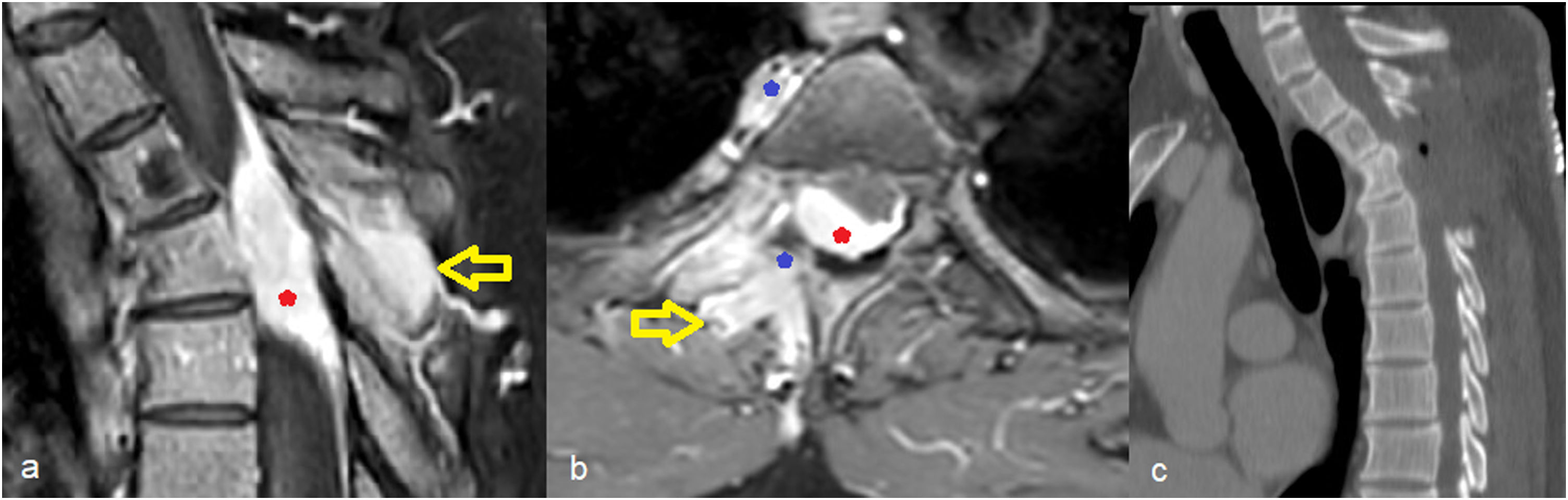
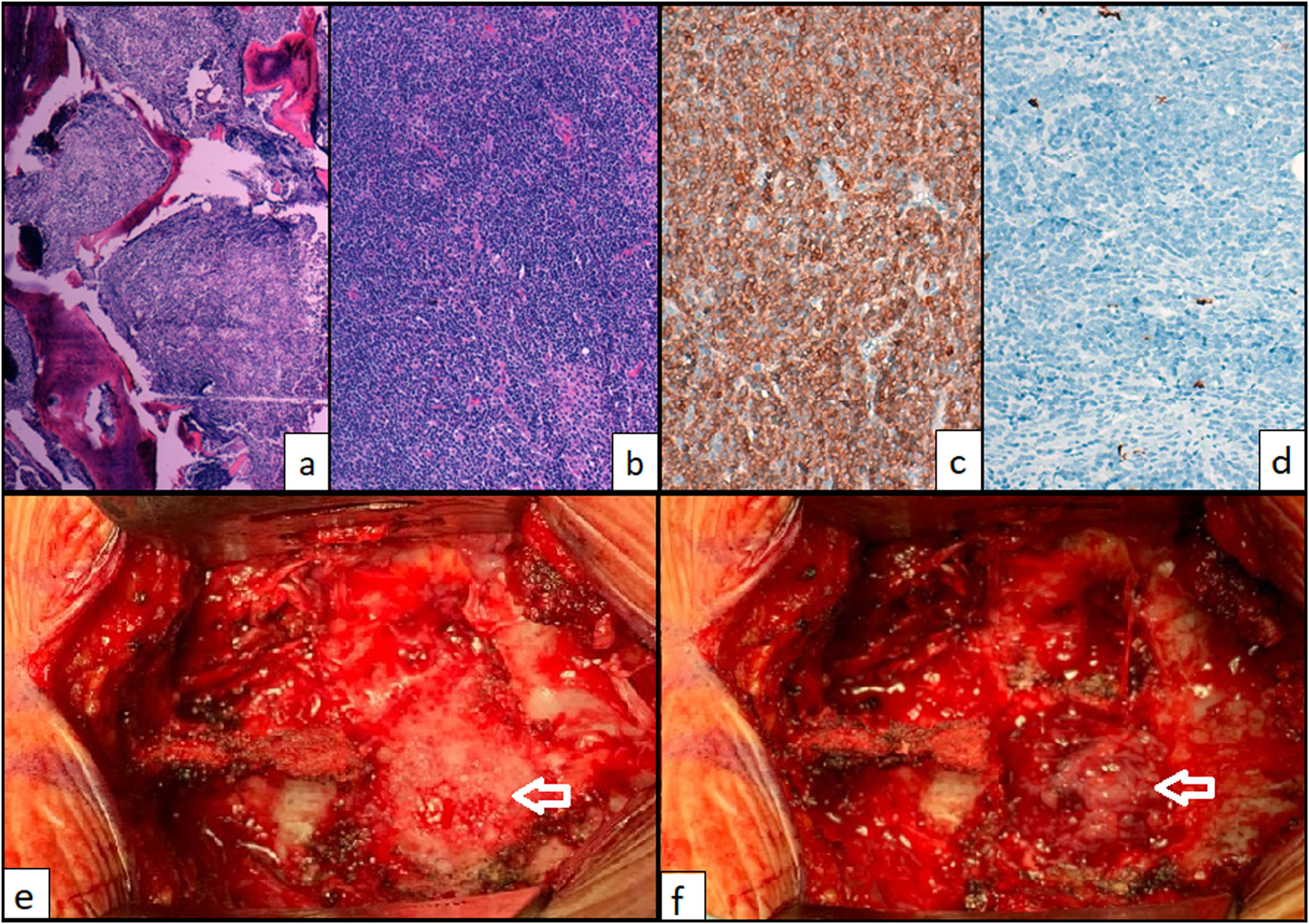
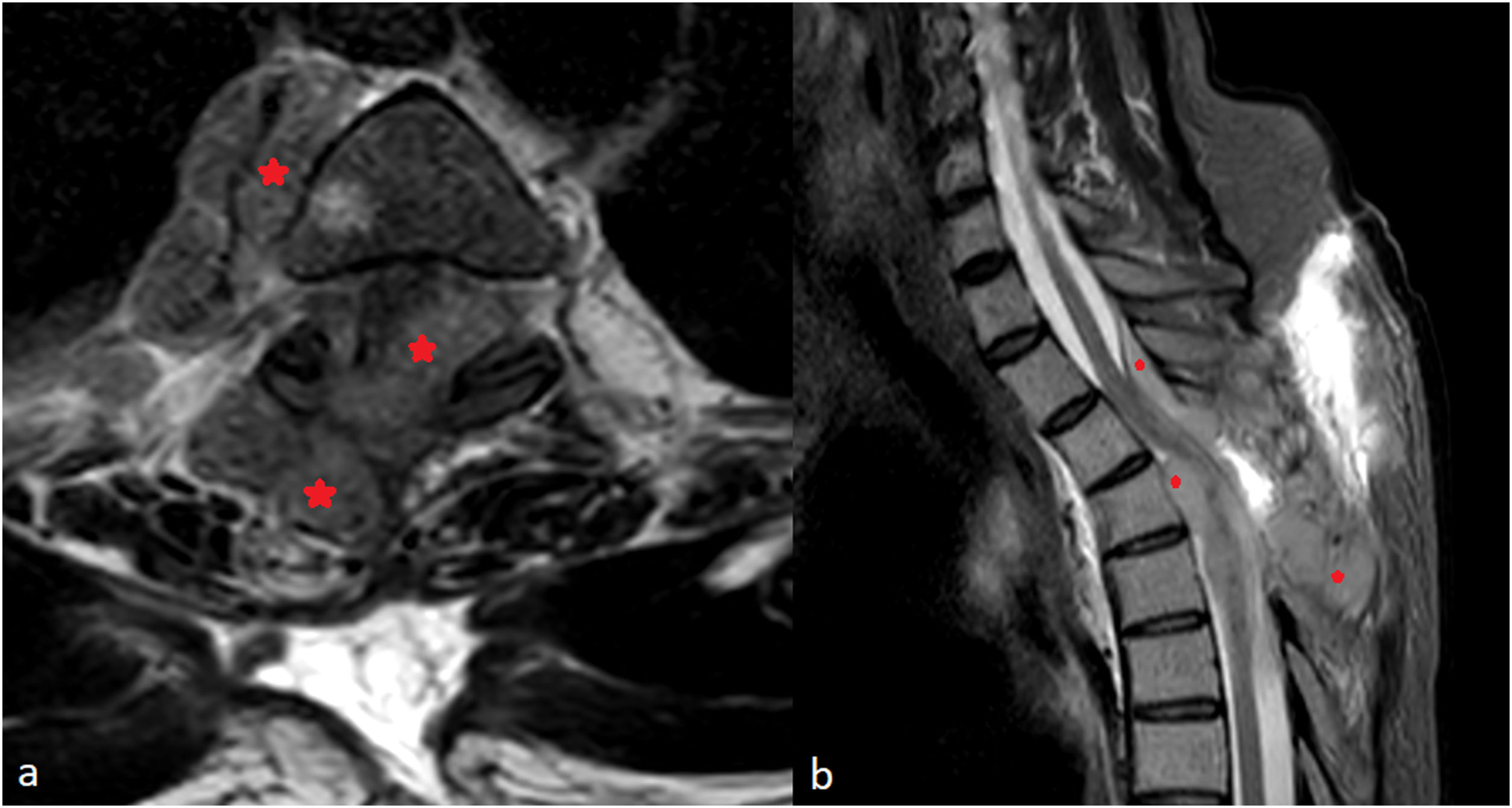
During lymphoma’s natural history of disease, 5–10% of cases may develop Central Nervous affectation. We present the case of a 57-years-old man with less than 24 h of onset symptoms of paraparesis, lower limb hypoesthesia and sphincter dysfunction who was operated due to dorsal tumor with epidural component which caused severe cord compression. Pathological analysis concluded atypical T-cell lymphoblastic lymphoma, a rare subtype of lymphoma which accounts 1%−2% of all Non-Hodgkin Lymphomas. Our case was particularly aggressive and atypical due to its origin in paraspinal soft tissue. Despite specific treatment, the patient presented an early epidural relapse, frequent in this lymphoma subtype.
Durante la historia natural del linfoma, entre el 5 y el 10% de los casos pueden desarrollar afectación del Sistema Nervioso Central. Se presenta el caso de un varón de 57 años con menos de 24 horas de inicio de síntomas de paraparesia, hipoestesia de miembros inferiores y disfunción de esfínteres quien fue intervenido de un tumor dorsal con componente epidural que provocaba compresión medular severa. El informe anatomo-patológico concluyó que se trataba de un linfoma linfoblástico de células T atípico, un subtipo raro de linfoma que representa entre el 1% y el 2% de todos los linfomas no Hodgkin. Nuestro caso fue particularmente agresivo y atípico por su origen en tejidos blandos paraespinales. A pesar del tratamiento específico, el paciente presentó una recidiva epidural precoz, frecuente en este subtipo de linfoma.
Article

If it is the first time you have accessed you can obtain your credentials by contacting Elsevier Spain in suscripciones@elsevier.com or by calling our Customer Service at902 88 87 40 if you are calling from Spain or at +34 932 418 800 (from 9 to 18h., GMT + 1) if you are calling outside of Spain.
If you already have your login data, please click here .
If you have forgotten your password you can you can recover it by clicking here and selecting the option ¿I have forgotten my password¿.