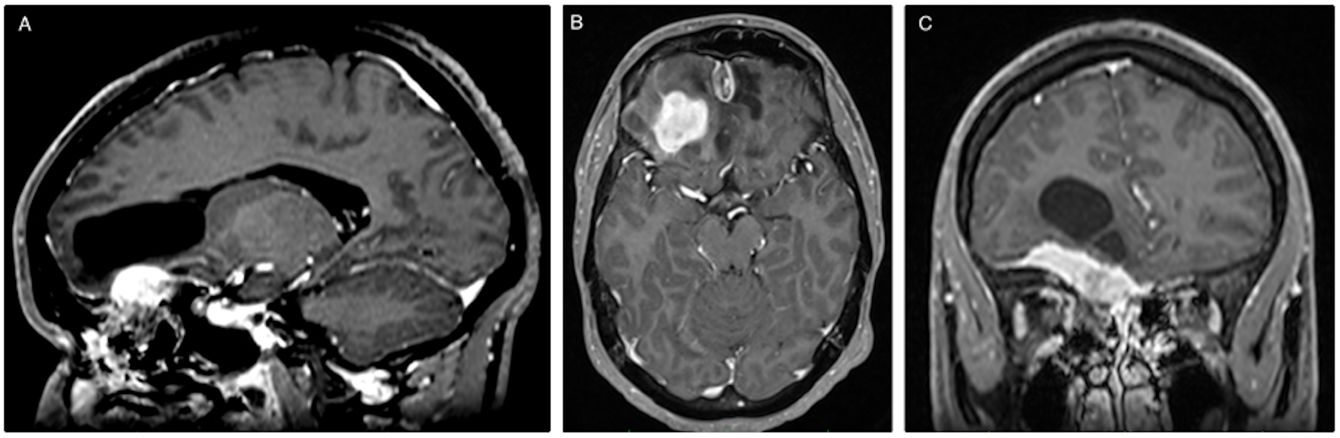
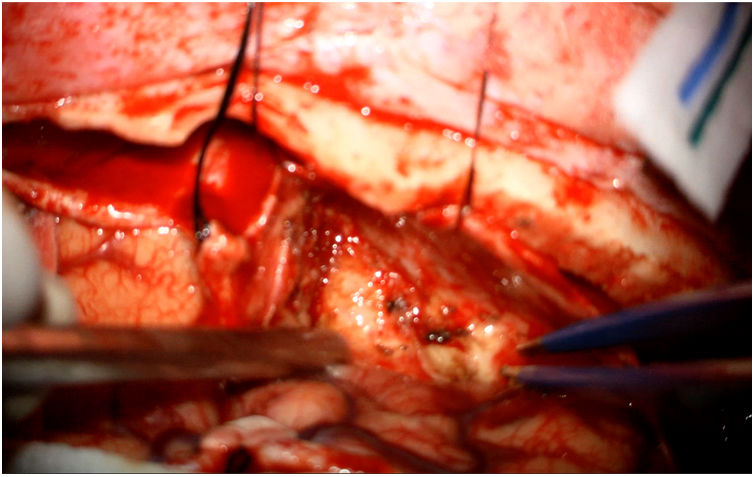
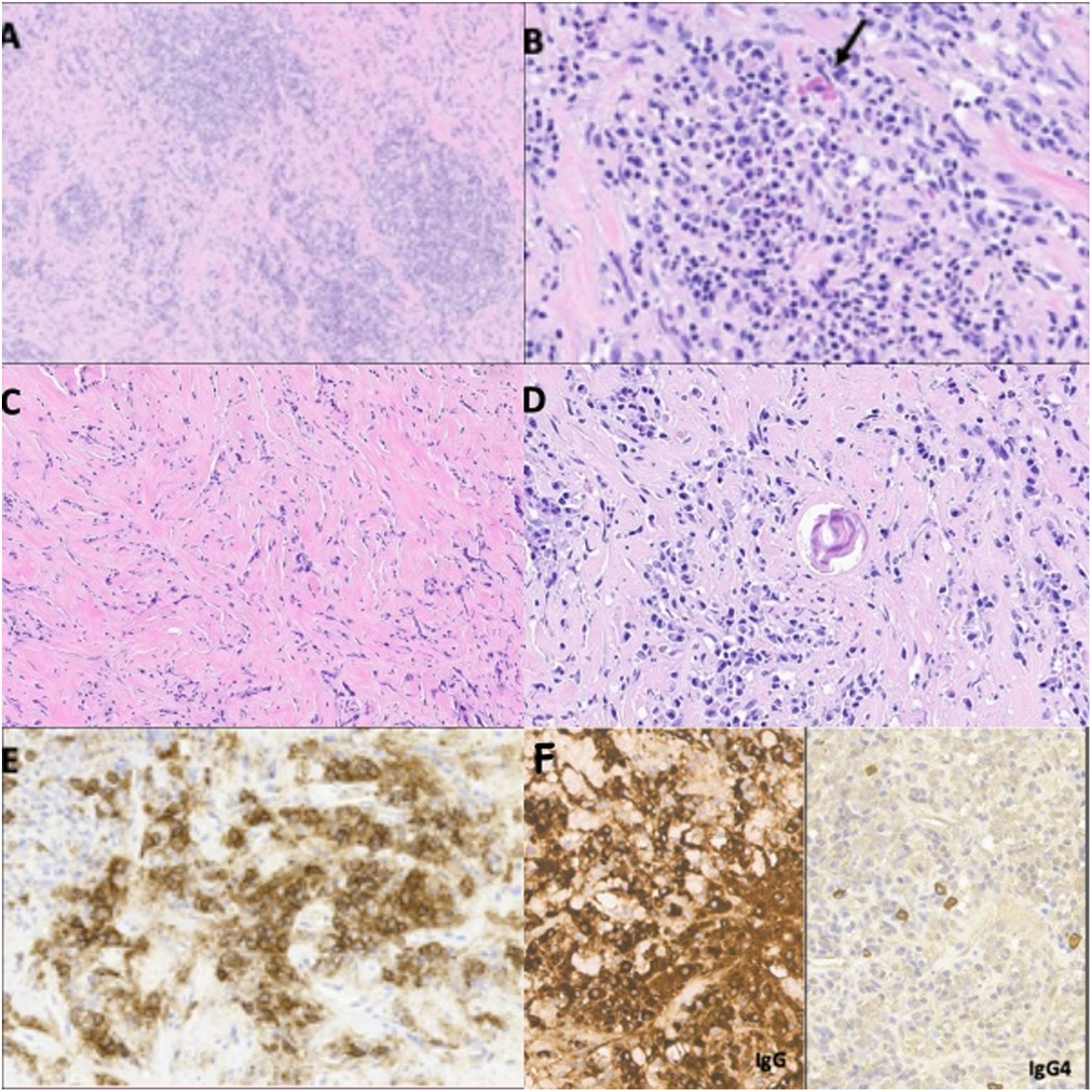
Inflammatory pseudotumor is a rare lesion, especially at the level of the central nervous system. Its etiology is unknown and the most accepted hypothesis is that it is the consequence of an exaggerated immune response. We present the clinical case of a young Senegalese male, with a history of epilepsy secondary to severe cranioencephalic trauma in childhood, who presented with new epileptic seizures. Imaging tests showed a lesion in the anterior fossa intimately attached to the meninges, so the initial diagnosis was meningioma. A bifrontal craniotomy and microsurgical excision were performed. The definitive anatomopathological analysis concluded that the lesion is an inflammatory pseudotumor whose origin is secondary to a disproportionate reparative process after cranioencephalic trauma.
El pseudotumor inflamatorio es una lesión poco frecuente, especialmente a nivel del sistema nervioso central. Su etiología es desconocida y la hipótesis más aceptada es que es consecuencia de una respuesta inmunitaria exagerada. Presentamos el caso clínico de un varón joven senegalés, con antecedentes de epilepsia secundaria a traumatismo craneoencefálico severo en la infancia, que presentó nuevas crisis epilépticas. Las pruebas de imagen mostraron una lesión en la fosa anterior íntimamente adherida a las meninges, por lo que el diagnóstico inicial fue de meningioma. Se realizó una craneotomía bifrontal y exéresis microquirúrgica. El análisis anatomopatológico definitivo concluyó que la lesión es un pseudotumor inflamatorio cuyo origen es secundario a un proceso reparativo desproporcionado tras el traumatismo craneoencefálico.
Article

If it is the first time you have accessed you can obtain your credentials by contacting Elsevier Spain in suscripciones@elsevier.com or by calling our Customer Service at902 88 87 40 if you are calling from Spain or at +34 932 418 800 (from 9 to 18h., GMT + 1) if you are calling outside of Spain.
If you already have your login data, please click here .
If you have forgotten your password you can you can recover it by clicking here and selecting the option ¿I have forgotten my password¿.