There are different techniques for the reconstruction of the temporal muscle (TM) in the pterional approach (PA) in order to avoid and reduce atrophy, it has not been able to avoid it in its entirety.
The administration of bupivacaine generates regeneration of muscle fibres. There are no studies in the medical literature that evaluate the time of TM manipulation and the use of bupivacaine for the treatment of atrophy after pterional approach, the present investigation aim is to describe the effects of these variables.
Patient and methodsLongitudinal study, including patients from 18-80 years old with pterional approach at 2016–2017. We evaluated the effects of the TM manipulation times and the administration of 0.5% bupivacaine on the trophism and function of TM.
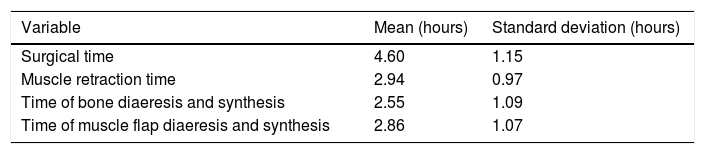
ResultsTwenty-nine patients underwent a PA; 16(55.17%) count with criteria for 0.5% bupivacain infiltration.
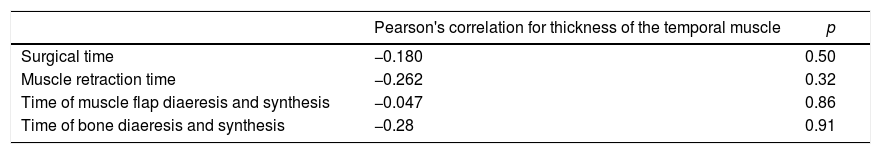
We found a negative correlation between manipulation times and trophism, with no statistically significance (p>.05).
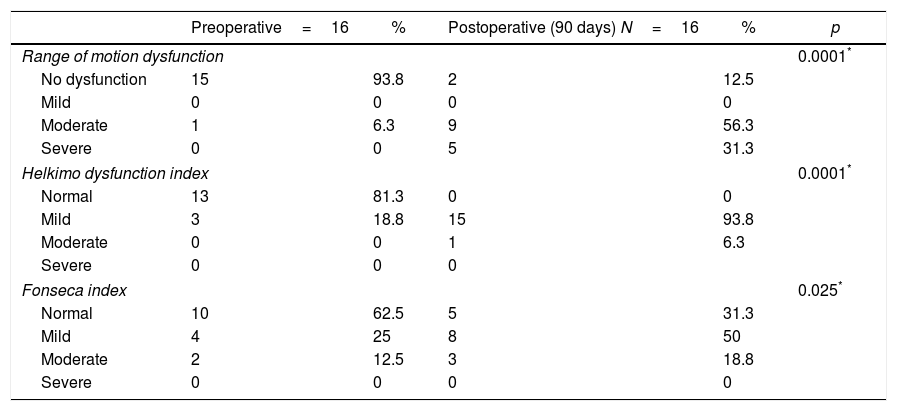
We evaluated presurgical and postsurgical index of Helkimo and Fonseca's index, finding an increase of disfunction with statistically significance (p<.05).
In patients who were infiltrated with 0.5% bupivacaine we observed a mean difference in the TM's trophism of 0.275±1.18mm, in contrast with no infiltrated which was 2.39±1.30mm (t[27]=−5.118, p=.0001).
ConclusionsThe manipulation of the TM during a pterional approach conditioned an impact on the quality of life according to the disfunction indexes, due to atrophy. This investigation exhibits that de administration of 0.5% bupivacaine during surgery offers a decrease in the TM atrophy.
Existen diferentes técnicas para reconstrucción del músculo temporal (MT) en el abordaje pterional (AP) con el objetivo de evitar y disminuir la atrofia, hasta el momento ninguna ha logrado evitarla en su totalidad.
La administración de bupivacaína genera regeneración de fibras musculares. Aún no existe en la literatura médica estudios que evalúen el tiempo de manipulación del MT y que den uso a la bupivacaína para el tratamiento de la atrofia después de un abordaje pterional, el presente estudio pretende describir los efectos de estas variables.
Pacientes y métodosEstudio longitudinal, incluyendo pacientes de 18-80 años y sometidos a abordaje pterional en los años 2016-2017. Evaluamos los efectos de la manipulación del MT y la administración de bupivacaína al 0,5% sobre el trofismo y la función del MT.
ResultadosVeintinueve pacientes fueron sometidos a AP; 16(55,17%) contaron con criterios para infiltración con bupivacina al 0,5%.
Se encontró una correlación negativa entre los tiempos de manipulación y el trofismo, no estadísticamente significativo (p>0,05).
Se evalúo los índices de disfunción de Helkimo y Fonseca prequirúrgicos y posquirúrgicos encontrándose un incremento estadísticamente significativo en la disfunción (p<0,05).
En pacientes infiltrados con bupivacaína al 0,5% se observó una diferencia media del espesor de MT de 0,275±1,18mm, en contraste con los no infiltrados de 2,39±1,30mm (t[27] = -5,118, p=0,0001).
ConclusionesLa manipulación del MT durante el abordaje pterional, condiciona un impacto sobre la calidad de vida de acuerdo con los índices de disfunción, debido a la atrofia. Esta investigación presenta que la administración de bupivacaína al 0,5% durante la cirugía ofrece una disminución en la atrofia del MT.
Article

If it is the first time you have accessed you can obtain your credentials by contacting Elsevier Spain in suscripciones@elsevier.com or by calling our Customer Service at902 88 87 40 if you are calling from Spain or at +34 932 418 800 (from 9 to 18h., GMT + 1) if you are calling outside of Spain.
If you already have your login data, please click here .
If you have forgotten your password you can you can recover it by clicking here and selecting the option ¿I have forgotten my password¿.