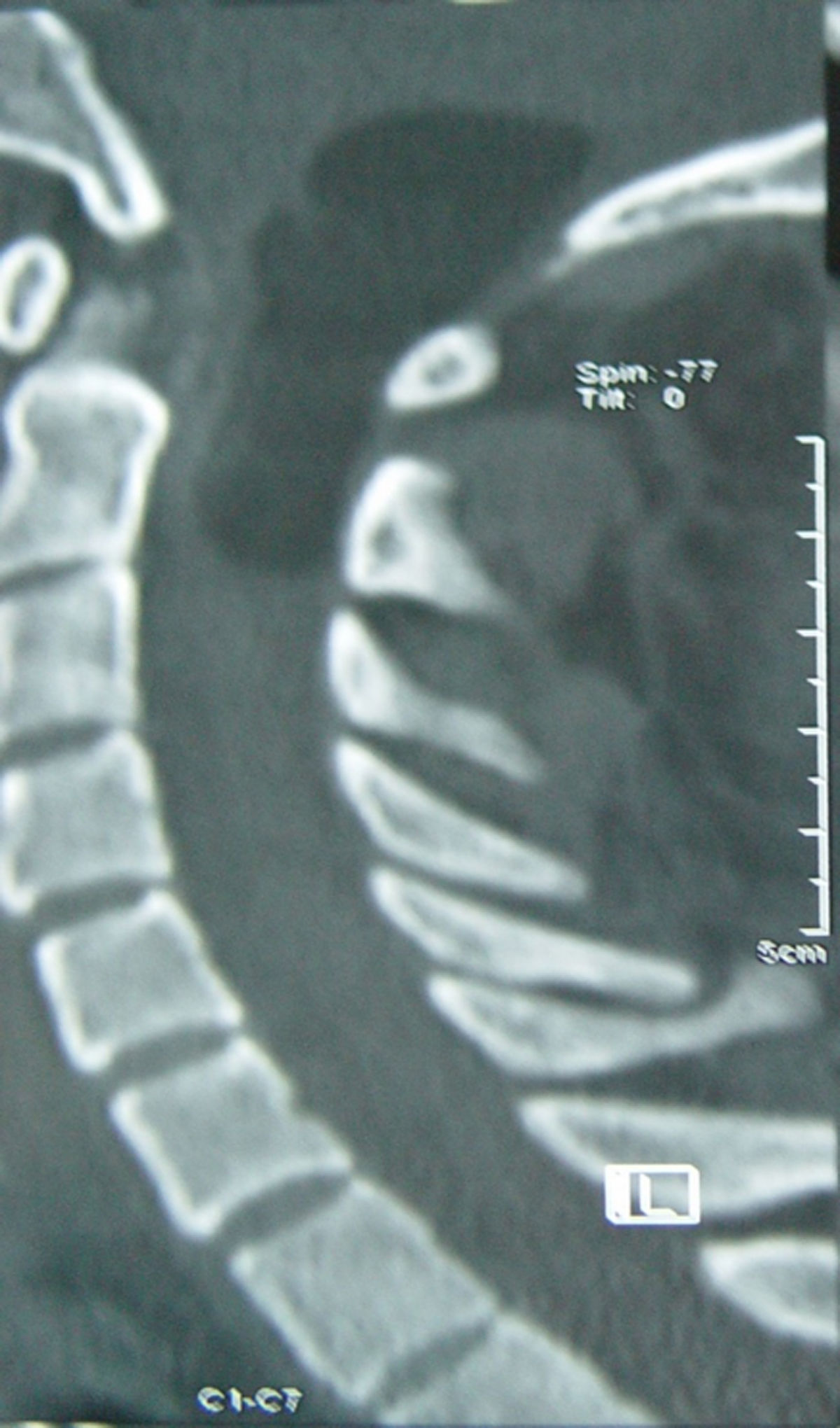
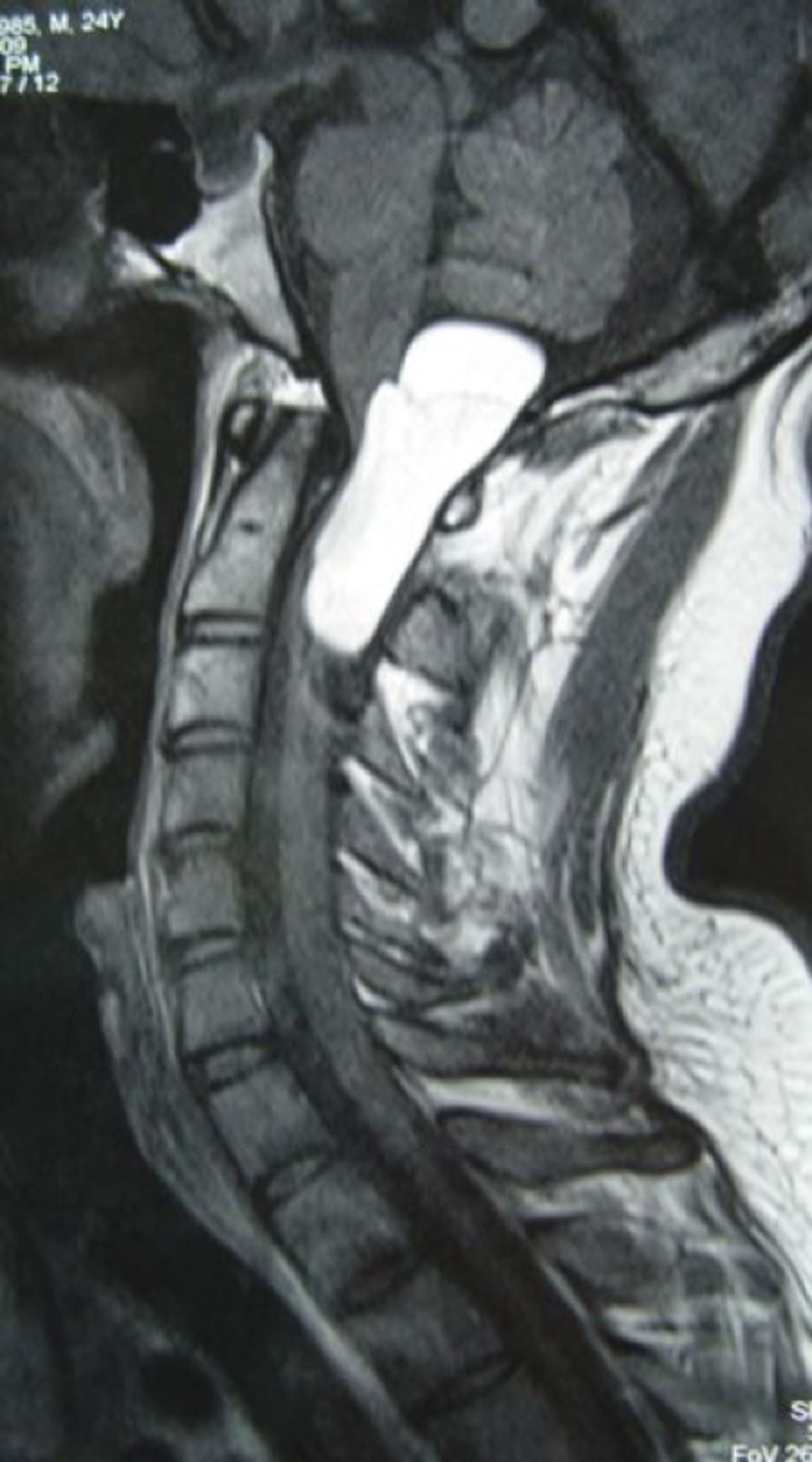
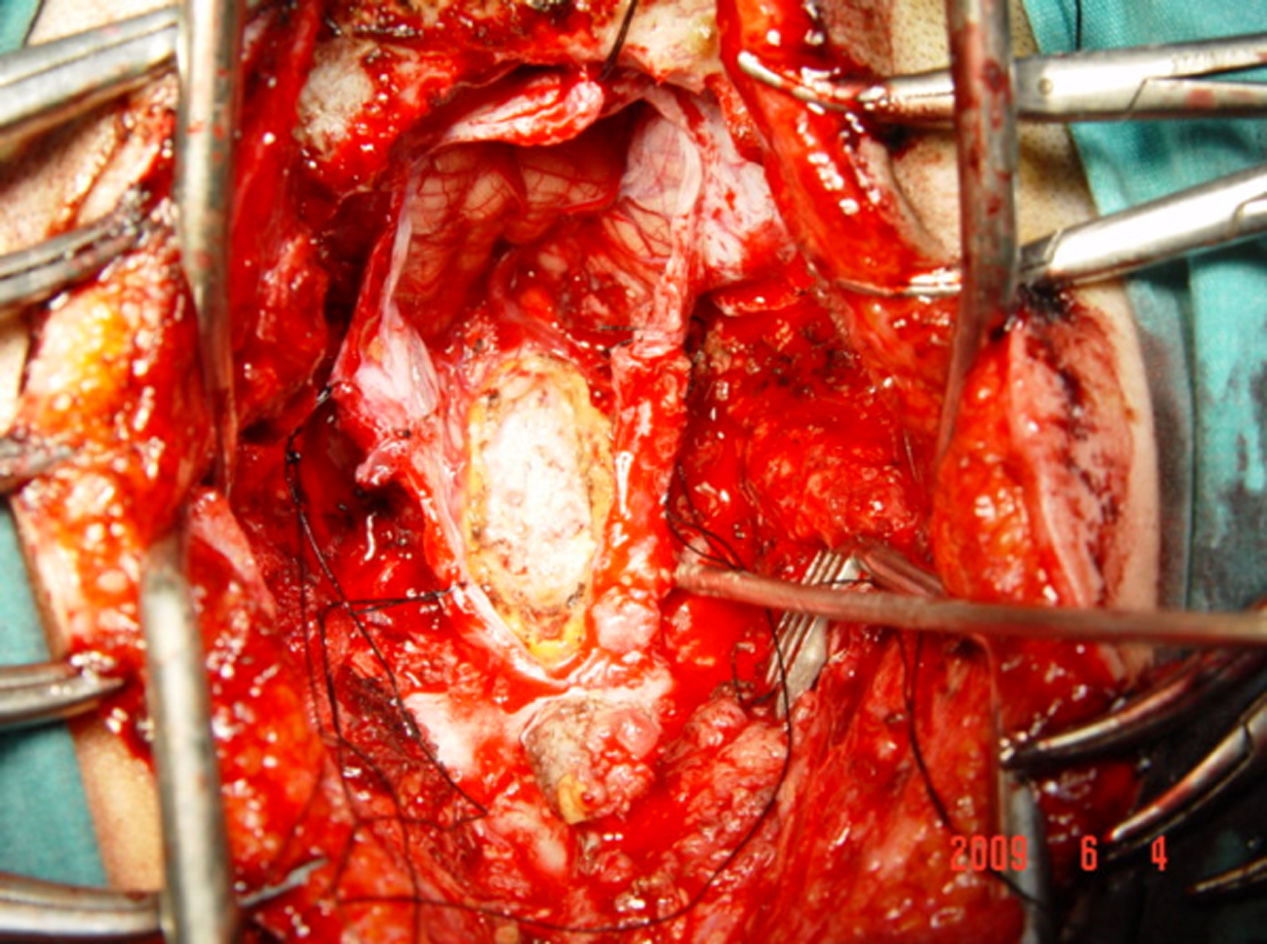
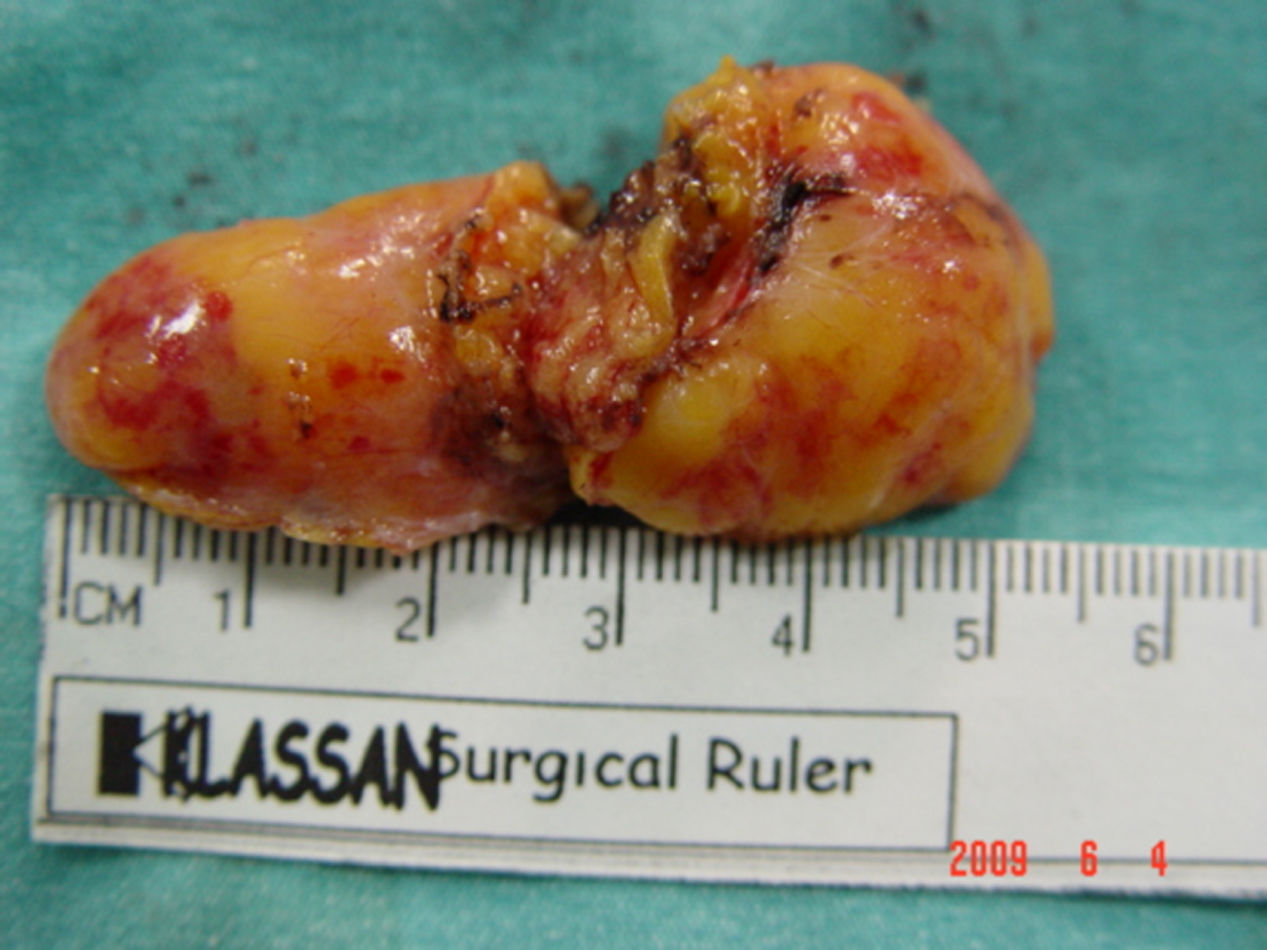
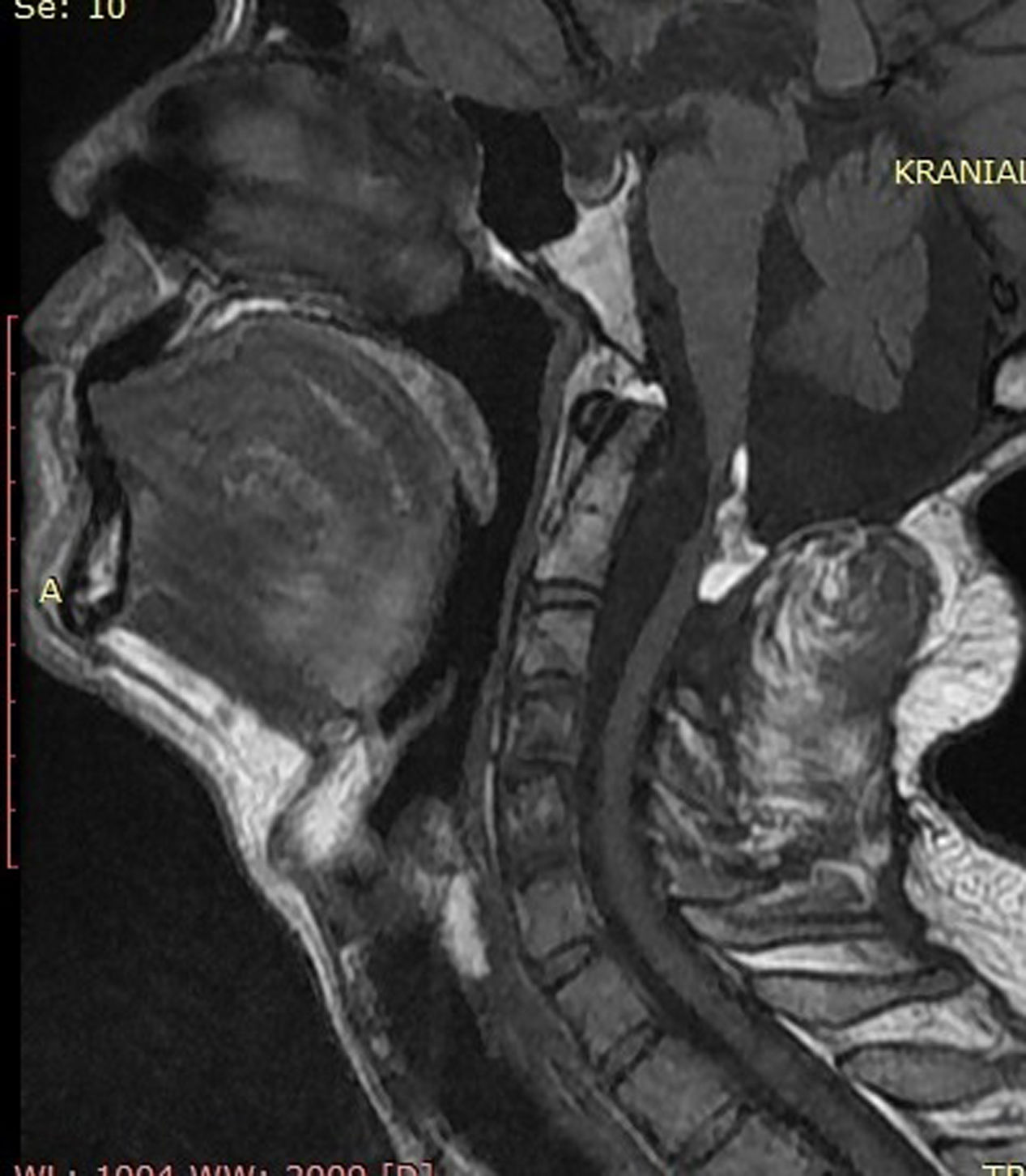
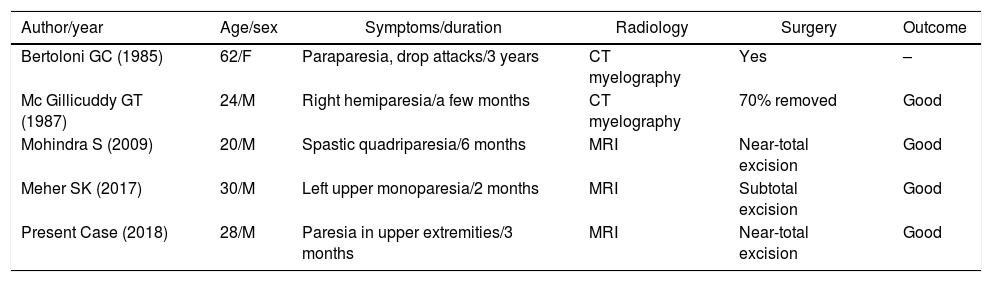
Intradural spinal lipomas with intracranial extension are very rare and are typically diagnosed in childhood. Radical surgical excision usually causes a high rate of morbidity because of the firm adherence between the lipoma and neural tissues. In this report, we present a case of craniocervical intradural intramedullary lipoma in an adult patient. The patient underwent surgery with excision of the mass, leaving a sheet of lipoma on the tumor bed.
Los lipomas espinales intradurales con extensión intracraneal son muy raros y suelen diagnosticarse en la infancia. La escisión quirúrgica radical generalmente causa una alta tasa de morbilidad debido a la adherencia firme entre el lipoma y los tejidos neurales. En este artículo, presentamos un caso de lipoma intramedular craneocervical intradural en un paciente adulto. El paciente se sometió a una cirugía con exéresis de la masa, dejando una lámina de lipoma en el lecho tumoral.
Artículo

Si es la primera vez que accede a la web puede obtener sus claves de acceso poniéndose en contacto con Elsevier España en suscripciones@elsevier.com o a través de su teléfono de Atención al Cliente 902 88 87 40 si llama desde territorio español o del +34 932 418 800 (de 9 a 18h., GMT + 1) si lo hace desde el extranjero.
Si ya tiene sus datos de acceso, clique aquí.
Si olvidó su clave de acceso puede recuperarla clicando aquí y seleccionando la opción "He olvidado mi contraseña".