The aim of this project is to assess diagnostic reclassification based on molecular data over morphology in a series of glial tumours since the introduction of the 2016 WHO classification of brain tumours.
Materials and methodsRetrospective review of glial tumours (oligodendrogliomas and astrocytomas) treated in our centre between January 2012 and June 2016 in which a review of diagnosis was performed when molecular studies were added. Statistical analysis included evaluation of variables of epidemiology, morphology and molecular data (mainly IDH mutation and 1p19q codeletion), diagnostic changes after new classification was considered, and clinical impact in cases of diagnostic reclassification.
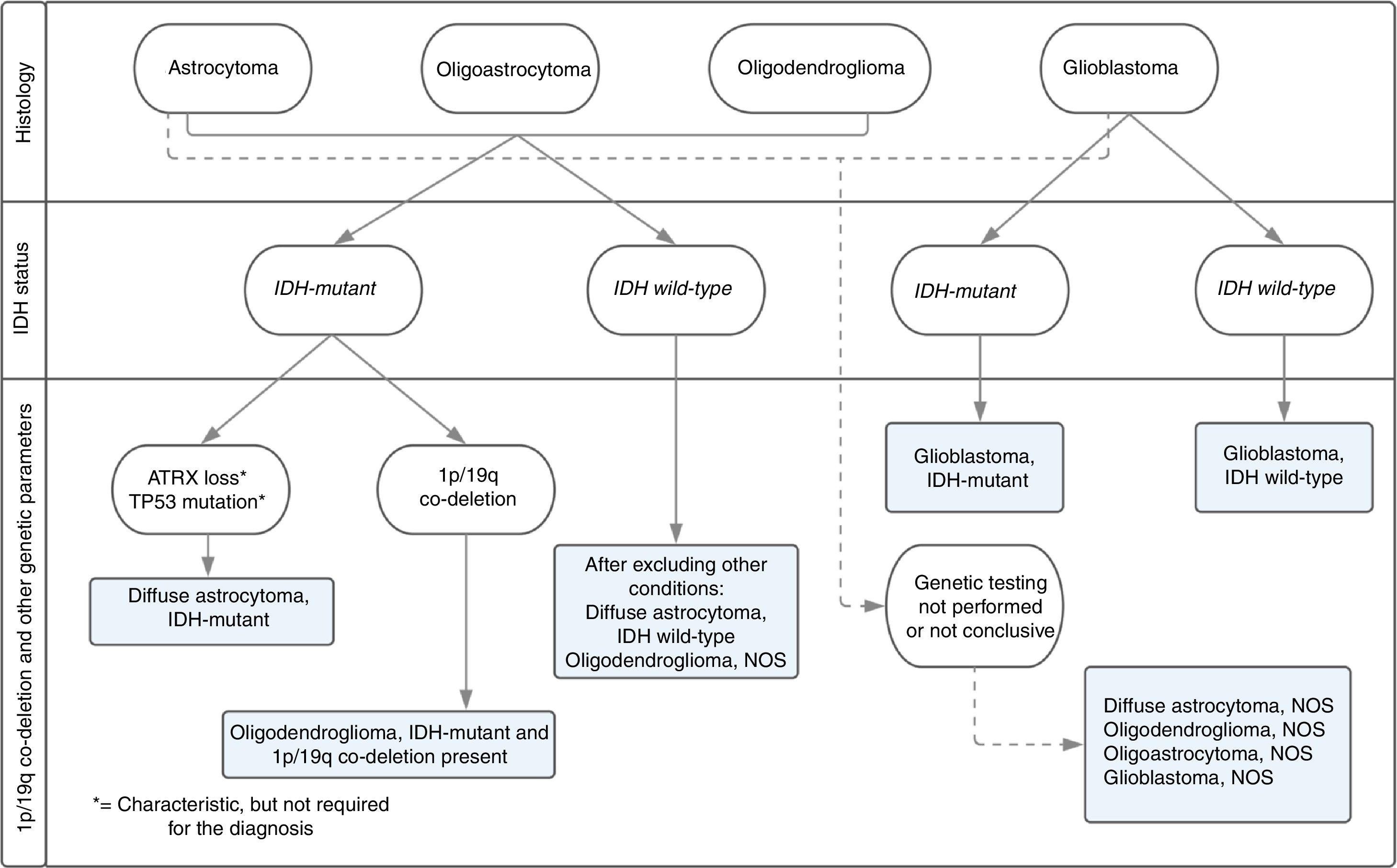
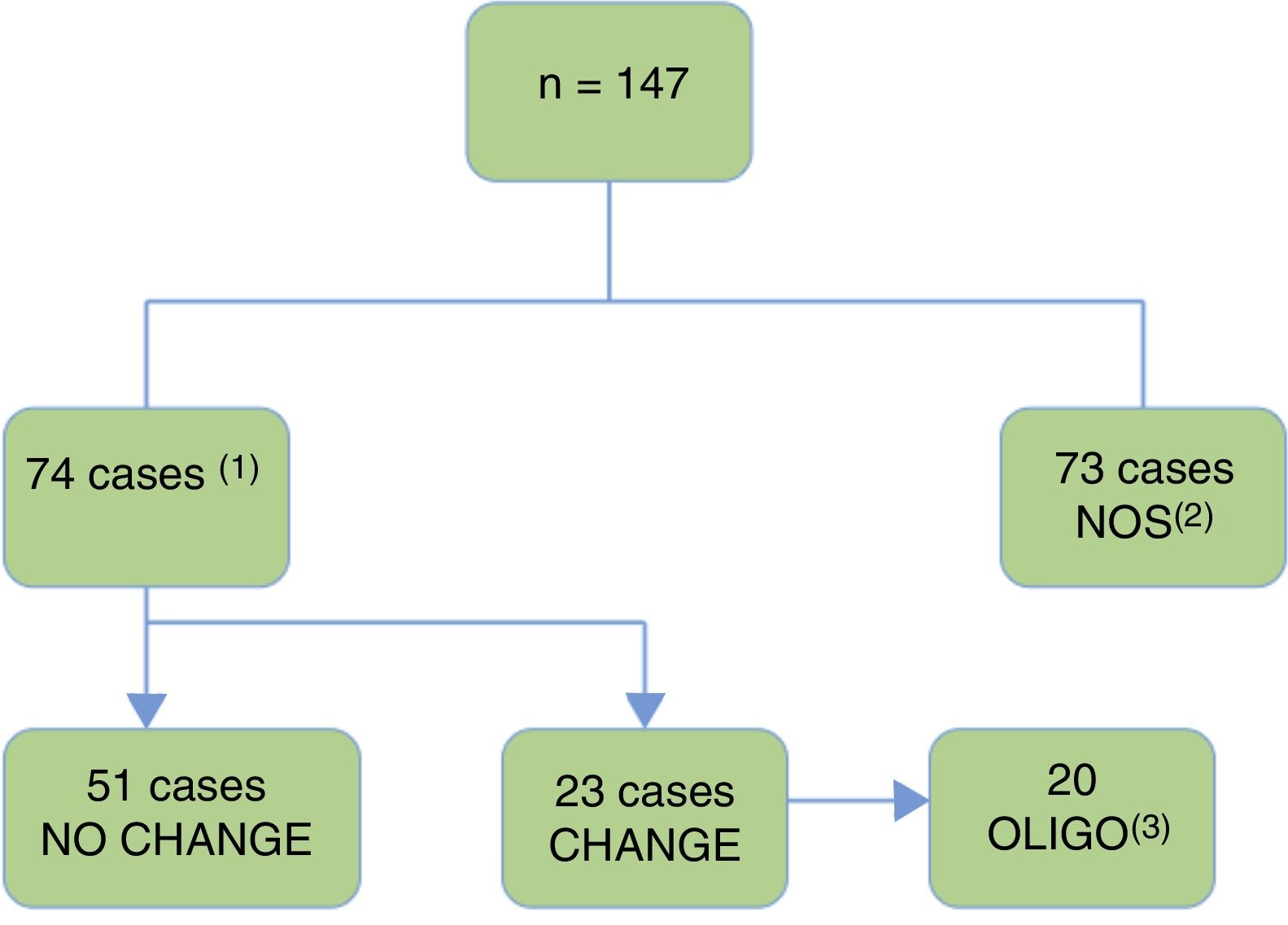
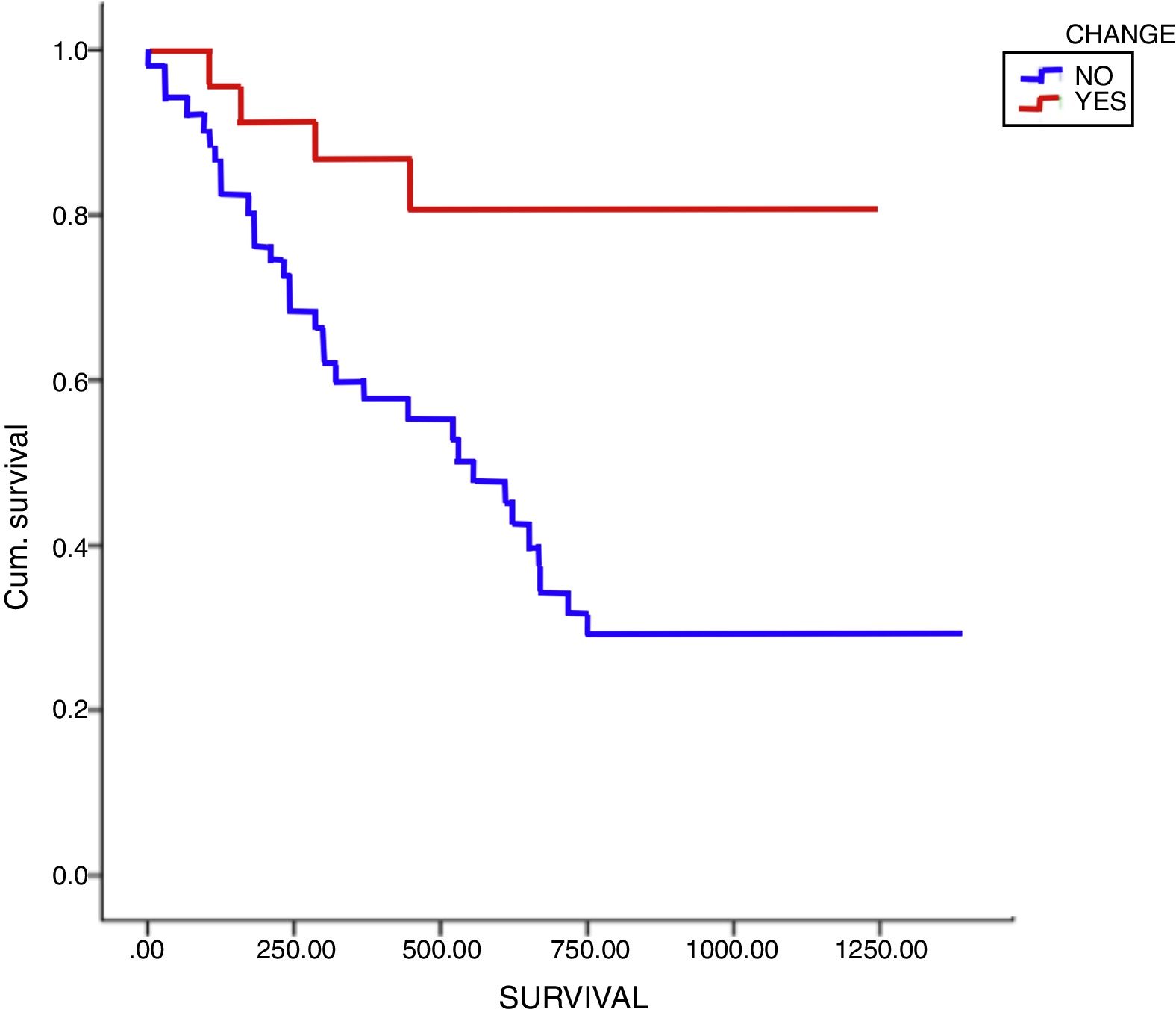
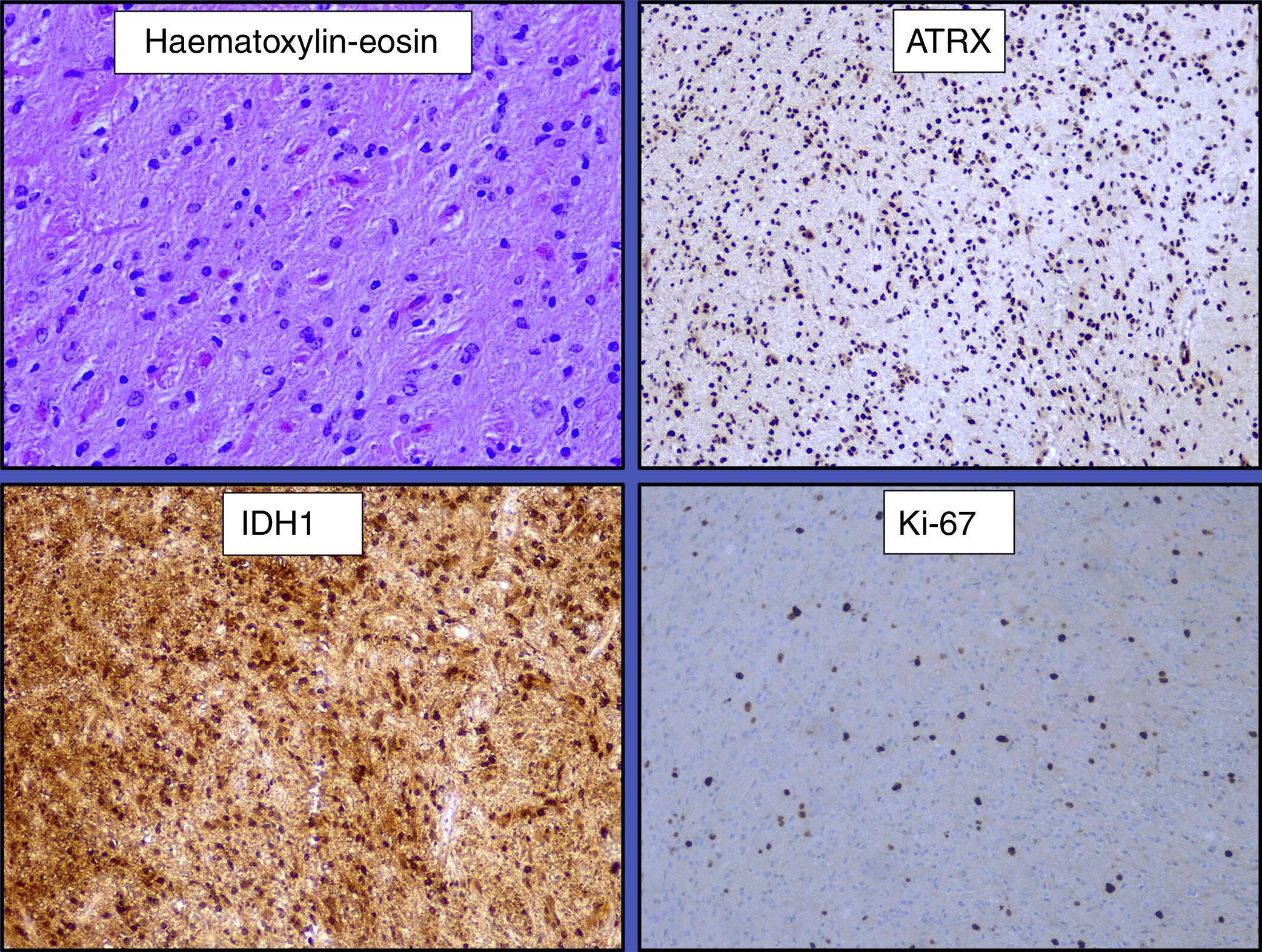
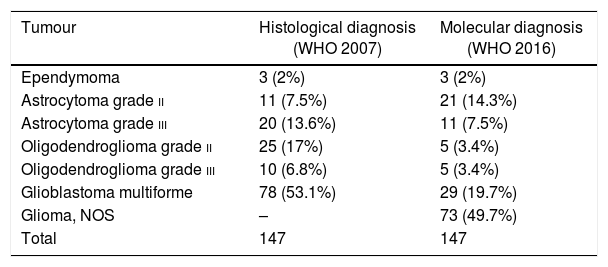
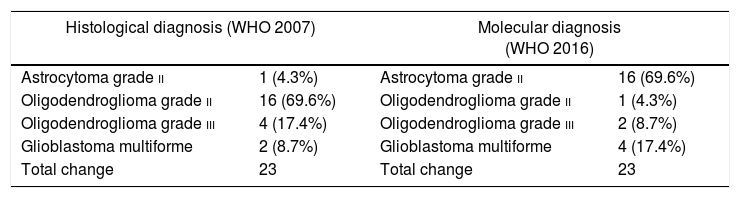
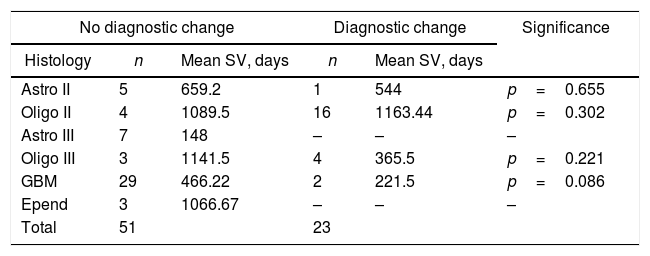
ResultsFrom a total of 147 glial tumours reviewed in our centre, molecular diagnosis was obtained in 74 cases (50.3%). Initial diagnosis changed in 23 cases (31%), and 20 (87%) of them had a prior histological diagnosis of oligodendroglioma (69.6% grade ii and 17.4% grade iii). Only 3 of these 23 cases diagnosis changed from astrocytoma to oligodendroglioma. Among reclassified tumours, there was a common molecular pattern, as findings showed mutant IDH in 16 cases (69.6%) and no codeletion in 20 cases (87%). According to the cell of origin, of the whole group of 27 oligodendrogliomas in our series (reclassified and non-reclassified), 20 cases (74%) became astrocytomas, despite typical oligodendroglial morphology, due to absence of 1p19q codeletion. There was a trend for diagnosis reclassification in younger patients (<40 years), p=0.065, mainly in those with a prior diagnosis of oligodendroglioma, with no statistical differences based on gender or clinical data. Besides, reclassification was more common among tumours with mutant IDH (69.6%), p=0.003, than those with wild type IDH. In terms of survival, despite receiving different treatments, no significant changes were detected between reclassified and non-reclassified tumours after a mean follow-up of 16 months, partly related to lower grade of these lesions.
ConclusionsWithin the spectrum of the glial tumours treated in our institution, this new classification including molecular genetics over morphological data has provided marked diagnostic changes. These changes appear mainly in tumours previously diagnosed as oligodendrogliomas and in younger patients, with molecular patterns of mutant IDH and 1p19q codeletion. Although diagnosis reclassification may affect clinic, prognosis or therapeutic management of these tumours, deeper and prospective studies on these specific aspects are needed.
El objetivo de este trabajo es evaluar el cambio del diagnóstico molecular sobre el histológico de una serie de tumores gliales al revisar el diagnóstico con la clasificación de la OMS de 2016.
Materiales y métodosSe realiza un estudio retrospectivo de los tumores gliales (oligodendrogliomas y astrocitomas) tratados en nuestro centro entre enero de 2012 y junio de 2016, y una revisión diagnóstica según su estudio molecular. Se lleva a cabo el análisis estadístico de variables epidemiológicas, histológicas y de genética molecular (mutaciones en IDH y presencia de codeleción 1p19q), variación en el diagnóstico al introducir la nueva clasificación tumoral e impacto clínico de dicha reclasificación.
ResultadosDe los 147 casos de tumores gliales revisados, se obtuvo el diagnóstico molecular en 74 casos (50,3%). En 23 casos (31%) cambió el diagnóstico, predominando en 20 (87%) el diagnóstico previo de oligodendroglioma (69,6% grado ii y 17,4% grado iii). Solo 3 de los 23 casos cambiaron de diagnóstico inicial astrocitario al oligodendroglial. Respecto al patrón molecular en estos 23 casos, se detectó IDH mutado en 16 (69,6%) y codeleción 1p19q negativa en 20 (87%). Según la estirpe celular, de los 27 oligodendrogliomas de esta serie, 20 (74%) cambiaron de diagnóstico por tener la codeleción negativa, pasando a ser astrocitomas. Se observó una tendencia a un mayor cambio de diagnóstico en pacientes jóvenes (<40 años), p=0,065, mayoritariamente con diagnóstico previo de oligodendrogliomas, sin relación con el sexo. Además, se detectó una mayor frecuencia de cambio de diagnóstico entre los tumores con IDH mutado (69,6%), p=0,003. Respecto a la supervivencia o el patrón clínico, no se detectaron cambios significativos entre los tumores con o sin cambio diagnóstico, a pesar de no recibir tratamiento de elección, tras un seguimiento medio de 16 meses, en probable relación con el bajo grado lesional.
ConclusionesDentro del espectro de tumores astrocitarios y oligodendrogliales en nuestro centro, la clasificación diagnóstica con genética molecular evidencia importantes cambios respecto al diagnóstico morfológico. Estos cambios afectan especialmente a los diagnósticos previos de oligodendrogliomas y a los pacientes jóvenes en los casos revisados, y con patrones moleculares de mutación en la IDH y de ausencia de codeleción 1p19q. Si bien se pueden plantear dudas respecto a la clínica, el pronóstico y el tratamiento realizado en estos casos, se requieren estudios específicos en estos aspectos para lograr unas conclusiones apropiadas.
Article

If it is the first time you have accessed you can obtain your credentials by contacting Elsevier Spain in suscripciones@elsevier.com or by calling our Customer Service at902 88 87 40 if you are calling from Spain or at +34 932 418 800 (from 9 to 18h., GMT + 1) if you are calling outside of Spain.
If you already have your login data, please click here .
If you have forgotten your password you can you can recover it by clicking here and selecting the option ¿I have forgotten my password¿.