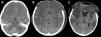
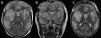
Acute fulminant cerebral edema is a type of rapidly progressive encephalitis that occurs in children and is associated with significant morbidity and mortality.
We present a clinical case with seizures, rapid neurological deterioration and the early appearance of cerebral herniation signs. Although the radiological tests were initially normal and there are no established parameters that predict the evolution of encephalitis to a rapidly progressive subtype, the clinical evolution forced to consider the decompressive craniectomy due to the lack of response to the medical management of the cerebral edema. It may be necessary take a brain biopsy to confirm the etiology of the encephalitis origin of acute fulminant cerebral edema. The objective of surgery should be not only to increase survival, but also to reduce subsequent neurological sequelae.
El edema cerebral fulminante agudo es un cuadro clínico dentro de las encefalitis con una evolución rápidamente progresiva de aparición en la edad pediátrica y que se asocia a una importante morbimortalidad.
Presentamos un caso clínico que cursa con crisis comiciales, deterioro neurológico rápido y la aparición precoz de signos de herniación cerebral. Aunque las pruebas radiológicas fueron normales inicialmente y no hay establecidos parámetros que predigan la evolución de encefalitis a un subtipo rápidamente progresiva, la evolución clínica que presentó obligó a la realización de una craniectomía descompresiva ante la falta de respuesta al manejo médico del edema cerebral. En ocasiones puede ser necesario la toma de una biopsia cerebral para llegar al diagnóstico de la causa que ha producido la encefalitis origen del edema cerebral agudo fulminante. El objetivo de la cirugía debe ser no sólo el aumento de la supervivencia, sino la disminución de las secuelas neurológicas posteriores.
Article

If it is the first time you have accessed you can obtain your credentials by contacting Elsevier Spain in suscripciones@elsevier.com or by calling our Customer Service at902 88 87 40 if you are calling from Spain or at +34 932 418 800 (from 9 to 18h., GMT + 1) if you are calling outside of Spain.
If you already have your login data, please click here .
If you have forgotten your password you can you can recover it by clicking here and selecting the option ¿I have forgotten my password¿.