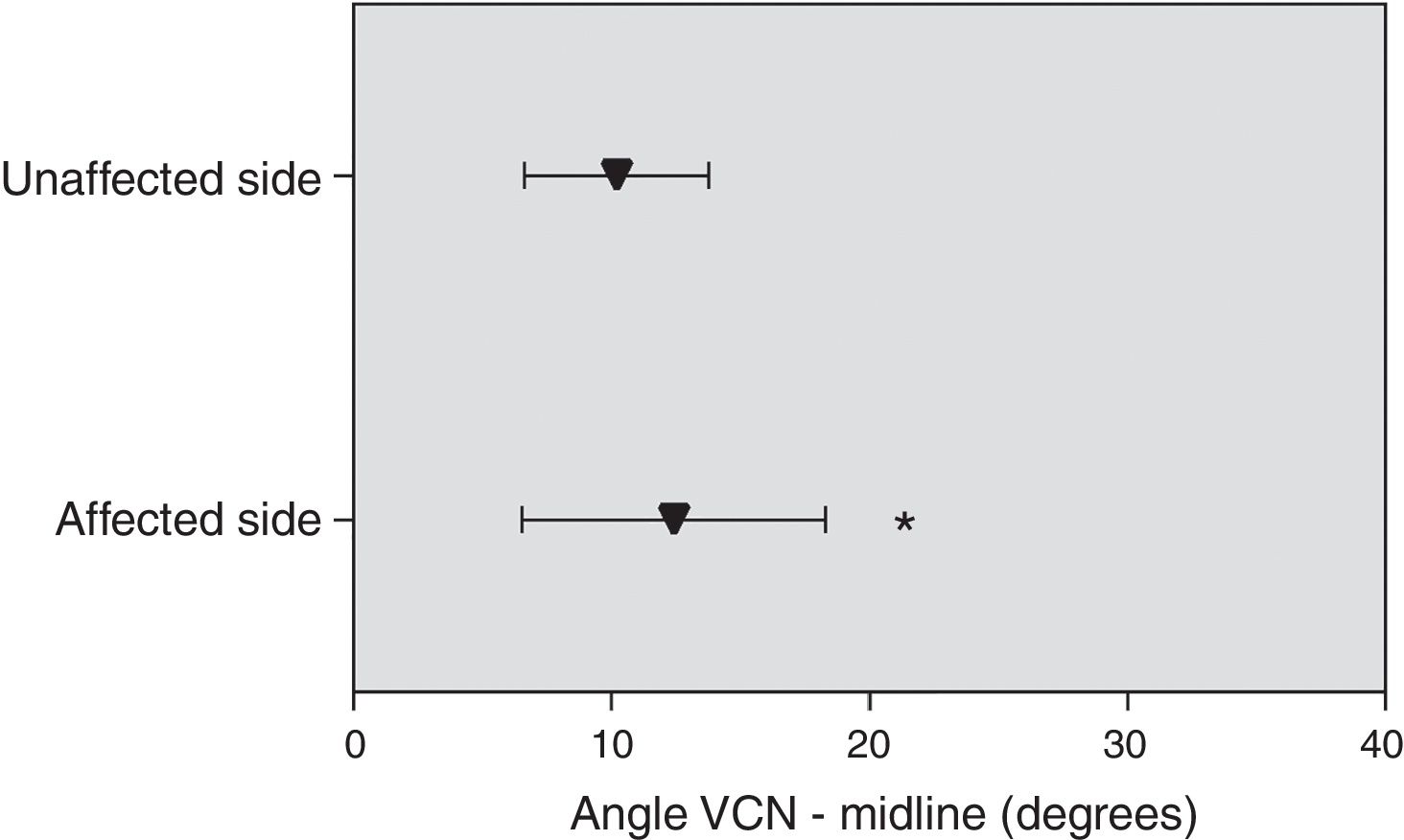
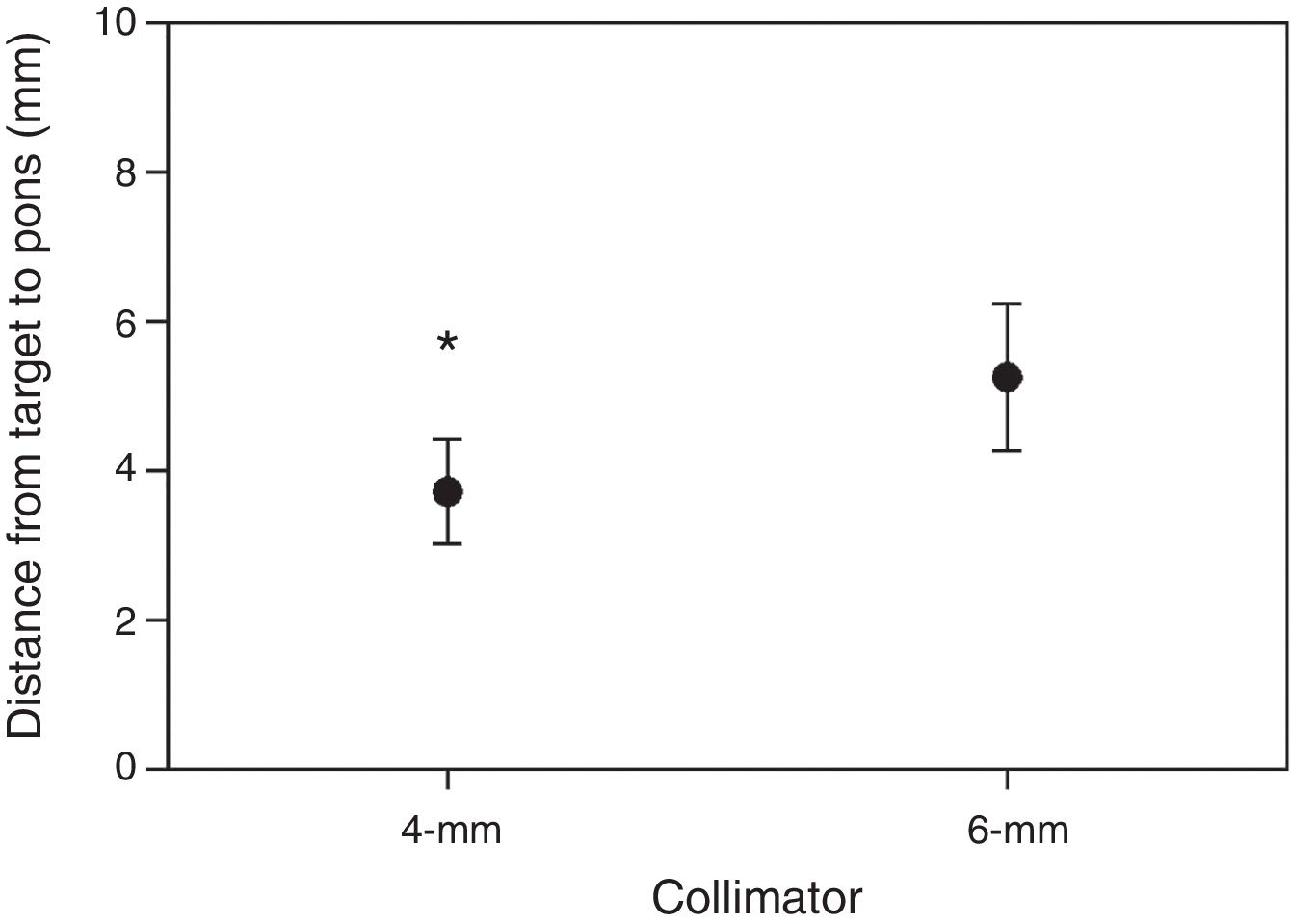
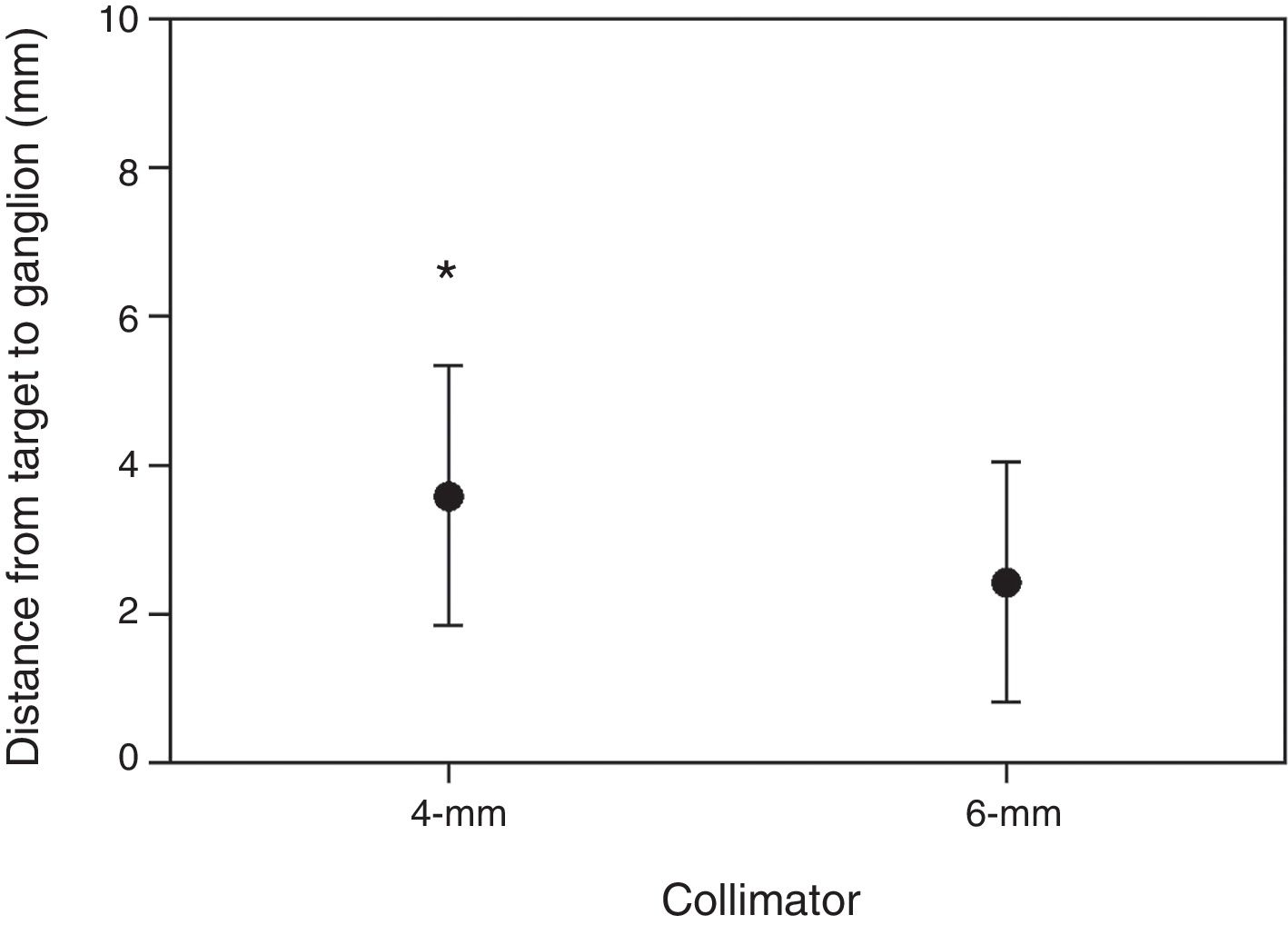
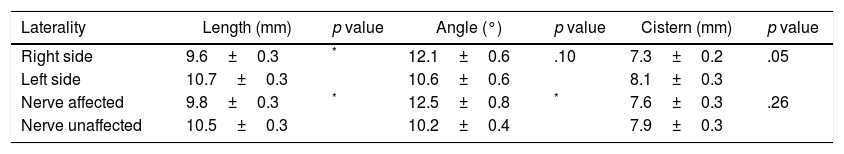
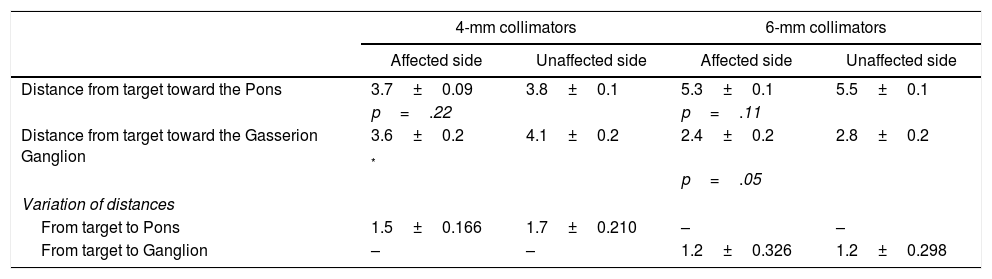
ResultsRight trigeminal nerve was affected in 36 patients (67.9%), and left one in 17 (32.1%) patients. The mean length of the trigeminal nerve was 9.8mm (range: 4.6–16.8mm) on the affected side, and 10.5mm (range: 5.6–18.4mm) on the unaffected side (p=.02). The mean trigeminal-pontine angle was 12.5° (range: 5.4° to 19.5°) on the affected side, and 10.2° (range: 5.0° to 30.5°) on the unaffected side (p=.01). In the simulations, the distances from the estimated targets to the pons and the Gasserian ganglion were not statistically different between sides. The variation of target-pons and target-ganglion distances was statistically significant on the affected side with the change of collimators (p<.001).
ConclusionsIn this anatomical study, significant differences were identified in the length of the affected trigeminal nerve and trigeminal-pontine angle compared to the unaffected side in TN patients in Fiesta sequences prior to surgery or radiosurgery. Significant variation of the target location was found on the REZ between the 4- and 6-collimators during the Linac-based SRS simulations with the estimated radiation dosage of 90Gy and 30% isodose line tangential to the pons.
Describir las mediciones anatómicas del nervio trigémino en pacientes con neuralgia del trigémino (NT) en la simulación para radiocirugía estereotáctica (SRS) con acelerador lineal (LINAC), utilizando como blanco la zona de entrada de la raíz (REZ), con una línea de isodosis del 30% tangencial al puente, usando colimadores de 4 y 6mm.
MétodosEn este estudio retrospectivo, fueron evaluados 53 pacientes con NT con una secuencia FIESTA de RM previo a recibir alguna modalidad de tratamiento. Las mediciones obtenidas bilateralmente fueron la longitud de la porción cisternal del nervio trigémino, del ángulo trigémino-pontino y la anchura lateral de la cisterna pontina. Las simulaciones de SRS con LINAC fueron estimadas con una dosis de radiación de 90Gy a una línea de isodosis del 30% tangencial al puente, tanto con colimadores de 4 y 6mm. Las distancias desde los blancos calculados al puente y al ganglio de Gasser, bajo estos parámetros, fueron medidas. El análisis estadístico fue realizado comparando el lado afectado contra el lado no afectado.
ResultadosEl nervio trigémino derecho se encontró afectado en 36 pacientes (67,9%), y el izquierdo en 17 (32,1%) pacientes. La longitud media del nervio trigémino fue 9,8mm (rango: 4,6-16,8mm) en el lado afectado, y 10,5mm (rango: 5,6-18,4mm) en el lado no afectado, con una diferencia media estadísticamente significativa (p=0,02). El ángulo trigémino-pontino fue 12,5° (rango: 5,4-19,5°) en el lado afectado y 10,2° (rango: 5,0-30,5°) en el lado no afectado, con una diferencia media significativa (p=0,01). En las simulaciones, las distancias desde los blancos estimados al puente y al ganglio de Gasser no fueron significativamente diferentes entre ambos lados. La variación de las distancias blanco-puente y blanco-ganglio fue estadísticamente significativa en el lado afectado con el cambio de colimadores (p<0,001).
ConclusionesEn este estudio anatómico, diferencias significativas fueron identificadas en la longitud del nervio trigémino y el ángulo trigémino-pontino en el lado afectado al compararse con el lado no afectado en pacientes con NT idiopática en secuencias FIESTA previo a cirugía o radiocirugía. Se observó variación en la localización del blanco sobre la REZ en las simulaciones de SRS con LINAC entre los colimadores de 4 y 6mm, con una dosis de radiación estimada de 90Gy y una línea de isodosis del 30% paralela al puente.
Article

If it is the first time you have accessed you can obtain your credentials by contacting Elsevier Spain in suscripciones@elsevier.com or by calling our Customer Service at902 88 87 40 if you are calling from Spain or at +34 932 418 800 (from 9 to 18h., GMT + 1) if you are calling outside of Spain.
If you already have your login data, please click here .
If you have forgotten your password you can you can recover it by clicking here and selecting the option ¿I have forgotten my password¿.